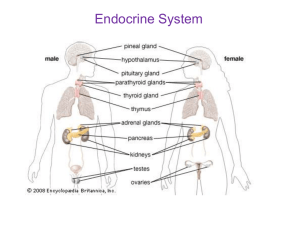
The Endocrine System
... which in turn delivers to all body cells The cells that recognize a particular hormone will be the one to respond (target cell) ...
... which in turn delivers to all body cells The cells that recognize a particular hormone will be the one to respond (target cell) ...
Nitrogen-containing components of normal urine Urea Cycle The
... 4. Offer a genetic explanation for the observation that this disease is usually lethal in males but not in affected females. 5. This patient was treated using procedures available at the time. He was given a daily diet of 1.5 g of protein/kg body weight. After 2 years on this diet, his height and we ...
... 4. Offer a genetic explanation for the observation that this disease is usually lethal in males but not in affected females. 5. This patient was treated using procedures available at the time. He was given a daily diet of 1.5 g of protein/kg body weight. After 2 years on this diet, his height and we ...
Chapter 11 - Endocrine System 11.1 Introduction (p. 293) A. The
... Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates and fats. a. Growth hormone-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus increases the amount of GH released, GH release-inhibiting hormone inhibits its release. b. Nutritional status ...
... Growth hormone (GH) stimulates body cells to grow and reproduce; it also speeds the rate at which cells use carbohydrates and fats. a. Growth hormone-releasing hormone from the hypothalamus increases the amount of GH released, GH release-inhibiting hormone inhibits its release. b. Nutritional status ...
Endocrine System
... 4. Parathormone – Control use of calcium phosphorus 5. Insulin – Secreted by pancreas 6. Calcitonin – Affects neuromuscular functioing, blood clotting, and holds cells together 7. Estrogen – Governs reproduction and fertility 8. Oxytocin – Causes the uterus to contract during labor ...
... 4. Parathormone – Control use of calcium phosphorus 5. Insulin – Secreted by pancreas 6. Calcitonin – Affects neuromuscular functioing, blood clotting, and holds cells together 7. Estrogen – Governs reproduction and fertility 8. Oxytocin – Causes the uterus to contract during labor ...
Hormonal Regula on of Homeostasis
... kidneys more permeable to water (more water retained by the body) ...
... kidneys more permeable to water (more water retained by the body) ...
hormone
... – insulin promotes the uptake of blood glucose (glycogen in the liver and triglycerides in fat cells) – glucagon causes liver cells to release stored glucose and fat cells to break down triglycerides ...
... – insulin promotes the uptake of blood glucose (glycogen in the liver and triglycerides in fat cells) – glucagon causes liver cells to release stored glucose and fat cells to break down triglycerides ...
05 Endocrine System note
... (nervous system adjusts to short term more on this later) So… How does it work? the hypothalamus regulates the pituitary gland through nerve stimulation, but it is the pituitary gland that stimulates the glands of the endocrine system to release hormones How did scientists find out about the h ...
... (nervous system adjusts to short term more on this later) So… How does it work? the hypothalamus regulates the pituitary gland through nerve stimulation, but it is the pituitary gland that stimulates the glands of the endocrine system to release hormones How did scientists find out about the h ...
The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands.
... secretions in the skin or inside the mouth. ...
... secretions in the skin or inside the mouth. ...
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
... Slow Initial Effects, but Effects Persist much longer Hormones act on specific Targets ...
... Slow Initial Effects, but Effects Persist much longer Hormones act on specific Targets ...
ANSWERS TO CHAPTER 10
... amino acids, both of which can be used as an energy source. In the liver and in skeletal muscle, the glucose is stored as glycogen. In adipose tissue glucose is converted to fat. The amino acids can be used to synthesize proteins or glucose. ...
... amino acids, both of which can be used as an energy source. In the liver and in skeletal muscle, the glucose is stored as glycogen. In adipose tissue glucose is converted to fat. The amino acids can be used to synthesize proteins or glucose. ...
hGH - ISpatula
... infundibulum and divided in to: • Anterior pituitary or adenohypophysis • Posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • The anterior pituitary receives signalling molecules from the hypothalamus, and in response, synthesizes and secretes seven important hormones. • The posterior pituitary does not produc ...
... infundibulum and divided in to: • Anterior pituitary or adenohypophysis • Posterior pituitary or neurohypophysis • The anterior pituitary receives signalling molecules from the hypothalamus, and in response, synthesizes and secretes seven important hormones. • The posterior pituitary does not produc ...
electrolyte regulation
... between the diaphysis and epiphysis B. Bone Growth Bone growth occurs as the epiphyseal plate lays down new bone at the end of the shaft. During development, the epiphyseal plate narrows and eventually disappears; this occurs in an orderly sequence at different times for different bones and permits ...
... between the diaphysis and epiphysis B. Bone Growth Bone growth occurs as the epiphyseal plate lays down new bone at the end of the shaft. During development, the epiphyseal plate narrows and eventually disappears; this occurs in an orderly sequence at different times for different bones and permits ...
L7 - Endocrine system - Moodle
... • Endocrine glands (ductless glands) – secretions (hormones) discharged into blood (or lymph) directly ...
... • Endocrine glands (ductless glands) – secretions (hormones) discharged into blood (or lymph) directly ...
start living. - Valley OBGYN Medical Group Inc.
... A clinical study showed that following treatment, most women can expect lighter and less painful periods, or possibly no periods at all. Nearly 9 out of 10 women treated had a reduction in menstrual pain and cramping 1 year after treatment. In addition, 2 out of 3 women treated experienced mild or n ...
... A clinical study showed that following treatment, most women can expect lighter and less painful periods, or possibly no periods at all. Nearly 9 out of 10 women treated had a reduction in menstrual pain and cramping 1 year after treatment. In addition, 2 out of 3 women treated experienced mild or n ...
Slide 1
... produce hormones that are released directly into the bloodstream – Glucagon: increases blood glucose (hyperglycemic) – Insulin: decreases blood glucose, only hormone that is hypoglycemic, absolutely necessary is only way that glucose can get to cells to be used – How insulin works ...
... produce hormones that are released directly into the bloodstream – Glucagon: increases blood glucose (hyperglycemic) – Insulin: decreases blood glucose, only hormone that is hypoglycemic, absolutely necessary is only way that glucose can get to cells to be used – How insulin works ...
Summary - Union High School
... After a few days, the egg reaches the uterus. The uterus is connected to the outside of the body by a canal called the vagina. One egg develops each month during the menstrual cycle. The cycle is controlled by hormones. It has four phases: follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase, and menstruation. ...
... After a few days, the egg reaches the uterus. The uterus is connected to the outside of the body by a canal called the vagina. One egg develops each month during the menstrual cycle. The cycle is controlled by hormones. It has four phases: follicular phase, ovulation, luteal phase, and menstruation. ...
the muscular system
... These are the male glands and are found in the groin, in the scrotum. The testes produce the hormone testosterone responsible for male sexual characteristics and for the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as the deepening of the voice and beard growth. ...
... These are the male glands and are found in the groin, in the scrotum. The testes produce the hormone testosterone responsible for male sexual characteristics and for the development of secondary sexual characteristics such as the deepening of the voice and beard growth. ...
Endocrine System Part 1
... Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gonadotropic hormones Regulate hormonal activity of the gonads Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Stimulates follicle development in ovaries Stimulates sperm development in testes Luteinizing hormone (LH) Triggers ovulation of an egg in females Sti ...
... Hormones of the Anterior Pituitary Gonadotropic hormones Regulate hormonal activity of the gonads Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Stimulates follicle development in ovaries Stimulates sperm development in testes Luteinizing hormone (LH) Triggers ovulation of an egg in females Sti ...
Uterine Fibroids: Uncommon Approaches to a Common Problem
... extremely large Record: 141 pounds (64 kg) ...
... extremely large Record: 141 pounds (64 kg) ...
13 Physiologicoanatomical peculiarities of endocrine system
... The thyroid (from the Greek word for "shield", after its shape) is one of the larger endocrine glands in the body. It is a double-lobed structure located in the neck and produces hormones, principally thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), that regulate the rate of metabolism and affect the growt ...
... The thyroid (from the Greek word for "shield", after its shape) is one of the larger endocrine glands in the body. It is a double-lobed structure located in the neck and produces hormones, principally thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), that regulate the rate of metabolism and affect the growt ...
Dr. AASHISH H. PANCHAL (M.PHARM., Ph.D.) GSEB, CBSE, ICSE
... Note: (1) In this section total 50 questions, each carry 1 mark (2) All questions are compulsory 1) Endocrine glands can be defined as those glands which pour their secretion :(A) Directly into blood (B) Into blood or ducts (C) When they are cut (D) Into particular organ 2) Sella turcica" is a :(A) ...
... Note: (1) In this section total 50 questions, each carry 1 mark (2) All questions are compulsory 1) Endocrine glands can be defined as those glands which pour their secretion :(A) Directly into blood (B) Into blood or ducts (C) When they are cut (D) Into particular organ 2) Sella turcica" is a :(A) ...
Endocrine System
... • Release of hormones is controlled by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus • Hypothlamus produces two hormones that are transorted to neurosecretory cells of the posterior pituitary • The poterior pituitary is not strictly an endocrine gland, but does release hormones ...
... • Release of hormones is controlled by releasing and inhibiting hormones produced by the hypothalamus • Hypothlamus produces two hormones that are transorted to neurosecretory cells of the posterior pituitary • The poterior pituitary is not strictly an endocrine gland, but does release hormones ...
IVF
... located in the laboratory which enables fertilization to occur. In some cases where fertilization is suspected to be low, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be used. Through this procedure, a single sperm is injected directly into the egg in an attempt to achieve fertilization. The eggs are ...
... located in the laboratory which enables fertilization to occur. In some cases where fertilization is suspected to be low, intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) may be used. Through this procedure, a single sperm is injected directly into the egg in an attempt to achieve fertilization. The eggs are ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.