Skip to content
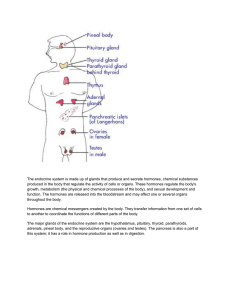
... The endocrine system is a complex collection of hormone-producing glands that control basic body functions such as metabolism, growth and sexual development. The amount of hormones produced by each gland is carefully balanced. Too much or too little of a certain hormone can have effects throughout t ...
... The endocrine system is a complex collection of hormone-producing glands that control basic body functions such as metabolism, growth and sexual development. The amount of hormones produced by each gland is carefully balanced. Too much or too little of a certain hormone can have effects throughout t ...
Endocrine System
... body fluids ductless glands that act together with the nervous system. By controlling cellular activities, endocrine glands play important roles in the maintenance homeostasis of _____________. The hypothalamus controls the ____________. pituitary gland The master gland is the _______________. pitui ...
... body fluids ductless glands that act together with the nervous system. By controlling cellular activities, endocrine glands play important roles in the maintenance homeostasis of _____________. The hypothalamus controls the ____________. pituitary gland The master gland is the _______________. pitui ...
Understanding Bio-Identical Hormone Replacement Therapy (BHRT
... approved 75mg testosterone pellet. Why pellets? Pellets deliver consistent, healthy levels of hormones for 3-5 months in women and 4-6 months in men. They avoid the fluctuations, or ups and downs, of hormone levels seen with every other method of delivery. Estrogen delivered by subcutaneous pellets, ...
... approved 75mg testosterone pellet. Why pellets? Pellets deliver consistent, healthy levels of hormones for 3-5 months in women and 4-6 months in men. They avoid the fluctuations, or ups and downs, of hormone levels seen with every other method of delivery. Estrogen delivered by subcutaneous pellets, ...
“Approved” on the meeting of methodical board Department of
... ambiguous genitalia. Sex assignment depends on the degree of masculinization present; if a male sex assignment is made, caution should be taken because gynecomastia may occur during puberty, if androgen receptor presence is inadequate. o 5-alpha reductase deficiency is a condition in genotypic mal ...
... ambiguous genitalia. Sex assignment depends on the degree of masculinization present; if a male sex assignment is made, caution should be taken because gynecomastia may occur during puberty, if androgen receptor presence is inadequate. o 5-alpha reductase deficiency is a condition in genotypic mal ...
MD0807 6-1 LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 6 Review of the
... b. Effects of Thyroxin. When thyroxin reaches the cells of the body, it stimulates them to use more oxygen. This increases the metabolic rate (basal metabolism) of the body. Basal metabolism is defined as the amount of oxygen the body uses per unit of weight when the body is at rest. Thyroxin also ...
... b. Effects of Thyroxin. When thyroxin reaches the cells of the body, it stimulates them to use more oxygen. This increases the metabolic rate (basal metabolism) of the body. Basal metabolism is defined as the amount of oxygen the body uses per unit of weight when the body is at rest. Thyroxin also ...
Endocrine System
... Testicular cancer, which is the most common form of cancer for males between ages 15 and 35, may need to be treated by surgical removal of one or both testicles. The resulting decrease or absence of testosterone may cause decreased sexual drive, impotence, altered body image, and other symptoms. ...
... Testicular cancer, which is the most common form of cancer for males between ages 15 and 35, may need to be treated by surgical removal of one or both testicles. The resulting decrease or absence of testosterone may cause decreased sexual drive, impotence, altered body image, and other symptoms. ...
Maternal Physiologic Changes
... of the hormones produced by that organ. Decreases in human chorionic somatomammotropin, estrogens, cortisol, and the placental enzyme insulinase reverse the diabetogenic effects of pregnancy, resulting in significantly lower blood sugar levels in the immediate puerperium. Mothers with type 1 diabete ...
... of the hormones produced by that organ. Decreases in human chorionic somatomammotropin, estrogens, cortisol, and the placental enzyme insulinase reverse the diabetogenic effects of pregnancy, resulting in significantly lower blood sugar levels in the immediate puerperium. Mothers with type 1 diabete ...
El-Etr 10 Hormones in MS Mat
... worsening of symptoms. The present pharmacological treatment of MS is limited to the administration of immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory drugs, which are only palliative and do not significantly slow progress of the disease. What are needed are agents that target different cell types in the CNS t ...
... worsening of symptoms. The present pharmacological treatment of MS is limited to the administration of immunomodulatory and anti-inflammatory drugs, which are only palliative and do not significantly slow progress of the disease. What are needed are agents that target different cell types in the CNS t ...
Pituitary hormones - Department of Molecular & Cell Biology
... testosterone at puberty result in the further growth of genitalia and the development of male secondary sex characteristics such as facial hair. DHT - Dihydrotestosterone - The enzyme 5 alpha reductase converts testosterone into its more potent form DHT. considered to be an aging-biomarker. Among it ...
... testosterone at puberty result in the further growth of genitalia and the development of male secondary sex characteristics such as facial hair. DHT - Dihydrotestosterone - The enzyme 5 alpha reductase converts testosterone into its more potent form DHT. considered to be an aging-biomarker. Among it ...
The Endocrine System - Biology at Lakeland
... Posterior Pituitary hormones: ◦ Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): decreases urine production; too little water in the bloodstream triggers release and less urine, too much water stops release and more urine is produced ◦ Oxytocin (OT): contracts smooth muscle in walls of uterus; stimulates uterine contrac ...
... Posterior Pituitary hormones: ◦ Antidiuretic hormone (ADH): decreases urine production; too little water in the bloodstream triggers release and less urine, too much water stops release and more urine is produced ◦ Oxytocin (OT): contracts smooth muscle in walls of uterus; stimulates uterine contrac ...
Chapter 18 - Martini
... • Produces melatonin – Stimulated by darkness – Contributes to maintaining day/cycles – Linked to seasonal affective disorder ...
... • Produces melatonin – Stimulated by darkness – Contributes to maintaining day/cycles – Linked to seasonal affective disorder ...
Pre-requisites to a successful clerkship
... o Check cervical effacement and dilation as well as fetal station o Assess fetal heart rate o Monitor uterine contractions every 30mins via palpation Pain management during labor o Nonpharmacologic methods: Education and psychoprophylaxis, emotional support, back massage, hydrotherapy, biofeedback ...
... o Check cervical effacement and dilation as well as fetal station o Assess fetal heart rate o Monitor uterine contractions every 30mins via palpation Pain management during labor o Nonpharmacologic methods: Education and psychoprophylaxis, emotional support, back massage, hydrotherapy, biofeedback ...
IVF - Texas Fertility Center
... control pills) for one cycle in order to allow a large group of developing oocytes to become synchronized. The purpose of oocyte synchronization is to increase the chance that multiple oocytes will develop at the same rate, resulting in a large number of mature eggs. The pills also reduce the likeli ...
... control pills) for one cycle in order to allow a large group of developing oocytes to become synchronized. The purpose of oocyte synchronization is to increase the chance that multiple oocytes will develop at the same rate, resulting in a large number of mature eggs. The pills also reduce the likeli ...
Endocrine Power PointPresentation1
... stimulates production of milk after childbirth THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE – TSH - stimulates thyroxine ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE – ACTH – stimulates adrenal cortex FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE – FSH -stimulates growth of graafian follicle and production of estrogen in females, sperm in males LUTE ...
... stimulates production of milk after childbirth THYROID-STIMULATING HORMONE – TSH - stimulates thyroxine ADRENOCORTICOTROPIC HORMONE – ACTH – stimulates adrenal cortex FOLLICLE-STIMULATING HORMONE – FSH -stimulates growth of graafian follicle and production of estrogen in females, sperm in males LUTE ...
CHAPTER 45
... • Cortex responsible for secretion of corticosteroids - regulated by nervous system in response to stress, 3 types. • AGlucocorticoids help to raise blood glucose levels. • High doses help in inflammation response. ...
... • Cortex responsible for secretion of corticosteroids - regulated by nervous system in response to stress, 3 types. • AGlucocorticoids help to raise blood glucose levels. • High doses help in inflammation response. ...
CH23 Gynecology
... • The process of fertilization begins in the vagina. – Sperm are deposited from the male penis, passes through cervix to uterus, and up the fallopian tubes. ...
... • The process of fertilization begins in the vagina. – Sperm are deposited from the male penis, passes through cervix to uterus, and up the fallopian tubes. ...
Chemical Signaling in Animals
... • Cortex responsible for secretion of corticosteroids - regulated by nervous system in response to stress, 3 types. • AGlucocorticoids help to raise blood glucose levels. • High doses help in inflammation response. ...
... • Cortex responsible for secretion of corticosteroids - regulated by nervous system in response to stress, 3 types. • AGlucocorticoids help to raise blood glucose levels. • High doses help in inflammation response. ...
The Endocrine System - St. Ambrose School
... • Hormones are chemical messengers that target specific cells • The specific cells that are effected by the specific hormones are called target cells • If a cell does not have receptors, or the receptors do not respond to a particular hormone, the hormone has no effect on it • The body’s response to ...
... • Hormones are chemical messengers that target specific cells • The specific cells that are effected by the specific hormones are called target cells • If a cell does not have receptors, or the receptors do not respond to a particular hormone, the hormone has no effect on it • The body’s response to ...
Chapter 31
... This produces the “flight or fight” reaction. In a fraction of a second, this hormone can be secreted in response to fear, anger, pain or physical exertion. – The adrenal cortex produces a hormone that helps the body deal with long-term stress. It is a steroid called cortisal. When stressful situati ...
... This produces the “flight or fight” reaction. In a fraction of a second, this hormone can be secreted in response to fear, anger, pain or physical exertion. – The adrenal cortex produces a hormone that helps the body deal with long-term stress. It is a steroid called cortisal. When stressful situati ...
Chapter 17
... At the target sites they diffuse out from the capillaries. Some hormones such as, steroids and thyroid hormones, are bound to specific plasma proteins reversibly. hormone + plasma protein = = hormone-protein ...
... At the target sites they diffuse out from the capillaries. Some hormones such as, steroids and thyroid hormones, are bound to specific plasma proteins reversibly. hormone + plasma protein = = hormone-protein ...
ES Note Booklet - Morinville Community High School
... A2. Defining endocrine glands, hormones, and negative feedback A3. Location of endocrine glands Key Concept B: The hypothalamus and pituitary complex controls the secretion of many of the bodyʼs hormones B1. Hormones of the Hypothalamus, posterior and anterior pituitary glands B2. Growth Hormone • g ...
... A2. Defining endocrine glands, hormones, and negative feedback A3. Location of endocrine glands Key Concept B: The hypothalamus and pituitary complex controls the secretion of many of the bodyʼs hormones B1. Hormones of the Hypothalamus, posterior and anterior pituitary glands B2. Growth Hormone • g ...
Endocrinology
... a) --- Alfa cells: which is secreted hormone (insulin). b) --- Beta cells: which is secreted glucogon. 7. Testes: they are two which produce male sex hormones or androgens. 8. Ovary: there are two ovaries produce female sex hormones which they are two types: a) Estrogen: secreted from the theca inte ...
... a) --- Alfa cells: which is secreted hormone (insulin). b) --- Beta cells: which is secreted glucogon. 7. Testes: they are two which produce male sex hormones or androgens. 8. Ovary: there are two ovaries produce female sex hormones which they are two types: a) Estrogen: secreted from the theca inte ...
Endocrine System
... • Most common, 90% of all cases of diabetes • Typically found in obese people over age 35 • Can be controlled through diet, exercise and weight loss – Can be temporary ...
... • Most common, 90% of all cases of diabetes • Typically found in obese people over age 35 • Can be controlled through diet, exercise and weight loss – Can be temporary ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.