Anterior Pituitary: Growth Hormone (GH)
... Under conditions of fear or stress, a surge of the hormone adrenaline mobilizes the body for peak physical response. Flooding the bloodstream at up to 300 times the normal concentration, the adrenaline interacts with receptors on cells in various organs, increasing the heart rate and blood pressure ...
... Under conditions of fear or stress, a surge of the hormone adrenaline mobilizes the body for peak physical response. Flooding the bloodstream at up to 300 times the normal concentration, the adrenaline interacts with receptors on cells in various organs, increasing the heart rate and blood pressure ...
I-Introduction
... Virtually all cells in the body that use chemicals to communicate with one another ...
... Virtually all cells in the body that use chemicals to communicate with one another ...
chapter 50 endocrine systems
... Lipid hormone receptors Receptors located within the cell (in cytosol or nucleus) Steroid hormone-receptor complex acts as transcriptional activator to enhance particular genes Transcription of gene enhance and more of that gene’s product produced Can influence a number of genes within a sing ...
... Lipid hormone receptors Receptors located within the cell (in cytosol or nucleus) Steroid hormone-receptor complex acts as transcriptional activator to enhance particular genes Transcription of gene enhance and more of that gene’s product produced Can influence a number of genes within a sing ...
Ch 11 study outline
... Their receptors are located in the target cell's ________________________. The hormone-receptor complex binds with the ____________ and activates specific _________________ that, in turn, direct the synthesis of specific _______________. ______________________ hormones combine with receptors in targ ...
... Their receptors are located in the target cell's ________________________. The hormone-receptor complex binds with the ____________ and activates specific _________________ that, in turn, direct the synthesis of specific _______________. ______________________ hormones combine with receptors in targ ...
Endocrine glands
... Adrenal glands They are two, fitting like a cap on the upper pole of each kidney, the outer part of each gland is called the adrenal cortex , the inner part is called the adrenal medulla. ...
... Adrenal glands They are two, fitting like a cap on the upper pole of each kidney, the outer part of each gland is called the adrenal cortex , the inner part is called the adrenal medulla. ...
Swyer syndrome in a woman with pure 46,XY gonadal dysgenesis
... gonadectomy because of the high risk of neoplastic transformation. Therefore, females with Swyer syndrome required close follow up because of the high risk of neoplastic transformation in the dysgenetic gonads. In this case, after estrogen therapy patient had her first menstruation cycle but menstru ...
... gonadectomy because of the high risk of neoplastic transformation. Therefore, females with Swyer syndrome required close follow up because of the high risk of neoplastic transformation in the dysgenetic gonads. In this case, after estrogen therapy patient had her first menstruation cycle but menstru ...
Clues
... 17. Hormone produced by the pineal gland in the absence of light. 19. An increase in the rate of receptor molecule synthesis is called ___ regulation. 21. Disease that results from a hyperthyroidism. 22. General name given to male sex hormones. 24. The ____ pituitary secretes two neurohormones. (oxy ...
... 17. Hormone produced by the pineal gland in the absence of light. 19. An increase in the rate of receptor molecule synthesis is called ___ regulation. 21. Disease that results from a hyperthyroidism. 22. General name given to male sex hormones. 24. The ____ pituitary secretes two neurohormones. (oxy ...
Fibrocystic Breasts - Facey Medical Group
... Signs and symptoms differ among women and with age, and generally include: • May have no symptoms. • Your breasts are swollen. • They feel tender or painful. Can be described as a dull or aching pain, heaviness, or soreness. • Your breasts feel lumpy. Cystic areas feel thick. • Some lumps remain in ...
... Signs and symptoms differ among women and with age, and generally include: • May have no symptoms. • Your breasts are swollen. • They feel tender or painful. Can be described as a dull or aching pain, heaviness, or soreness. • Your breasts feel lumpy. Cystic areas feel thick. • Some lumps remain in ...
GLANDS AT A GLANCE
... day-to-day details. Both sexes produce male and female hormones, but at different levels, depending on gender. • Testosterone, the primary androgen, or male hormone, maintains sperm production, contributes to secondary sex characteristics and fires libido. • Estrogen, produced by an active follicle, ...
... day-to-day details. Both sexes produce male and female hormones, but at different levels, depending on gender. • Testosterone, the primary androgen, or male hormone, maintains sperm production, contributes to secondary sex characteristics and fires libido. • Estrogen, produced by an active follicle, ...
NS440 Exam 3 - WordPress.com
... dec’s 1cm/24h); placental site does not scar; locia (rubra- 13days, bright red; serosa- 10-22days, pinkish brownish; albaup to 6wks, whitish) -cervix- begins to regenerate 2-3days pp; normal by 1wk -vagina- muscle tone never completely returns, but back to normal size 6-10wks -ovarian fxn & menstrua ...
... dec’s 1cm/24h); placental site does not scar; locia (rubra- 13days, bright red; serosa- 10-22days, pinkish brownish; albaup to 6wks, whitish) -cervix- begins to regenerate 2-3days pp; normal by 1wk -vagina- muscle tone never completely returns, but back to normal size 6-10wks -ovarian fxn & menstrua ...
Ch 18 Notes: Endocrine System 2014
... 7. growth and development 8. processes of reproduction Note: Hormones only affect SPECIFIC TARGET CELLS that have receptors for that particular hormone. ...
... 7. growth and development 8. processes of reproduction Note: Hormones only affect SPECIFIC TARGET CELLS that have receptors for that particular hormone. ...
Endocrine System
... 4. Parathormone – Control use of calcium phosphorus 5. Insulin – Secreted by pancreas 6. Calcitonin – Affects neuromuscular functioing, blood clotting, and holds cells together 7. Estrogen – Governs reproduction and fertility 8. Oxytocin – Causes the uterus to contract during ...
... 4. Parathormone – Control use of calcium phosphorus 5. Insulin – Secreted by pancreas 6. Calcitonin – Affects neuromuscular functioing, blood clotting, and holds cells together 7. Estrogen – Governs reproduction and fertility 8. Oxytocin – Causes the uterus to contract during ...
Hormones
... A. releases chemicals into the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body. B. releases hormones that alter the metabolic activities of many different tissues and organs simultaneously. C. produces effects that can last for hours, days and even longer. D. Both A and B are correct. E. A, B and C ...
... A. releases chemicals into the bloodstream for distribution throughout the body. B. releases hormones that alter the metabolic activities of many different tissues and organs simultaneously. C. produces effects that can last for hours, days and even longer. D. Both A and B are correct. E. A, B and C ...
Lecture Slides - Austin Community College
... – Keeping blood sugar levels relatively constant – Maintaining blood volume and preventing water shift into tissue ...
... – Keeping blood sugar levels relatively constant – Maintaining blood volume and preventing water shift into tissue ...
doc Lectures 1
... Inflammatory disease (traditional hypothesis). RCT (randomised control trials) are being conducted now to explore MS more. The Endocrine System Endocrine means 'the internal secretion of a biologically active substance'. The system is hierarchical, some glands control other glands. Hormone Definitio ...
... Inflammatory disease (traditional hypothesis). RCT (randomised control trials) are being conducted now to explore MS more. The Endocrine System Endocrine means 'the internal secretion of a biologically active substance'. The system is hierarchical, some glands control other glands. Hormone Definitio ...
Classification of Hormones Lecture 1
... • Their half-life is very short and their action is also for a very short time. • They bind to receptors on the cell membrane and their further action is mediated through a second messenger, the hormone itself being the first messenger. • Most peptide hormones like insulin, glucagon, and hormones of ...
... • Their half-life is very short and their action is also for a very short time. • They bind to receptors on the cell membrane and their further action is mediated through a second messenger, the hormone itself being the first messenger. • Most peptide hormones like insulin, glucagon, and hormones of ...
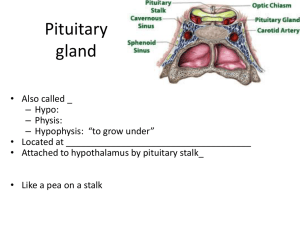
Pituitary gland
... • Also has ___________________________________, but not as strong as ADH • Causes ___________________________________: – Uterine wall: childbirth – One of the few _______________________________________________ ___ systems: – uterus stretches signals hypothalamus to release Oxytocin causes uteri ...
... • Also has ___________________________________, but not as strong as ADH • Causes ___________________________________: – Uterine wall: childbirth – One of the few _______________________________________________ ___ systems: – uterus stretches signals hypothalamus to release Oxytocin causes uteri ...
Pharmacist Information
... absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) are greater than or equal to 1.5 x 109/L (1500/µL) and both the nadir and Day 29, Day 1 of next cycle platelet counts are greater than or equal to 100 x 109/L (100,000/µL), the TEMODAR dose may be increased to 200 mg/m2/day for 5 consecutive days per 28-day treatment ...
... absolute neutrophil counts (ANC) are greater than or equal to 1.5 x 109/L (1500/µL) and both the nadir and Day 29, Day 1 of next cycle platelet counts are greater than or equal to 100 x 109/L (100,000/µL), the TEMODAR dose may be increased to 200 mg/m2/day for 5 consecutive days per 28-day treatment ...
Endocrine System
... – moves amino acids out of the blood and into the cells, accelerating the building of proteins – also affects the fat and carbohydrate metabolism and thus affects blood glucose levels – increases blood glucose where insulin decreases blood glucose – Hypersecretion of GH during the early years of lif ...
... – moves amino acids out of the blood and into the cells, accelerating the building of proteins – also affects the fat and carbohydrate metabolism and thus affects blood glucose levels – increases blood glucose where insulin decreases blood glucose – Hypersecretion of GH during the early years of lif ...
Chapter (3) Unexplained Infertility
... In addition to a thorough menstrual history, other methods used to evaluate ovulation include basal body temperature (BBT) recordings, urinary luteinizing hormone (LH) ovulation predictor kits, mid luteal serum progesterone testing, and endometrial biopsy to assess for secretory endometrial developm ...
... In addition to a thorough menstrual history, other methods used to evaluate ovulation include basal body temperature (BBT) recordings, urinary luteinizing hormone (LH) ovulation predictor kits, mid luteal serum progesterone testing, and endometrial biopsy to assess for secretory endometrial developm ...
Document
... control devices and ask specifically about the patient’s last menstrual period. The EMT should also inquire about the possibility of sexually transmitted diseases and the possibility of pregnancy. ...
... control devices and ask specifically about the patient’s last menstrual period. The EMT should also inquire about the possibility of sexually transmitted diseases and the possibility of pregnancy. ...
Chapter 21: Gynecological Emergencies
... control devices and ask specifically about the patient’s last menstrual period. The EMT should also inquire about the possibility of sexually transmitted diseases and the possibility of pregnancy. ...
... control devices and ask specifically about the patient’s last menstrual period. The EMT should also inquire about the possibility of sexually transmitted diseases and the possibility of pregnancy. ...
Ob/Gyn Turkey Book
... Surgical – ovarian wedge resection, lap ovarian laser electrocautery Pharmacological – if patient NOT wishing to be pregnant: OCPs, antiandrogen (i.e. spironolactone), metformin; if desiring pregnancy: clomid and metformin Comps: Increased risk of PIH, GDM, endometrial & ovarian cancer, metabolic sy ...
... Surgical – ovarian wedge resection, lap ovarian laser electrocautery Pharmacological – if patient NOT wishing to be pregnant: OCPs, antiandrogen (i.e. spironolactone), metformin; if desiring pregnancy: clomid and metformin Comps: Increased risk of PIH, GDM, endometrial & ovarian cancer, metabolic sy ...
Gonadotropins - Center for Human Reproduction
... 10 pounds and severe pelvic pain may occur. Hospitalization may be required if ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome progresses to a severe state. This can be a life threatening condition. In correlation induction cycles human menopausal gonadotropins may cause more than 1 egg to be released in a single ...
... 10 pounds and severe pelvic pain may occur. Hospitalization may be required if ovarian hyperstimulation syndrome progresses to a severe state. This can be a life threatening condition. In correlation induction cycles human menopausal gonadotropins may cause more than 1 egg to be released in a single ...
New classification of Abnormal Uterine Bleeding: Why is it
... No significant past medical / family history Rx: COC – contraception & improved HMB Now symptoms changed: heavier menses & developed inter-menstrual bleeding. No changes in her medication Abd and Gynae exam: NAD ...
... No significant past medical / family history Rx: COC – contraception & improved HMB Now symptoms changed: heavier menses & developed inter-menstrual bleeding. No changes in her medication Abd and Gynae exam: NAD ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.