Women`s Health Partners, LLC
... Endometrial = pertaining to the tissue layer that forms the inner lining (endometrium) of the uterine (womb) wall Ablation = Removal of a body part or the destruction of its function, as by a surgery, disease, or noxious substance. Hystero = of or denoting the womb (uterus) Scopy = examination with ...
... Endometrial = pertaining to the tissue layer that forms the inner lining (endometrium) of the uterine (womb) wall Ablation = Removal of a body part or the destruction of its function, as by a surgery, disease, or noxious substance. Hystero = of or denoting the womb (uterus) Scopy = examination with ...
The Endocrine System
... Because of its peripheral effects & the need for parenteral administration, dopamine is not useful in the control of hyperprolactinemia, but bromocrptine & other orally active ergot –derivatives (eg. Cabergoline, pergoline) are effective in reducing prolactin secretion from the normal glands as well ...
... Because of its peripheral effects & the need for parenteral administration, dopamine is not useful in the control of hyperprolactinemia, but bromocrptine & other orally active ergot –derivatives (eg. Cabergoline, pergoline) are effective in reducing prolactin secretion from the normal glands as well ...
13 year old Female with Too Many Periods Materials for
... secondary amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, anovulatory regular menses, and frequent cycles with abnormal uterine bleeding. These adolescents typically also have signs of androgen excess (acne, hirsutism) or insulin resistance such as acanthosis nigricans; over half are obese. Adolescents have mostly anov ...
... secondary amenorrhea, oligomenorrhea, anovulatory regular menses, and frequent cycles with abnormal uterine bleeding. These adolescents typically also have signs of androgen excess (acne, hirsutism) or insulin resistance such as acanthosis nigricans; over half are obese. Adolescents have mostly anov ...
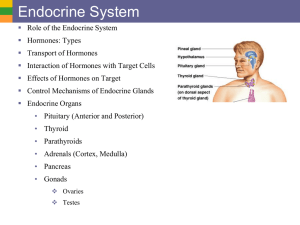
Chapter 20 Endocrine system
... Negative feedback seeks to decrease a stimulus. When a desired effect is achieved, the negative feedback system works to stop the stimulus and bring the body into homeostasis. A positive feedback system works to enhance the body reaction, so that hormones are then released in response to a stimulus. ...
... Negative feedback seeks to decrease a stimulus. When a desired effect is achieved, the negative feedback system works to stop the stimulus and bring the body into homeostasis. A positive feedback system works to enhance the body reaction, so that hormones are then released in response to a stimulus. ...
Chapter 20 Endocrine system part 2
... GH stimulates growth in all body tissues. Helps assist amino acids into body tissues to build up proteins. Gonadotropin releasing hormone ( GnRH) causes the anterior pituitary to secrete two hormones called gonadotripins that stimulate the sex glands in the body. These two hormones are called follic ...
... GH stimulates growth in all body tissues. Helps assist amino acids into body tissues to build up proteins. Gonadotropin releasing hormone ( GnRH) causes the anterior pituitary to secrete two hormones called gonadotripins that stimulate the sex glands in the body. These two hormones are called follic ...
McHenry Western Lake County EMS System Paramedic, EMT
... For example, for the hormones that are regulated by the pituitary gland, a signal is sent from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland in the form of a “releasing hormone.” This causes the pituitary to secrete a “stimulating hormone” into the circulation. The stimulating hormone then signals the tar ...
... For example, for the hormones that are regulated by the pituitary gland, a signal is sent from the hypothalamus to the pituitary gland in the form of a “releasing hormone.” This causes the pituitary to secrete a “stimulating hormone” into the circulation. The stimulating hormone then signals the tar ...
The Endocrine System - Catherine Huff's Site
... • Produces small amounts of estrogen and progesterone • Produces chorionic gonadotropin • What is tested for in pregnancy tests. ...
... • Produces small amounts of estrogen and progesterone • Produces chorionic gonadotropin • What is tested for in pregnancy tests. ...
Diagnosis and treatment of PCOS
... has been a promising approach, and initial studies seemed to show effectiveness.14,16 However, subsequent reviews in 2008 and 2009 have noted that randomised control trials have, in general, not shown the promise suggested by the early observational studies.17 ...
... has been a promising approach, and initial studies seemed to show effectiveness.14,16 However, subsequent reviews in 2008 and 2009 have noted that randomised control trials have, in general, not shown the promise suggested by the early observational studies.17 ...
a11 Endocrine System
... • Helps establish the body’s wake and sleep cycles • May have other asyetunsubstantiated functions ...
... • Helps establish the body’s wake and sleep cycles • May have other asyetunsubstantiated functions ...
Chapter 11 The Endocrine System
... • Its symptoms are often less dramatic than primary adrenal insufficiency, because aldosterone secretion, which does not rely on ACTH, is maintained by other mechanisms. • Adrenal insufficiency can be life-threatening if not treated aggressively. ...
... • Its symptoms are often less dramatic than primary adrenal insufficiency, because aldosterone secretion, which does not rely on ACTH, is maintained by other mechanisms. • Adrenal insufficiency can be life-threatening if not treated aggressively. ...
Nerve activates contraction
... Luteinizing hormone (LH) Triggers ovulation Causes ruptured follicle to become the corpus luteum Stimulates testosterone production in males Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
... Luteinizing hormone (LH) Triggers ovulation Causes ruptured follicle to become the corpus luteum Stimulates testosterone production in males Referred to as interstitial cell-stimulating hormone (ICSH) ...
parafollicular cell hormone
... Gland source= Adrenal Cortex (Zona Reticularis) Target=High levels occur mostly in the fetus and in early puberty, after this time has past, the gonads take over. Action=Increases cell metabolism, red blood cell production in infants. In adult females, may play a role in the level of sex drive (libi ...
... Gland source= Adrenal Cortex (Zona Reticularis) Target=High levels occur mostly in the fetus and in early puberty, after this time has past, the gonads take over. Action=Increases cell metabolism, red blood cell production in infants. In adult females, may play a role in the level of sex drive (libi ...
Hypopituitarism
... pressure and blood glucose (sugar) levels, especially during stress, illness, or injury ...
... pressure and blood glucose (sugar) levels, especially during stress, illness, or injury ...
Chemical coordina Answer 1: (a) Exocrine gland
... the Ca2+ levels in the blood. PTH promotes the reabsorption of calcium from nephrons and also, promotes the absorption of calcium from digested food. Thus, it plays an important role in calcium balance in the body. (b) Thyroid hormones: Thyroid hormones play an important role in the regulation of th ...
... the Ca2+ levels in the blood. PTH promotes the reabsorption of calcium from nephrons and also, promotes the absorption of calcium from digested food. Thus, it plays an important role in calcium balance in the body. (b) Thyroid hormones: Thyroid hormones play an important role in the regulation of th ...
Chapter 8: Chemical Signals Maintain Homeostasis
... • They regulate body metabolism, growth, and differentiation ...
... • They regulate body metabolism, growth, and differentiation ...
the endocrine system
... Insulin and glucagon which are important in controlling blood sugar levels. Glucagon - increases blood sugar levels by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen in hepatocytes (storage form in liver) to glucose in the blood. Insulin - serves to decrease blood sugar levels by moving sugar from the blood ...
... Insulin and glucagon which are important in controlling blood sugar levels. Glucagon - increases blood sugar levels by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen in hepatocytes (storage form in liver) to glucose in the blood. Insulin - serves to decrease blood sugar levels by moving sugar from the blood ...
The Endocrine System
... 444. Sperm cells ___. A. start to migrate towards uterus immediately after being ejaculated into vagina B. are not able to fertilize an egg without capacitation C. can all find the egg ...
... 444. Sperm cells ___. A. start to migrate towards uterus immediately after being ejaculated into vagina B. are not able to fertilize an egg without capacitation C. can all find the egg ...
Hormones and the Endocrine System Intercellular communication
... Long-term stress response • Glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, influence glucose metabolism and the immune system • Mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone, affect salt and water balance • The adrenal cortex also produces small amounts of steroid hormones that function as sex hormones ...
... Long-term stress response • Glucocorticoids, such as cortisol, influence glucose metabolism and the immune system • Mineralocorticoids, such as aldosterone, affect salt and water balance • The adrenal cortex also produces small amounts of steroid hormones that function as sex hormones ...
Hormonal Control
... posterior pituitary. It is carried by the blood to the kidneys. The kidneys respond by decreasing urine output, and more water is retained. The ADH also decreases the rate of perspiration. ADH can also increase blood pressure caused by the constriction of arterioles. If the water concentration in th ...
... posterior pituitary. It is carried by the blood to the kidneys. The kidneys respond by decreasing urine output, and more water is retained. The ADH also decreases the rate of perspiration. ADH can also increase blood pressure caused by the constriction of arterioles. If the water concentration in th ...
PREG Minimal IVF Comparison and Consent (.doc)
... breathing becomes difficult. Patients with severe OHSS require hospitalization until the symptoms improve. If pregnancy occurs, OHSS can worsen. Occasionally, termination of pregnancy must be considered in the most severe cases. Although initial reports suggested that women who use fertility drugs h ...
... breathing becomes difficult. Patients with severe OHSS require hospitalization until the symptoms improve. If pregnancy occurs, OHSS can worsen. Occasionally, termination of pregnancy must be considered in the most severe cases. Although initial reports suggested that women who use fertility drugs h ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.