hormones
... 2- Glucocorticoids(cortisol) Essential to life, they : -influence the energy metabolism of most body cells - help us to resist stressors as hemorrhage, infection, or physical or emotional trauma . -keep blood glucose levels fairly constant (hyperglycemic) by breaking down of fats and even proteins(g ...
... 2- Glucocorticoids(cortisol) Essential to life, they : -influence the energy metabolism of most body cells - help us to resist stressors as hemorrhage, infection, or physical or emotional trauma . -keep blood glucose levels fairly constant (hyperglycemic) by breaking down of fats and even proteins(g ...
Primolut N PI
... Norethisterone is mainly metabolised by saturation of the double bond in ring A and the reduction of the 3-keto group to a hydroxyl group followed by conjugation to the corresponding sulfates and glucuronides. Some of these metabolites are eliminated slowly from plasma, building approximately to a p ...
... Norethisterone is mainly metabolised by saturation of the double bond in ring A and the reduction of the 3-keto group to a hydroxyl group followed by conjugation to the corresponding sulfates and glucuronides. Some of these metabolites are eliminated slowly from plasma, building approximately to a p ...
Hormones - prakashamarasooriya
... Oral Contraception and Synthetic Hormones Progesterone is quite expensive and breaks down rapidly in the liver. Progesterone-like synthetic chemicals such as norethynodrel and norethindrone are now commonly used in birth control pills. They are combined with an estradiol-like compound to prevent ir ...
... Oral Contraception and Synthetic Hormones Progesterone is quite expensive and breaks down rapidly in the liver. Progesterone-like synthetic chemicals such as norethynodrel and norethindrone are now commonly used in birth control pills. They are combined with an estradiol-like compound to prevent ir ...
Hysteroscopic Myomectomy (morcellation)
... typically cause irregular bleeding and fibroids commonly cause heavy bleeding. Endometrial polyps are growths extending from the lining of uterus, called the “endometrium”. Polyps cause irregular spotting or pre or postmenstrual staining. In rare cases, polyps can become cancerous. The risk for canc ...
... typically cause irregular bleeding and fibroids commonly cause heavy bleeding. Endometrial polyps are growths extending from the lining of uterus, called the “endometrium”. Polyps cause irregular spotting or pre or postmenstrual staining. In rare cases, polyps can become cancerous. The risk for canc ...
Chapter 10: Hormonal Control Systems
... Chapter 11: Hormonal Control Systems Name several endocrine glands that secrete more than one hormone and list those hormones. Give an example of a hormone that is secreted by three different glands. What are the three chemical classes of hormones? How do the classes of hormones differ with respect ...
... Chapter 11: Hormonal Control Systems Name several endocrine glands that secrete more than one hormone and list those hormones. Give an example of a hormone that is secreted by three different glands. What are the three chemical classes of hormones? How do the classes of hormones differ with respect ...
Endocrine Physiology
... • LH in females and in males leads to sex hormone secretion • FSH in females causes growth and development of egg cellcontaining follicles in the ovary, and causes estrogen secretion • FSH in males instigates sperm production • both hormones are regulated by GnRH, which is not significant in concent ...
... • LH in females and in males leads to sex hormone secretion • FSH in females causes growth and development of egg cellcontaining follicles in the ovary, and causes estrogen secretion • FSH in males instigates sperm production • both hormones are regulated by GnRH, which is not significant in concent ...
Endocrine Virtual Lab! AP Biology
... sustains the female reproductive tract. A woman who lacks ovaries (and therefore follicles) will not produce estrogen. However, the pituitary gland will secrete excess LH because the feedback inhibition no longer exists. Excess levels of estrogen cause early sexual development in the female as do hi ...
... sustains the female reproductive tract. A woman who lacks ovaries (and therefore follicles) will not produce estrogen. However, the pituitary gland will secrete excess LH because the feedback inhibition no longer exists. Excess levels of estrogen cause early sexual development in the female as do hi ...
The Endocrine System - Highland 4U Biology with Mr. Byrnes
... dramatically demonstrate the actions of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, hormones and target cells/organs • Use cue cards and markers to illustrate which components of the system each person represents • Be sure to include details such as what each hormone does and which component is stimulating w ...
... dramatically demonstrate the actions of the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, hormones and target cells/organs • Use cue cards and markers to illustrate which components of the system each person represents • Be sure to include details such as what each hormone does and which component is stimulating w ...
ABNORMAL UTERINE BLEEDING
... Adrenal hyperplasia and Cushings Pituitary adenoma or hyperprolactinemia Hypothalamic suppression (from stress, weight loss, excessive exercise ...
... Adrenal hyperplasia and Cushings Pituitary adenoma or hyperprolactinemia Hypothalamic suppression (from stress, weight loss, excessive exercise ...
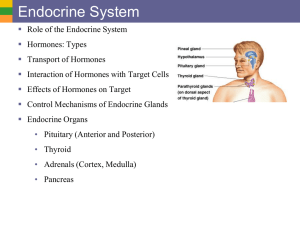
Endocrine System
... that signals a response • They are secreted in blood stream and go to certain tissues called target tissue/cell • Target cell (tissue)— cell that can only can be signaled by a certain hormone – They get to the tissue by traveling thru blood ...
... that signals a response • They are secreted in blood stream and go to certain tissues called target tissue/cell • Target cell (tissue)— cell that can only can be signaled by a certain hormone – They get to the tissue by traveling thru blood ...
presentation source
... A. Insulin lowers blood glucose and stimulates the production of glycogen, fat, and protein. B. Glucagon raises blood glucose by stimulating the breakdown of liver glycogen. It also promotes lipolysis and the formation of ketone bodies. C. The secretion of insulin is stimulated by a rise in blood gl ...
... A. Insulin lowers blood glucose and stimulates the production of glycogen, fat, and protein. B. Glucagon raises blood glucose by stimulating the breakdown of liver glycogen. It also promotes lipolysis and the formation of ketone bodies. C. The secretion of insulin is stimulated by a rise in blood gl ...
Guide for Families - the National Urea Cycle Disorders Foundation
... of the urea cycle. Babies in this situation, usually present with drowsiness, rapid breathing and vomiting. It is likely that a spell in hospital will be necessary to lower the level of ammonia in the blood and to aid the baby with breathing. Older children with a urea cycle disorder, may become ver ...
... of the urea cycle. Babies in this situation, usually present with drowsiness, rapid breathing and vomiting. It is likely that a spell in hospital will be necessary to lower the level of ammonia in the blood and to aid the baby with breathing. Older children with a urea cycle disorder, may become ver ...
1 Endocrine System
... communication system than the nervous system Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes ...
... communication system than the nervous system Uses chemical messages (hormones) that are released into the blood Hormones control several major processes ...
ANP 201 Dr Smith - University of Agriculture Abeokuta
... cholesterol in the gonads (testes and ovaries) and adrenal cortex of both sexes. They include estrogens, androgens and progesterone. 1. Testosterone (androgen) The androgens of which testosterone is the most prominent are produced mainly by the interstitial cells of the testes. They affect most tiss ...
... cholesterol in the gonads (testes and ovaries) and adrenal cortex of both sexes. They include estrogens, androgens and progesterone. 1. Testosterone (androgen) The androgens of which testosterone is the most prominent are produced mainly by the interstitial cells of the testes. They affect most tiss ...
REVIEW History of the study of uterine cavity O&G Forum 2006;16:38-42
... beneficial to patients with menorrhagia. Medical and hormonal treatment Hormone therapy will benefit approximately 65% of patients. High dose estrogen can be used initially to treat women who are haemodynamically stable. The result is rapid regrowth of the endometrium and an increase in fibrinogen a ...
... beneficial to patients with menorrhagia. Medical and hormonal treatment Hormone therapy will benefit approximately 65% of patients. High dose estrogen can be used initially to treat women who are haemodynamically stable. The result is rapid regrowth of the endometrium and an increase in fibrinogen a ...
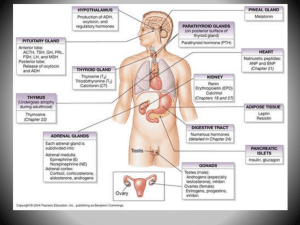
CHAPTER 13: ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
... consist of 4 small glands; are located within the thyroid gland; produce a hormone called Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): a. release of PTH is stimulated by decreased blood calcium levels; b. PTH targets bone cells (activates osteoclasts to resorb bone), proximal convoluted tubules (causes PCT’s to reabs ...
... consist of 4 small glands; are located within the thyroid gland; produce a hormone called Parathyroid Hormone (PTH): a. release of PTH is stimulated by decreased blood calcium levels; b. PTH targets bone cells (activates osteoclasts to resorb bone), proximal convoluted tubules (causes PCT’s to reabs ...
Policy (Word)
... secondary care to specialist IVF services and maintained during treatment. This applies equally for same-sex couples as passive smoking may affect the fertility of the partner undergoing fertility treatment. Smoking status should be ascertained by carbon monoxide testing in secondary care and specia ...
... secondary care to specialist IVF services and maintained during treatment. This applies equally for same-sex couples as passive smoking may affect the fertility of the partner undergoing fertility treatment. Smoking status should be ascertained by carbon monoxide testing in secondary care and specia ...
The Endocrine System
... _____________________ in infants and children Produces ___________________________ Matures some types of white blood cells Important in developing the __________________ system ...
... _____________________ in infants and children Produces ___________________________ Matures some types of white blood cells Important in developing the __________________ system ...
w3.lphs.org
... A general hormonal response to stress would be 1. An increase in epinephrine 2. A decrease in cortisol 3. A decrease in glucagon 4. An increase in FSH ...
... A general hormonal response to stress would be 1. An increase in epinephrine 2. A decrease in cortisol 3. A decrease in glucagon 4. An increase in FSH ...
Chapter 15-B Endocrine Glands
... • ACTH, MSH, endorphins and lipotropins all derived from the same large precursor molecule when stimulated by CRH • MSH (Melanocyte-stimulating hormone) causes melanocytes to produce more melanin • Endorphins act as an analgesic; produced during times of stress • Lipotropins cause adipose cells to ...
... • ACTH, MSH, endorphins and lipotropins all derived from the same large precursor molecule when stimulated by CRH • MSH (Melanocyte-stimulating hormone) causes melanocytes to produce more melanin • Endorphins act as an analgesic; produced during times of stress • Lipotropins cause adipose cells to ...
Principles of Endocrinology
... Adenohypophysis & Neurohypophysis • Adenohypophysis constitutes anterior three-quarters of pituitary – linked to hypothalamus by hypophyseal portal system • primary capillaries in hypothalamus connected to secondary capillaries in adenohypophysis by portal venules • hypothalamic hormones regulate a ...
... Adenohypophysis & Neurohypophysis • Adenohypophysis constitutes anterior three-quarters of pituitary – linked to hypothalamus by hypophyseal portal system • primary capillaries in hypothalamus connected to secondary capillaries in adenohypophysis by portal venules • hypothalamic hormones regulate a ...
Bio-identical Hormone replacement tHerapy
... progesterone was very short and researchers were looking for an agent that would give a longer half life and yet produce or mimic the effects of progesterone. Birth control pills contain, in most cases, a synthetic progestin and a synthetic estrogen. The very potent synthetic progestins prevent ovul ...
... progesterone was very short and researchers were looking for an agent that would give a longer half life and yet produce or mimic the effects of progesterone. Birth control pills contain, in most cases, a synthetic progestin and a synthetic estrogen. The very potent synthetic progestins prevent ovul ...
The Endocrine Glands
... Hormones regulate body’s growth, metabolism and sexual development and function In charge of body processes that happen slowly ...
... Hormones regulate body’s growth, metabolism and sexual development and function In charge of body processes that happen slowly ...
CRYDERS-Endocrine System
... • ACTH, MSH, endorphins and lipotropins all derived from the same large precursor molecule when stimulated by CRH • MSH (Melanocyte-stimulating hormone) causes melanocytes to produce more melanin • Endorphins act as an analgesic; produced during times of stress • Lipotropins cause adipose cells to ...
... • ACTH, MSH, endorphins and lipotropins all derived from the same large precursor molecule when stimulated by CRH • MSH (Melanocyte-stimulating hormone) causes melanocytes to produce more melanin • Endorphins act as an analgesic; produced during times of stress • Lipotropins cause adipose cells to ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.