ADOLESCENT GYNECOLOGY
... ovarian cysts in the postmenarchal adolescent is quite extensive (Table). Despite the vastness of the differential, the most common type of lesion in It is controversial this population is a functional whether laparotomy cyst. It represents 45% of adnex- or laparoscopy is the al pathology in childre ...
... ovarian cysts in the postmenarchal adolescent is quite extensive (Table). Despite the vastness of the differential, the most common type of lesion in It is controversial this population is a functional whether laparotomy cyst. It represents 45% of adnex- or laparoscopy is the al pathology in childre ...
hormones and behavior
... • Specific hormones only affect certain c cells and hormones affect different cells in different ways – T Targett cells ll possess receptors t f r specific for ifi h hormones – Target cells vary in the transductio on machinery they possess – Diverse responses to particular ho ormones possible ...
... • Specific hormones only affect certain c cells and hormones affect different cells in different ways – T Targett cells ll possess receptors t f r specific for ifi h hormones – Target cells vary in the transductio on machinery they possess – Diverse responses to particular ho ormones possible ...
The Endocrine System
... • eight hormones produced in hypothalamus – six regulate the anterior pituitary – two are released into capillaries in the posterior pituitary when hypothalamic neurons are stimulated (oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone) ...
... • eight hormones produced in hypothalamus – six regulate the anterior pituitary – two are released into capillaries in the posterior pituitary when hypothalamic neurons are stimulated (oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone) ...
Endocrine System
... Negative feedback control mechanisms operate to maintain whatever set point is established for that time. ...
... Negative feedback control mechanisms operate to maintain whatever set point is established for that time. ...
AP 2 Exam Chapter 16 Endocrie Due Wed. night 4/22 or Thurs
... reactions involving receptor and kinase activation. In order for cells to respond, it is necessary for first and second messengers to communicate. This is possible because ________. A) peptide hormones always enter the cell membrane and elicit a response without assistance from other messengers B) h ...
... reactions involving receptor and kinase activation. In order for cells to respond, it is necessary for first and second messengers to communicate. This is possible because ________. A) peptide hormones always enter the cell membrane and elicit a response without assistance from other messengers B) h ...
LECTURE OUTLINE
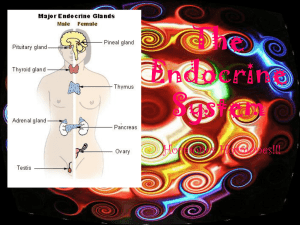
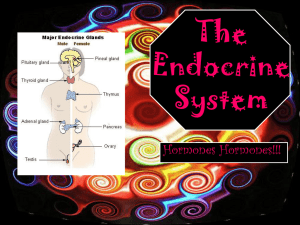
... 20.6 Other Endocrine Glands Testes and Ovaries The testes produce androgens, which are the male sex hormones. The female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, are produced by the ovaries. Thymus Gland The thymus gland secretes thymosins which aid in the differentiation of T lymphocytes. Pineal Gl ...
... 20.6 Other Endocrine Glands Testes and Ovaries The testes produce androgens, which are the male sex hormones. The female sex hormones, estrogen and progesterone, are produced by the ovaries. Thymus Gland The thymus gland secretes thymosins which aid in the differentiation of T lymphocytes. Pineal Gl ...
The endocrine system is founded on hormones and glands.
... There are two parts, each of which makes hormones and has a different function. The outer part, or the Arenal Cortex, makes hormones (corticosteroids) that control the salt and water balance in the body, responses to stress, metabolism, the immune system, and sexual development/function. The inner p ...
... There are two parts, each of which makes hormones and has a different function. The outer part, or the Arenal Cortex, makes hormones (corticosteroids) that control the salt and water balance in the body, responses to stress, metabolism, the immune system, and sexual development/function. The inner p ...
blood
... Glycoproteins- longer, FSH and LH Amines very small, derived from tryp or tyr Ex: epinephrine, melatonin Steroids- derived from cholesterol, ring structure sex steroids-testosterone, estrogen Corticosteroids- cortisol, aldosterone ...
... Glycoproteins- longer, FSH and LH Amines very small, derived from tryp or tyr Ex: epinephrine, melatonin Steroids- derived from cholesterol, ring structure sex steroids-testosterone, estrogen Corticosteroids- cortisol, aldosterone ...
Part B
... – Some of these are tropic hormones that regulate the secretion of hormones from other glands – Gonadotropins – control the production of sex hormones as well as gametes • Luteinizing hormone (LH) and Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) • Regulation by gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) – Figure 1 ...
... – Some of these are tropic hormones that regulate the secretion of hormones from other glands – Gonadotropins – control the production of sex hormones as well as gametes • Luteinizing hormone (LH) and Follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) • Regulation by gonadotropin releasing hormone (GnRH) – Figure 1 ...
Endocrine System
... • In guys the male gonads, or testes are located in the scrotum. They secrete hormones called androgens, the most important of which is testosterone. These hormones tell a guy's body when it's time to make the changes associated with puberty, like penis and height growth, deepening voice, and growth ...
... • In guys the male gonads, or testes are located in the scrotum. They secrete hormones called androgens, the most important of which is testosterone. These hormones tell a guy's body when it's time to make the changes associated with puberty, like penis and height growth, deepening voice, and growth ...
Endocrine System
... testes produce androgens (steroid hormones including testosterone) ovaries produces estrogen and progesterone (both steroids) sex hormones play key role in puberty and development of secondary sex characteristics FSH and LH stimulate the gonads to produce sex hormones ...
... testes produce androgens (steroid hormones including testosterone) ovaries produces estrogen and progesterone (both steroids) sex hormones play key role in puberty and development of secondary sex characteristics FSH and LH stimulate the gonads to produce sex hormones ...
Endocrinology: Endocrine System Function Nervous vs. Endocrine
... • Produces two groups of hormones – Thyroid hormones (amines) • Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) - Increase metabolic rate and body heat production ...
... • Produces two groups of hormones – Thyroid hormones (amines) • Thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3) - Increase metabolic rate and body heat production ...
P215 - Basic Human Physiology
... – Stimulates secretion of growth factors from various tissues – GF’s timulate growth, protein synthesis, fat breakdown and blood glucose levels ...
... – Stimulates secretion of growth factors from various tissues – GF’s timulate growth, protein synthesis, fat breakdown and blood glucose levels ...
Medicinal plants used for menstrual disorders in Latin America, the
... concerns by global health organizations, despite being disruptive to women's daily activities, particularly when access to sanitary facilities or analgesics is limited. Improving menstrual health requires access to safe and effective medication, but many women in Latin America, Africa or Asia prefer ...
... concerns by global health organizations, despite being disruptive to women's daily activities, particularly when access to sanitary facilities or analgesics is limited. Improving menstrual health requires access to safe and effective medication, but many women in Latin America, Africa or Asia prefer ...
chapter 18 the endocrine system
... 31. Upon entering the blood, steroid and thyroid hormones a. circulate freely as separate molecules b. attach to specific transport proteins c. combine with lipid carrier molecules d. react chemically with carbohydrates to inactivate them 32. The toxin of the cholera bacteria is very damaging to th ...
... 31. Upon entering the blood, steroid and thyroid hormones a. circulate freely as separate molecules b. attach to specific transport proteins c. combine with lipid carrier molecules d. react chemically with carbohydrates to inactivate them 32. The toxin of the cholera bacteria is very damaging to th ...
unc fibroid care clinic
... diagnose abnormalities such as scarring, polyps, or fibroids that affect the uterine lining. Operative hysteroscopy involves treating these conditions by inserting small instruments, sometimes with electrical energy, alongside the hysteroscope to remove abnormal tissue. Hysteroscopy is generally an ...
... diagnose abnormalities such as scarring, polyps, or fibroids that affect the uterine lining. Operative hysteroscopy involves treating these conditions by inserting small instruments, sometimes with electrical energy, alongside the hysteroscope to remove abnormal tissue. Hysteroscopy is generally an ...
The Fertility_Gyna Acad Brochure_v8.indd
... the laboratory. The best embryos are then selected and returned to the uterus. There are various protocols used, some of which start with the administration of drugs to ‘down-regulate’ your own hormones (and to prevent ovulation). FSH (and sometimes LH) hormone is then administered by daily injectio ...
... the laboratory. The best embryos are then selected and returned to the uterus. There are various protocols used, some of which start with the administration of drugs to ‘down-regulate’ your own hormones (and to prevent ovulation). FSH (and sometimes LH) hormone is then administered by daily injectio ...
The Endocrine System Negative Feedback Mechanism
... • Both the nervous and endocrine systems are involved in homeostasis (balance) by regulating the body’s activities (i.e., growth, sleep, emotions, metabolism, sexual function, and development). • Compared to the nervous system, the endocrine system is more closely associated with growth and developm ...
... • Both the nervous and endocrine systems are involved in homeostasis (balance) by regulating the body’s activities (i.e., growth, sleep, emotions, metabolism, sexual function, and development). • Compared to the nervous system, the endocrine system is more closely associated with growth and developm ...
Fertility Care: Information for Couples
... she will ever have. Only about 300 will be ovulated during her reproductive years, which naturally come to an end about five years before menopause. The gradual decrease in number of follicles remaining is called “loss of ovarian reserve.” The more eggs a woman has left, the better her chance of get ...
... she will ever have. Only about 300 will be ovulated during her reproductive years, which naturally come to an end about five years before menopause. The gradual decrease in number of follicles remaining is called “loss of ovarian reserve.” The more eggs a woman has left, the better her chance of get ...
THE ENDOCRINE SYSTEM - Coastal Bend College
... • Insulin takes the sugars that your body creates during the digestion of food and carries these sugar into the cells. • There are almost 30 types of insulin made in the US • Insulin comes from either animals or is made in labs by bacteria that have gene instructions to make human insulin ...
... • Insulin takes the sugars that your body creates during the digestion of food and carries these sugar into the cells. • There are almost 30 types of insulin made in the US • Insulin comes from either animals or is made in labs by bacteria that have gene instructions to make human insulin ...
BIO 262 Unit 4 Review Sheet
... ______9. A nursing mother would need to produce which two hormones to get milk to her baby? a. ACTH ...
... ______9. A nursing mother would need to produce which two hormones to get milk to her baby? a. ACTH ...
9.1 Glands and Hormones of Endocrine System
... the body are receiving the appropriate chemical signals so that they can respond to different situations. ...
... the body are receiving the appropriate chemical signals so that they can respond to different situations. ...
Menstrual cycle

The menstrual cycle is the regular natural changes that occurs in the uterus and ovaries that make pregnancy possible. The cycle is required for the production of ovocytes, and for the preparation of the uterus for pregnancy. Up to 80% of women report having some symptoms during the one to two weeks prior to menstruation. Common symptoms include acne, tender breasts, bloating, feeling tired, irritability, and mood changes. These symptoms interfere with normal life and therefore qualify as premenstrual syndrome in 20 to 30% of women. In 3 to 8%, they are severe.The first period usually begins between twelve and fifteen years of age, a point in time known as menarche. They may occasionally start as early as eight, and this onset may still be normal. The average age of the first period is generally later in the developing world and earlier in developed world. The typical length of time between the first day of one period and the first day of the next is 21 to 45 days in young women and 21 to 31 days in adults (an average of 28 days). Menstruation stops occurring after menopause which usually occurs between 45 and 55 years of age. Bleeding usually lasts around 2 to 7 days.The menstrual cycle is governed by hormonal changes. These changes can be altered by using hormonal birth control to prevent pregnancy. Each cycle can be divided into three phases based on events in the ovary (ovarian cycle) or in the uterus (uterine cycle). The ovarian cycle consists of the follicular phase, ovulation, and luteal phase whereas the uterine cycle is divided into menstruation, proliferative phase, and secretory phase.Stimulated by gradually increasing amounts of estrogen in the follicular phase, discharges of blood (menses) flow stop, and the lining of the uterus thickens. Follicles in the ovary begin developing under the influence of a complex interplay of hormones, and after several days one or occasionally two become dominant (non-dominant follicles shrink and die). Approximately mid-cycle, 24–36 hours after the luteinizing hormone (LH) surges, the dominant follicle releases an ovocyte, in an event called ovulation. After ovulation, the ovocyte only lives for 24 hours or less without fertilization while the remains of the dominant follicle in the ovary become a corpus luteum; this body has a primary function of producing large amounts of progesterone. Under the influence of progesterone, the uterine lining changes to prepare for potential implantation of an embryo to establish a pregnancy. If implantation does not occur within approximately two weeks, the corpus luteum will involute, causing a sharp drops in levels of both progesterone and estrogen. The hormone drop causes the uterus to shed its lining in a process termed menstruation. Menstruation also occur in some other animals including shrews, bats, and other primates such as apes and monkeys.