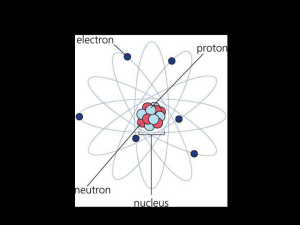
Lesson 5 Atomic Theory File
... - unlike charges (i.e. “+” and “-“ or p+ and e- ) attract each other - like charges (i.e. “+” and “+” or “-“ and “-“) repel each other ...
... - unlike charges (i.e. “+” and “-“ or p+ and e- ) attract each other - like charges (i.e. “+” and “+” or “-“ and “-“) repel each other ...
3lou3atch - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... nonmetals = second largest region right side What are some properties of nonmetals? good insulators (poor conductors) of heat and electricity, most are either brittle solids or gases at room temp. metalloids = located between the metals and nonmetals Metalloids have properties of both metals and non ...
... nonmetals = second largest region right side What are some properties of nonmetals? good insulators (poor conductors) of heat and electricity, most are either brittle solids or gases at room temp. metalloids = located between the metals and nonmetals Metalloids have properties of both metals and non ...
1 Atomic Mass
... Atomic Mass Because the mass of a single atoms is so small, for convenience, chemists use the unit called atomic mass unit (amu) also known as dalton (Da). One amu is defined as 1/12 the mass of an atom of 12C and is equal to 1.66054 x 10 -24 g. Mass of one 12C atom = 12.000 amu Because electrons ma ...
... Atomic Mass Because the mass of a single atoms is so small, for convenience, chemists use the unit called atomic mass unit (amu) also known as dalton (Da). One amu is defined as 1/12 the mass of an atom of 12C and is equal to 1.66054 x 10 -24 g. Mass of one 12C atom = 12.000 amu Because electrons ma ...
Atoms - Dr. Vickie M. Williamson
... ! Atoms of the _______ element are exactly alike and differ from those of other elements. ! __________ are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements. ! A given compound always has the ______ number and type of atoms. ! Atoms are not created or destroyed, only ______________, in chem ...
... ! Atoms of the _______ element are exactly alike and differ from those of other elements. ! __________ are formed by the joining of atoms of two or more elements. ! A given compound always has the ______ number and type of atoms. ! Atoms are not created or destroyed, only ______________, in chem ...
Chapter 2_Atoms and Periodic Table
... Valence electrons: An electron in an outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are loosely held, they are most important in determining an element’s properties. ...
... Valence electrons: An electron in an outermost shell of an atom. These electrons are loosely held, they are most important in determining an element’s properties. ...
PVS103 - unit 6 notes
... Periodic Properties of the Elements Groups 1a & 2a Metals and Non-metals Groups 3a to 8a; the Non-metals Groups 3b to 12b; the Transition Metals ...
... Periodic Properties of the Elements Groups 1a & 2a Metals and Non-metals Groups 3a to 8a; the Non-metals Groups 3b to 12b; the Transition Metals ...
The atomic number tells how many protons Protons make an atom
... 79 protons make gold. If I added another proton it would actually turn into Mercury! ...
... 79 protons make gold. If I added another proton it would actually turn into Mercury! ...
History of the Atom
... > The cathode ray is deflected by a magnetic field. > The cathode ray is repelled by a negative electric field. > The cathode ray is the same kind of negative particle no matter what metal is used. ...
... > The cathode ray is deflected by a magnetic field. > The cathode ray is repelled by a negative electric field. > The cathode ray is the same kind of negative particle no matter what metal is used. ...
CHEM 1405 CHAPTER 4
... When energy is given to an atom in the form of heat energy or electrical energy, the electrons in the atom get excited to higher energy levels by absorbing energy. This is the excited state of an atom, which is unstable. The electrons then start falling from higher levels to lower levels, releasing ...
... When energy is given to an atom in the form of heat energy or electrical energy, the electrons in the atom get excited to higher energy levels by absorbing energy. This is the excited state of an atom, which is unstable. The electrons then start falling from higher levels to lower levels, releasing ...
Chemistry (CP) Final Exam Study Guide 1
... ____ 44. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in O. a. 4 c. 16 b. 8 d. 24 ____ 45. Which of the following statements is NOT true? a. Atoms of the same element can have different masses. b. Atoms of isotopes of an element have different numbers of protons. c. The nucleus of an ...
... ____ 44. Using the periodic table, determine the number of neutrons in O. a. 4 c. 16 b. 8 d. 24 ____ 45. Which of the following statements is NOT true? a. Atoms of the same element can have different masses. b. Atoms of isotopes of an element have different numbers of protons. c. The nucleus of an ...
Unit Expectations – Polymers, Atom Model, Electron Configurations
... Elements as a class of substances composed of a single kind of atom, Compounds as two or more different elements chemically combined, and Mixtures as two or more different elements and/or compounds physically combined. 2. P4.p2 Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I recognize tha ...
... Elements as a class of substances composed of a single kind of atom, Compounds as two or more different elements chemically combined, and Mixtures as two or more different elements and/or compounds physically combined. 2. P4.p2 Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I recognize tha ...
Definitions - Loreto Science
... • is defined as half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element that are joined together by a single covalent bond. AG ...
... • is defined as half the distance between the nuclei of two atoms of the same element that are joined together by a single covalent bond. AG ...
GHW - Louisiana Tech University
... table, Mendeleev used atomic weights not atomic numbers. a) In the periodic table what elements should have been swapped if Mendeleev was to following order of increasing atomic masses strictly? ...
... table, Mendeleev used atomic weights not atomic numbers. a) In the periodic table what elements should have been swapped if Mendeleev was to following order of increasing atomic masses strictly? ...
The Atom - cloudfront.net
... What are the only two parts of an atom that have mass? Protons have a mass of 1 amu Neutrons have a mass of 1 amu Electrons are so teeny they don’t weigh ...
... What are the only two parts of an atom that have mass? Protons have a mass of 1 amu Neutrons have a mass of 1 amu Electrons are so teeny they don’t weigh ...
Topic 3 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... scientists have discovered that atoms are not the smallest particles. What do you suppose could be smaller than an atom? Scientists who investigate the structure of the atom are faced with several challenges. How can they describe something they cannot see? What tests can reveal the inner workings o ...
... scientists have discovered that atoms are not the smallest particles. What do you suppose could be smaller than an atom? Scientists who investigate the structure of the atom are faced with several challenges. How can they describe something they cannot see? What tests can reveal the inner workings o ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.