* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Unit Expectations – Polymers, Atom Model, Electron Configurations
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
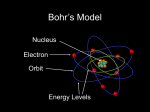
Student Expectations – Composition and Classification of Matter Big Ideas / Question(s): 1. What are the fundamental building blocks of all matter? 2. What models can be used to describe those fundamental building blocks of matter? Overview: This unit will introduce the concepts of atomic structure as the foundation for understanding of matter. We also will incorporate some review of the differences between the terms element, compound and mixture. We will be using models to help us understand the composition of matter. Specifically we will study models of atoms. Of the models we will discuss, we will spend the most time with the Bohr model of the atom. The Bohr model of the atom is not the most updated version of the atom model, but it is most useful for a high school chemistry course. In later units, we will use the Bohr model of the atom to discuss how atoms chemically react, become charged, how the electromagnetic emission from and absorption to atoms can be used to identify the type of atoms in a substance, etc.. As a subtext we will be discussing how any model has strengths and weaknesses. Resources: Course Notes – Atomic Structure Section 1.2 Matter (Pages 11 - 14) – Element, Compound, Mixture (Information on Physical Change, Chemical Change, and States of Matter will be covered in later Student Expectations) Section 3.1 and 3.2 Atom Model – Democritus through Rutherford Section 4.1 discusses the relationship between frequency and energy, electron energy levels, spectrometers and line spectra History of Atom Model PowerPoint Available on Mr. Cole’s Website Know These Vocabulary Terms: ___ Element ___ Electron ___ Compound ___ Electromagnetic Force ___ Mixture ___ Neutron ___ Atom ___ Proton ___ Nucleus ___ Strong Force ___ Quark ___ Atomic Number ___ Atomic Mass ___ Orbital / Electron Energy Level Assignments: ___ WS – Element, Compound, Mixture ___ Activity – Modeling Elements, Compounds and Mixtures ___ Formative Quiz – Element Compound and Mixture (Optional) ___ WS – Discussing Atomic Structure Using a Bohr Model ___ WS – Atom Model Timeline ___ Formative Quiz – Understanding the Bohr Model of Atom and Basic History Atomic Model (Optional) ___ WS – Bohr/Chadwick Model of Atoms for Elements #1-20 ___ Practice Test - Matter, Atomic Structure ___ Summative Test – Matter, Atomic Structure CONCEPTS TO KNOW (BOLDED ARE MORE IMPORTANT): 1. P4.p2 Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I can describe Elements as a class of substances composed of a single kind of atom, Compounds as two or more different elements chemically combined, and Mixtures as two or more different elements and/or compounds physically combined. 2. P4.p2 Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I recognize that each element and compound has physical and chemical properties, such as boiling point, density, color, and conductivity, which are independent of the amount of the sample, but do relate to the elements subatomic structure. 3. Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I know and can draw the basic Atomic Structure of a Bohr/Chadwick Atom with all the protons, electrons and neutrons being shown in the atom. 4. C4.8A Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I can describe the subatomic particles of an atom including relative mass, position within the atom, charge and interaction with other subatomic particles. 5. C4.8B Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I can describe the atom as mostly empty space with an extremely small, dense nucleus consisting of the protons and neutrons and an electron cloud surrounding the nucleus. 6. C4.8C Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I can describe the basic influence that electromagnetic and strong forces have on the structure and stability of the atom. 7. C4.8C Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ Recognize that protons repel each other and that a strong force needs to be present to keep the nucleus intact. The strong force is only evident at nuclear distances (distances as small as the nucleus of an atom) and holds the particles of the nucleus together against the electrical repulsion between the protons. 8. C4.8i Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I know and can explain that the electron location cannot be exactly determined at any given time and how the electron cloud model of the atom demonstrates this uncertainty. 9. Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I can recite a basic history of the atom model and be able to logically order the developments of the atom model. 10. C2.4x Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ I can relate that for each element, the arrangement of electrons surrounding the nucleus is unique. 11. C4.10C Introduced: _______ Basic: _________ Mastered: _________ Recognize that an element always contains the same number of protons.