1 Subatomic Particles – Lets Review Again! General Information: An
... ♦ Atomic Number (Z) - The number of protons (and electrons) in the nucleus of an atom. ♦ Mass Number (A) – The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ♦ Isotope – Atoms of an element having the same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons. ♦ Average A ...
... ♦ Atomic Number (Z) - The number of protons (and electrons) in the nucleus of an atom. ♦ Mass Number (A) – The total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom. ♦ Isotope – Atoms of an element having the same number of protons and electrons but different number of neutrons. ♦ Average A ...
OME General Chemistry
... Rutherford deduced from that (and from other experiments) that an electron will not diffract an a-particle from its track: → Matter consists mainly of empty space in which the point-shaped electrons move. The atomic nucleus including protons and neutrons contains almost the whole mass.: 1/1836 and i ...
... Rutherford deduced from that (and from other experiments) that an electron will not diffract an a-particle from its track: → Matter consists mainly of empty space in which the point-shaped electrons move. The atomic nucleus including protons and neutrons contains almost the whole mass.: 1/1836 and i ...
Atomic Structure - s3.amazonaws.com
... Early Models of the Atom Dalton’s Atomic Theory (Between 1766-1844) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element are neve ...
... Early Models of the Atom Dalton’s Atomic Theory (Between 1766-1844) Atoms of different elements can physically mix together or can chemically combine in simple whole-number ratios to form compounds. Chemical reactions when atoms are separated, joined, or rearranged. Atoms of one element are neve ...
Unit 3 Practice Test
... A. Non-metals generally have the higher electronegativities and tend to attract electrons to themselves in a chemical bond. B. Elements with high ionization energies tend to have small atomic radii. C. Elements with high electronegativities generally form ions with small radii. D. The second ionizat ...
... A. Non-metals generally have the higher electronegativities and tend to attract electrons to themselves in a chemical bond. B. Elements with high ionization energies tend to have small atomic radii. C. Elements with high electronegativities generally form ions with small radii. D. The second ionizat ...
Atomic Structure - Mr. Cervantes Science Classes
... reasonable to think that the mass of an atom should be expressed as a whole number B. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of that element 1. When calculating the average atomic mass you must take into account the relative abundance of each isotope ...
... reasonable to think that the mass of an atom should be expressed as a whole number B. The atomic mass of an element is the weighted average of the masses of all the isotopes of that element 1. When calculating the average atomic mass you must take into account the relative abundance of each isotope ...
Atomic Structure ppt
... 2) When the electron “jumps” to a higher energy level or orbital it is said to be in the excited state. 3) When the electron releases this excess energy, it releases the energy as a photon of light and falls to the ground state. 4) The color light that is emitted or released is determined by how man ...
... 2) When the electron “jumps” to a higher energy level or orbital it is said to be in the excited state. 3) When the electron releases this excess energy, it releases the energy as a photon of light and falls to the ground state. 4) The color light that is emitted or released is determined by how man ...
Name Date Class DEFINING THE ATOM Section Review Objectives
... b. the central core of an atom, which is composed of protons and neutrons ...
... b. the central core of an atom, which is composed of protons and neutrons ...
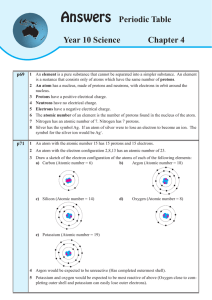
Answers - Dr Terry Dwyer National Curriculum mathematics and
... 2 Isotopes are different atoms of the same element. Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. 3 Calculate the atomic mass number of chlorine given that chlorine has two major isotopes: 35Cl (76%) and 37Cl (24%). 76% (or 0.76) of atoms have mass number o ...
... 2 Isotopes are different atoms of the same element. Isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons but a different number of neutrons. 3 Calculate the atomic mass number of chlorine given that chlorine has two major isotopes: 35Cl (76%) and 37Cl (24%). 76% (or 0.76) of atoms have mass number o ...
300 Chemistry Atomic Structure Notes Key questions: What is matter
... Atomic number = Whole number on the Periodic Table, indicates the # of protons In a NEUTRAL atom (atom with no charge), the # of protons must = the # of electrons…. So for neutral atoms, atomic number = # of electrons Atomic mass or average atomic mass = Decimal number on the Periodic Table Mass num ...
... Atomic number = Whole number on the Periodic Table, indicates the # of protons In a NEUTRAL atom (atom with no charge), the # of protons must = the # of electrons…. So for neutral atoms, atomic number = # of electrons Atomic mass or average atomic mass = Decimal number on the Periodic Table Mass num ...
Chemistry 1. The Periodic Table displays the
... how to use the Periodic Table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals and identify trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and in the relative size of ions and atoms. d. how to use the periodic table to determine the number of electrons available for bonding. e ...
... how to use the Periodic Table to identify alkali metals, alkaline earth metals and transition metals and identify trends in ionization energy, electronegativity, and in the relative size of ions and atoms. d. how to use the periodic table to determine the number of electrons available for bonding. e ...
How Good Is the Quantum Mechanical Explanation of the Periodic
... achieving a full-shell configuration, at atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 36, 54, and so forth. This is a separate question from the closing of the shells. For example, if the shells were to fill sequentially, Pauli’s scheme would predict that the second period should end with element number 28 or nickel, ...
... achieving a full-shell configuration, at atomic numbers 2, 10, 18, 36, 54, and so forth. This is a separate question from the closing of the shells. For example, if the shells were to fill sequentially, Pauli’s scheme would predict that the second period should end with element number 28 or nickel, ...
Chemistry: Nuclear Theory
... Uranium 234 is an isotope of Uranium ( 238U) that weighs 234 AMUs. It must have 92 protons to be Uranium, but it weighs about 4 AMUs less. This change in weight comes from having 4 fewer neutrons. Uranium usually has 146 neutrons, so 92234U must have 142 neutrons. Ions are atoms whose number of ...
... Uranium 234 is an isotope of Uranium ( 238U) that weighs 234 AMUs. It must have 92 protons to be Uranium, but it weighs about 4 AMUs less. This change in weight comes from having 4 fewer neutrons. Uranium usually has 146 neutrons, so 92234U must have 142 neutrons. Ions are atoms whose number of ...
Atom - Britannica
... smaller particles—electrons, protons, and neutrons. These are called subatomic particles. At the center of an atom is a nucleus. The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. Protons carry a positive electrical charge, while neutrons carry no electrical charge. Together, protons and neutrons are cal ...
... smaller particles—electrons, protons, and neutrons. These are called subatomic particles. At the center of an atom is a nucleus. The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. Protons carry a positive electrical charge, while neutrons carry no electrical charge. Together, protons and neutrons are cal ...
Syracuse University
... Summary of Dimensional Analysis Chapter 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 2.1 The Atomic Theory Basic Postulates of the Dalton Theory 2.2 The Discovery of Atomic Structure Cathode Rays and Electrons Radioactivity The Nuclear Atom 2.3 The Modern View of Atomic Structure Protons, neutrons and electrons (S ...
... Summary of Dimensional Analysis Chapter 2. Atoms, Molecules, and Ions 2.1 The Atomic Theory Basic Postulates of the Dalton Theory 2.2 The Discovery of Atomic Structure Cathode Rays and Electrons Radioactivity The Nuclear Atom 2.3 The Modern View of Atomic Structure Protons, neutrons and electrons (S ...
Structure - Britannica Encyclopedia Online
... smaller particles—electrons, protons, and neutrons. These are called subatomic particles. At the center of an atom is a nucleus. The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. Protons carry a positive electrical charge, while neutrons carry no electrical charge. Together, protons and neutrons are cal ...
... smaller particles—electrons, protons, and neutrons. These are called subatomic particles. At the center of an atom is a nucleus. The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons. Protons carry a positive electrical charge, while neutrons carry no electrical charge. Together, protons and neutrons are cal ...
Atomic Structure and Notes_AISD ppt
... that the electrons were in orbits. Rather like planets orbiting the sun. With each orbit only able to contain a set number of electrons. ...
... that the electrons were in orbits. Rather like planets orbiting the sun. With each orbit only able to contain a set number of electrons. ...
The Development of Atomic Theory
... protons and neutrons Electrons are found far away from the nucleus in an area called the electron cloud Electrons have a negative ...
... protons and neutrons Electrons are found far away from the nucleus in an area called the electron cloud Electrons have a negative ...
Chapter 4
... You can go up or down the steps, but only in whole-step increments. You cannot stand between steps on a staircase. Electrons cannot exist between energy levels. ...
... You can go up or down the steps, but only in whole-step increments. You cannot stand between steps on a staircase. Electrons cannot exist between energy levels. ...
The atomic radius
... atom is basically how well it is able to hold on to its most loosely held electron. ...
... atom is basically how well it is able to hold on to its most loosely held electron. ...
Unit 6 Worksheet Package
... between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the total _____________ charge. Ionic compounds in general have very _____________ melting points. This ...
... between these two types of ions forms an _____________ bond. Nearly all ionic compounds are _____________ solids at room temperature. In these solids the total _____________ charge is balanced by the total _____________ charge. Ionic compounds in general have very _____________ melting points. This ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.