Physical Science Chapter 6 Study Guide Every element consists of
... o All atoms of a particular element have the same ____________________ o Different elements have different properties because their atoms are different o Atoms of different elements can combine in specific ways to form ____________ o Chemical processes are the result of the rearrangement, combinatio ...
... o All atoms of a particular element have the same ____________________ o Different elements have different properties because their atoms are different o Atoms of different elements can combine in specific ways to form ____________ o Chemical processes are the result of the rearrangement, combinatio ...
04 Atoms_ molecules _ ions
... same number of protons, but different number of neutrons •Z constant, A variable ...
... same number of protons, but different number of neutrons •Z constant, A variable ...
The Periodic Table of Elements
... • The atomic mass of an element is often listed as the average atomic mass as found in nature. • This is a weighted average of the isotopes for that particular element. The more commonly found isotopes have a greater effect on the averages mass than the more rare isotopes. Ex: Cl 24% Cl-37 and 76% C ...
... • The atomic mass of an element is often listed as the average atomic mass as found in nature. • This is a weighted average of the isotopes for that particular element. The more commonly found isotopes have a greater effect on the averages mass than the more rare isotopes. Ex: Cl 24% Cl-37 and 76% C ...
Teacher timeline events
... that allowed for people to actually see those electron beams. 1869: Dmitri Mendeleev is the one who proposed what is now known as the Periodic Law. He organized all elements into seven categories sharing similar properties. They were arranged by the “functions of their atomic weights.” 1873: Scottis ...
... that allowed for people to actually see those electron beams. 1869: Dmitri Mendeleev is the one who proposed what is now known as the Periodic Law. He organized all elements into seven categories sharing similar properties. They were arranged by the “functions of their atomic weights.” 1873: Scottis ...
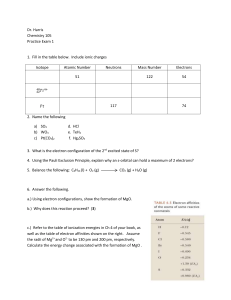
Dr. Harris Chemistry 105 Practice Exam 1 Isotope Atomic Number
... a.) Using electron configurations, show the formation of MgO. b.) Why does this reaction proceed? (3) ...
... a.) Using electron configurations, show the formation of MgO. b.) Why does this reaction proceed? (3) ...
Atomic History Notes.notebook
... Dalton devised an atomic theory (early 1800's) based on the following points: 1) Elements are composed of extremely small and indivisible particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and ...
... Dalton devised an atomic theory (early 1800's) based on the following points: 1) Elements are composed of extremely small and indivisible particles called atoms. 2) Atoms of the same element are identical. 3) Atoms combine chemically in simple whole number ratios, H2O is a 2:1 ratio of hydrogen and ...
1000 - Paint Valley Local Schools
... What is form compounds? The alkali metals, found in group 1 of the periodic table are metals that do not occur freely in nature. These metals have only one valence electron in their outer shell. Therefore, they are ready to lose that one electron in ionic bonding with other elements very easily. Thi ...
... What is form compounds? The alkali metals, found in group 1 of the periodic table are metals that do not occur freely in nature. These metals have only one valence electron in their outer shell. Therefore, they are ready to lose that one electron in ionic bonding with other elements very easily. Thi ...
Midterm Review
... • Which set of elements contains a metalloid? 1. K, Mn, As, Ar 2. Li, Mg, Ca, Kr 3. Ba, Ag, Sn, Xe 4. Fr, F, O, Rn ...
... • Which set of elements contains a metalloid? 1. K, Mn, As, Ar 2. Li, Mg, Ca, Kr 3. Ba, Ag, Sn, Xe 4. Fr, F, O, Rn ...
ATOMIC STRUCTURE
... 8.P.1 Understand the properties of matter and changes that occur when matter interacts in an open and closed container. 8.P.1.1 Classify matter as elements, compounds, or mixtures based on how the atoms are packed together in arrangements. ...
... 8.P.1 Understand the properties of matter and changes that occur when matter interacts in an open and closed container. 8.P.1.1 Classify matter as elements, compounds, or mixtures based on how the atoms are packed together in arrangements. ...
The Atom Part 1 Notes
... • We know that all these particles exist • How are they joined together? ...
... • We know that all these particles exist • How are they joined together? ...
Nickel 28 Ni 58.693
... Matter can be broken down into its simple parts called __________. Each element on the periodic table has its own ___________. How many elements can be found naturally? ...
... Matter can be broken down into its simple parts called __________. Each element on the periodic table has its own ___________. How many elements can be found naturally? ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Metalloid – A metalloid is any chemical element which has properties in between those of metals and nonmetals, or that has a mixture of them. Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical comb ...
... Metalloid – A metalloid is any chemical element which has properties in between those of metals and nonmetals, or that has a mixture of them. Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical comb ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Metalloid – A metalloid is any chemical element which has properties in between those of metals and nonmetals, or that has a mixture of them. Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical comb ...
... Metalloid – A metalloid is any chemical element which has properties in between those of metals and nonmetals, or that has a mixture of them. Mixture – a material system made up of two or more different substances which are mixed but are not combined chemically. A mixture refers to the physical comb ...
Atoms and Elements
... putting electrons into orbitals that have the same energy as each other. Put one electron into each orbital before pairing them up. Whichever way the first arrow (electron) points, the others must point the same way until they pair up, then they point in opposite directions. ...
... putting electrons into orbitals that have the same energy as each other. Put one electron into each orbital before pairing them up. Whichever way the first arrow (electron) points, the others must point the same way until they pair up, then they point in opposite directions. ...
Fall Review
... Bohr model – electrons in fixed orbit Quantum mechanical model – electrons in orbitals (s, p, d, and f-orbitals) electrons, protons, neutrons ...
... Bohr model – electrons in fixed orbit Quantum mechanical model – electrons in orbitals (s, p, d, and f-orbitals) electrons, protons, neutrons ...
Atomic Theory: the beginning
... out experiments that allowed him to calculate the charge and mass of an ...
... out experiments that allowed him to calculate the charge and mass of an ...
The New Alchemy
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
... Protons – one of the parts of an atom. Protons have a (+) charge and are found in the nucleus. Neutrons – one of the parts of an atom. Neutrons have no charge and are found in the nucleus. Nucleus – found in the center of an atom. It contains protons and neutrons. Nuclei is the plural of nucleus. Nu ...
File
... 1913 Ad Neil bohr proposes a theory “ Bohr Model” of the atom in which the electrons are restricted to specific shells around the nucleus. The amount of energy an electron has is related to how far it is from the nucleus. 1920’S Further discoveries were made about the behaviour of electrons in atoms ...
... 1913 Ad Neil bohr proposes a theory “ Bohr Model” of the atom in which the electrons are restricted to specific shells around the nucleus. The amount of energy an electron has is related to how far it is from the nucleus. 1920’S Further discoveries were made about the behaviour of electrons in atoms ...
study guide - atomic srtucture/_classification of matter
... The current atomic theory has come about over the past 2000 years. In the beginning, Democritus proposed the idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still be ...
... The current atomic theory has come about over the past 2000 years. In the beginning, Democritus proposed the idea that all things were made of particles too small to see. He was laughed at. In the 1800’s John Dalton proposed the idea of the “Atomic Theory”. He had 5 theories, 3 of which are still be ...
1 - M*W
... d) B & C 34) Halogens, like fluorine, are very reactive because a) They want to gain an electron to complete their outer energy level b) They want to lose an electron to complete their outer energy level c) They want to gain a proton in their nucleus d) They want to lose a proton from their nucleus ...
... d) B & C 34) Halogens, like fluorine, are very reactive because a) They want to gain an electron to complete their outer energy level b) They want to lose an electron to complete their outer energy level c) They want to gain a proton in their nucleus d) They want to lose a proton from their nucleus ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.