Variation in Properties of Group II Compounds
... II elements and their compounds are illustrated. Variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds include both physical and chemical properties. Variation in Physical Properties of the Elements Variation in Atomic and Ionic radii There is a general increase in atomic and ionic radii ...
... II elements and their compounds are illustrated. Variation in properties of group II elements and their compounds include both physical and chemical properties. Variation in Physical Properties of the Elements Variation in Atomic and Ionic radii There is a general increase in atomic and ionic radii ...
Chapter 5: The periodic table is a tool for organizing
... I CAN use a flow chart to illustrate the differences between elements, compounds and mixtures. I CAN classify pure substances as elements or compounds. I CAN select and integrate information from various print and electronic sources to construct visual representation of given elements. I CAN identif ...
... I CAN use a flow chart to illustrate the differences between elements, compounds and mixtures. I CAN classify pure substances as elements or compounds. I CAN select and integrate information from various print and electronic sources to construct visual representation of given elements. I CAN identif ...
What does an elements atomic # tell us about the element?
... Smallest part of a compound that still has all the properties of that compound Compound can have properties entirely unlike the elements of which it is made ...
... Smallest part of a compound that still has all the properties of that compound Compound can have properties entirely unlike the elements of which it is made ...
Chemistry Review- Answer all questions on loose
... a) Barium or Calcium - Both Ba and Ca are part of group 2, the alkaline earth metals. The reactivity increases as you move down the group. Calcium is less reactive as it is in period 4 and Barium is in period 6. b) Boron or Argon - Boron is more reactive than argon since argon is a noble gas. Noble ...
... a) Barium or Calcium - Both Ba and Ca are part of group 2, the alkaline earth metals. The reactivity increases as you move down the group. Calcium is less reactive as it is in period 4 and Barium is in period 6. b) Boron or Argon - Boron is more reactive than argon since argon is a noble gas. Noble ...
UNIT_6___ELECTRON___CONFIGURATIONS__NOTES
... absorbed when a gaseous substance has white light shone on it. ...
... absorbed when a gaseous substance has white light shone on it. ...
Chapter 3 – Atomic Structure - Mercer Island School District
... – Law of Constant Composition – compounds contain the same elements always in the same proportions. ...
... – Law of Constant Composition – compounds contain the same elements always in the same proportions. ...
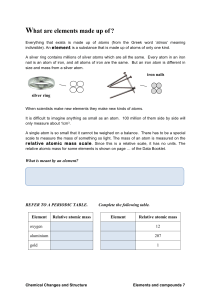
11 what are elements made of
... When scientists make new elements they make new kinds of atoms. It is difficult to imagine anything as small as an atom. 100 million of them side by side will only measure about 1cm3. A single atom is so small that it cannot be weighed on a balance. There has to be a special scale to measure the mas ...
... When scientists make new elements they make new kinds of atoms. It is difficult to imagine anything as small as an atom. 100 million of them side by side will only measure about 1cm3. A single atom is so small that it cannot be weighed on a balance. There has to be a special scale to measure the mas ...
Bill Nye Atoms and Molecules
... If a nucleus were the size of a baseball, how far away would the electrons be? ...
... If a nucleus were the size of a baseball, how far away would the electrons be? ...
Review Chemistry KEY - cms16-17
... 32. List each element in the following compounds and the number of atoms of each element present and the total number of atoms. a. C6H8O6 (Vitamin C): i. Elements: C, H, and O_____________________________________ ii. Atoms: C=6, H=8, and O=6 Total number of atoms=20___________ b. C8H10O2N4H2O (Caffe ...
... 32. List each element in the following compounds and the number of atoms of each element present and the total number of atoms. a. C6H8O6 (Vitamin C): i. Elements: C, H, and O_____________________________________ ii. Atoms: C=6, H=8, and O=6 Total number of atoms=20___________ b. C8H10O2N4H2O (Caffe ...
Unit 2 Practice Exam exam_2p_08_matter
... 42. Why do atomic radii increase dramatically with each additional row of the periodic table? a. atomic nuclei become increasingly attractive as more protons are added. b. another energy level is utilized by the electrons. c. the energy required to remove an electron is reduced by shielding of inter ...
... 42. Why do atomic radii increase dramatically with each additional row of the periodic table? a. atomic nuclei become increasingly attractive as more protons are added. b. another energy level is utilized by the electrons. c. the energy required to remove an electron is reduced by shielding of inter ...
I can describe an atom and its components I can relate energy levels
... ● The second energy level can hold 8 electrons ● The third energy level can hold 18 electrons ● The fourth energy level can hold 32 electrons. ...
... ● The second energy level can hold 8 electrons ● The third energy level can hold 18 electrons ● The fourth energy level can hold 32 electrons. ...
- Chapter 7 Chapter 7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Zeff = Z − S where Z is the atomic number and S is a screening constant, usually close to the number of inner electrons. ...
... Zeff = Z − S where Z is the atomic number and S is a screening constant, usually close to the number of inner electrons. ...
Periodic Trends.notebook January 15, 2015 Periodic Trends Atomic Radius
... ex. Na has 3 energy levels and K has 4 energy level. K has a larger ionic radius. ...
... ex. Na has 3 energy levels and K has 4 energy level. K has a larger ionic radius. ...
Name: Period
... 1. Another name for the representative elements is ________________. Where are these elements located on the periodic table? 2. Who was the first scientist to arrange the elements according to similar chemical and physical properties in order of increasing atomic mass? 3. What is characteristic of t ...
... 1. Another name for the representative elements is ________________. Where are these elements located on the periodic table? 2. Who was the first scientist to arrange the elements according to similar chemical and physical properties in order of increasing atomic mass? 3. What is characteristic of t ...
EXPERIMENT 4 – The Periodic Table
... Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements are composed of atoms, the smallest units that are characteristic of a particular element. Some elements occur in different forms, such as graphite and diamon ...
... Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 different elements known today. The elements are composed of atoms, the smallest units that are characteristic of a particular element. Some elements occur in different forms, such as graphite and diamon ...
Chapter 4 Study Guide Section 4.1 What was Dalton`s Atomic
... 2. Ionization energy is the amount of energy needed to pull away the outermost electron from an atom. 3. Electron affinity is the energy released when an electron is added to an atom. Section 4.6 1. Electromagnetic radiation is energy in a wave form that has electric and magnetic fields. 2. Waveleng ...
... 2. Ionization energy is the amount of energy needed to pull away the outermost electron from an atom. 3. Electron affinity is the energy released when an electron is added to an atom. Section 4.6 1. Electromagnetic radiation is energy in a wave form that has electric and magnetic fields. 2. Waveleng ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.