Unit(1:(Atomic(Structure(Review(Guide
... Though%you%may%know%how%to%do%each%of%the%calculations%and%configurations%listed%above,%you%still% need%to%study%the%information%that%is%found%in%your%notes.%% ...
... Though%you%may%know%how%to%do%each%of%the%calculations%and%configurations%listed%above,%you%still% need%to%study%the%information%that%is%found%in%your%notes.%% ...
john dalton - sced350akdeniz
... compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process; a chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped ...
... compounds; a given compound always has the same relative numbers of types of atoms. Atoms cannot be created, divided into smaller particles, nor destroyed in the chemical process; a chemical reaction simply changes the way atoms are grouped ...
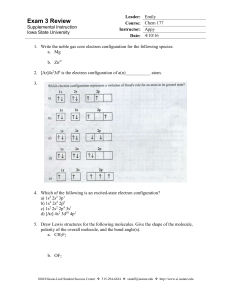
Exam 3 Review - Iowa State University
... c. Both K and Ca have the same second Ionization energy d. It’s impossible to tell 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether the following compounds contain nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic bonds. a. I—I b. NaI c. Cl—I d. H—I ...
... c. Both K and Ca have the same second Ionization energy d. It’s impossible to tell 10. In terms of electronegativity, determine whether the following compounds contain nonpolar covalent, polar covalent, or ionic bonds. a. I—I b. NaI c. Cl—I d. H—I ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... Groups Each group is also called a “family” of elements. Just like members of the same family, they share similar characteristics. Each element family has a unique name as well! Let’s look at them now… ...
... Groups Each group is also called a “family” of elements. Just like members of the same family, they share similar characteristics. Each element family has a unique name as well! Let’s look at them now… ...
General Chemistry First Semester Review General
... - solid: This could refer to a multitude of different substances: metals, flakes, crystals, and precipitates; use (s) - gas: Use (g), these are usually diatomic molecules such as O2, H2, Cl2, etc. - read given information carefully. Water vapor is noted with a (g) because it is a gas, not a liquid. ...
... - solid: This could refer to a multitude of different substances: metals, flakes, crystals, and precipitates; use (s) - gas: Use (g), these are usually diatomic molecules such as O2, H2, Cl2, etc. - read given information carefully. Water vapor is noted with a (g) because it is a gas, not a liquid. ...
Atoms, Elements, and the Periodic Table Part 1: The Atomic Model
... Groups Each group is also called a “family” of elements. Just like members of the same family, they share similar characteristics. Each element family has a unique name as well! Let’s look at them now… ...
... Groups Each group is also called a “family” of elements. Just like members of the same family, they share similar characteristics. Each element family has a unique name as well! Let’s look at them now… ...
Atomic Theory, and the Periodic Table
... 10. In 1926, Erwin Schrodinger proposed the electron cloud model. These regions of space containing the electrons are called electron clouds. ...
... 10. In 1926, Erwin Schrodinger proposed the electron cloud model. These regions of space containing the electrons are called electron clouds. ...
PP - myndrs.com
... the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electrons ...
... the nucleus of an atom in orbits or shells. • Each orbit is a certain distance from the nucleus and contains a definite number of electrons. • The orbits are filled in a routine way: – First orbit: 2 electrons – Second orbit: 8 electrons – Third orbit: 8 electrons ...
I. Historical Atomic Models - Hobbs Freshman High School
... E. **The outermost energy level can never have more than 8 e- even if that energy level can hold more than 8 e-! ...
... E. **The outermost energy level can never have more than 8 e- even if that energy level can hold more than 8 e-! ...
Periodicity PowerPoint
... • The number of valence electrons will affect the type(s) of bonds an atom can form with a specific element. • The number of valence electrons in an atom can be determined from the electron configuration or just by looking at its location on the periodic table. ...
... • The number of valence electrons will affect the type(s) of bonds an atom can form with a specific element. • The number of valence electrons in an atom can be determined from the electron configuration or just by looking at its location on the periodic table. ...
Chapter 2 Early philosophy of Matter Revolution
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • 1. Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms • 2. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from other elements • 3. Atom combine in small whole number ratios to form molecules of compounds • 4. ...
... Dalton’s Atomic Theory • 1. Each element is composed of tiny, indestructible particles called atoms • 2. All atoms of a given element have the same mass and other properties that distinguish them from other elements • 3. Atom combine in small whole number ratios to form molecules of compounds • 4. ...
Makeup of Atoms - chemmybear.com
... experimented with gases… different substances are different combinations of atoms J.J. Thomson [plum-pudding model] experimented with gas-discharge tubes… atoms have + and – parts… the negative e– ’s are the same for any atom Ernest Rutherford [nuclear model/solar system model] most of the mass of t ...
... experimented with gases… different substances are different combinations of atoms J.J. Thomson [plum-pudding model] experimented with gas-discharge tubes… atoms have + and – parts… the negative e– ’s are the same for any atom Ernest Rutherford [nuclear model/solar system model] most of the mass of t ...
EXPERIMENT
... INTRODUCTION – Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 elements known today. Within every element, exists atoms of the element, the smallest units that are characteristic of this element. There are different atoms for each element. In this exp ...
... INTRODUCTION – Primary substances, called elements, build all the materials around you. There are more than 109 elements known today. Within every element, exists atoms of the element, the smallest units that are characteristic of this element. There are different atoms for each element. In this exp ...
Atoms and Elements Class Notes and Class Work
... Modern Periodic Law: States that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, elements with similar properties occur at regular intervals. (Sometimes every 8 or 18 etc.) i.e. Elements with similar properties occur periodically. The State of Elements: · Most elements are solid at ...
... Modern Periodic Law: States that when elements are arranged in order of increasing atomic number, elements with similar properties occur at regular intervals. (Sometimes every 8 or 18 etc.) i.e. Elements with similar properties occur periodically. The State of Elements: · Most elements are solid at ...
Matter
... filled, by eight electrons. The third energy level has only three electrons, so it is not filled. ...
... filled, by eight electrons. The third energy level has only three electrons, so it is not filled. ...
Notetaking Workshee
... A. The Periodic Table. (Periodic means ______________________________. 1. In the 1800’s, Dmitri _________________________, a Russian chemist devised the first periodic table based on ___________ __________________________________. 2. In the ___________________________________, the elements are arran ...
... A. The Periodic Table. (Periodic means ______________________________. 1. In the 1800’s, Dmitri _________________________, a Russian chemist devised the first periodic table based on ___________ __________________________________. 2. In the ___________________________________, the elements are arran ...
Key Concepts - Chemistry Classes of Professor Alba
... electrons in their chemical changes. Elements on the upper right side of the periodic table are nonmetals and tend to gain electrons in their chemical changes. Elements located on the boundary between these two classes are called metalloids. The atomic mass of an element, listed directly below its s ...
... electrons in their chemical changes. Elements on the upper right side of the periodic table are nonmetals and tend to gain electrons in their chemical changes. Elements located on the boundary between these two classes are called metalloids. The atomic mass of an element, listed directly below its s ...
study guide for atoms/periodic table quiz
... Period ROWS in the Periodic Table are called periods. The elements in a period have very different properties. Family/Group COLUMNS in the Periodic Table represent groups or families. Elements in the same family have similar properties. Bohr Diagram A drawing which shows electrons in their energy le ...
... Period ROWS in the Periodic Table are called periods. The elements in a period have very different properties. Family/Group COLUMNS in the Periodic Table represent groups or families. Elements in the same family have similar properties. Bohr Diagram A drawing which shows electrons in their energy le ...
Periodic Table Review Key
... 9. Which elements have one valence electron? F,E 10. Which elements have a full outer cloud (octet)? B, H 11. Which element has 2 valence electrons? C 12. Which elements have 8 valence electrons? H 13. Which element is more reactive F or B? F 14. Which elements are considered noble gases? B, H 15. W ...
... 9. Which elements have one valence electron? F,E 10. Which elements have a full outer cloud (octet)? B, H 11. Which element has 2 valence electrons? C 12. Which elements have 8 valence electrons? H 13. Which element is more reactive F or B? F 14. Which elements are considered noble gases? B, H 15. W ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.