File
... 13. What does the quantum mechanical model determine about electrons in atoms? 14. How do two sublevels of the same principal energy level differ from each other? 15. What are the three rules for writing the electron configuration of elements? 16. Explain why the actual electron configurations for s ...
... 13. What does the quantum mechanical model determine about electrons in atoms? 14. How do two sublevels of the same principal energy level differ from each other? 15. What are the three rules for writing the electron configuration of elements? 16. Explain why the actual electron configurations for s ...
Chapter 4 Chemical Foundations: Elements, Atoms, and Ions
... • 13C has 6 protons and 7 neutrons (atomic mass number = 6 + 7 = 13) has 6 protons and 8 neutrons (atomic mass number = 6 + 8 = 14) ...
... • 13C has 6 protons and 7 neutrons (atomic mass number = 6 + 7 = 13) has 6 protons and 8 neutrons (atomic mass number = 6 + 8 = 14) ...
Unit 1 Atom
... when an x-ray photon transfers its energy to an orbital electron and ejects it from its shell. ...
... when an x-ray photon transfers its energy to an orbital electron and ejects it from its shell. ...
Periodicity - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... Main block elements - elements that represent the entire range of chemical properties and belongs to groups 1,2, and 13 through 18 in the periodic table. Halogens - elements that combine with most metals to form salts and that belong to group 17 of the periodic table. One element forms its own chemi ...
... Main block elements - elements that represent the entire range of chemical properties and belongs to groups 1,2, and 13 through 18 in the periodic table. Halogens - elements that combine with most metals to form salts and that belong to group 17 of the periodic table. One element forms its own chemi ...
Chem 115 POGIL Worksheet
... Metals occupy the left and center of the periodic table. Non-metals occupy the upper right corner of the periodic table. Metalloids fall along the border between the metals and nonmetals. 22. Are the majority of elements metals, nonmetals, or metalloids? The majority of elements are metals, followed ...
... Metals occupy the left and center of the periodic table. Non-metals occupy the upper right corner of the periodic table. Metalloids fall along the border between the metals and nonmetals. 22. Are the majority of elements metals, nonmetals, or metalloids? The majority of elements are metals, followed ...
Regents Review Packet B2 Answer Key
... chemistry. Three elements, represented by D, E, and Q, are located in Period 3. Some properties of these elements are listed in the table below. A student's experimental result indicates that the density of element Q is , at room temperature and standard pressure. ...
... chemistry. Three elements, represented by D, E, and Q, are located in Period 3. Some properties of these elements are listed in the table below. A student's experimental result indicates that the density of element Q is , at room temperature and standard pressure. ...
Elementary my dear Watson review
... The rows are called periods and they are arranged by atomic number. We use numbers to identify them. The columns are called families. Each column contains elements that have similar properties. The elements are metals, non-metals or metalloids (having both properties of metals and non-metals). ...
... The rows are called periods and they are arranged by atomic number. We use numbers to identify them. The columns are called families. Each column contains elements that have similar properties. The elements are metals, non-metals or metalloids (having both properties of metals and non-metals). ...
Evaluation for Topic 3
... Please fill in the following by ticking the boxes to show how well you have understood topic 3 ...
... Please fill in the following by ticking the boxes to show how well you have understood topic 3 ...
Document
... 18. mixture- A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined and can be separated by physical means. 19. chemical formula- Notation made up of the symbols of the elements and number of elements in a compound. B. Blocks 1, 3, and 5 1. electron subshell – Region of space withi ...
... 18. mixture- A combination of two or more substances that are not chemically combined and can be separated by physical means. 19. chemical formula- Notation made up of the symbols of the elements and number of elements in a compound. B. Blocks 1, 3, and 5 1. electron subshell – Region of space withi ...
Naming Ionic Compounds
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
... ** this is just like you learned for molecular compounds except you are not worried about the numbers of an element examples: NaCl – sodium chloride CaCl2 – calcium chloride Mg3N2 – magnesium nitride PbO – lead oxide ...
Worksheet - Models of the Atom - Teacher
... 7. On the back of this sheet, construct a timeline of the models of the atom. Include the names of the six models and important discoveries that led to each. (See Changing Atomic Models Notes.) 8. Draw pictures representing the models of Thomson and Rutherford. ...
... 7. On the back of this sheet, construct a timeline of the models of the atom. Include the names of the six models and important discoveries that led to each. (See Changing Atomic Models Notes.) 8. Draw pictures representing the models of Thomson and Rutherford. ...
Atoms - Peoria Public Schools
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses • Therefore isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons • Nuclide is a general term for a specific isotope of an element ...
... • Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different masses • Therefore isotopes are atoms with the same number of protons, but different numbers of neutrons • Nuclide is a general term for a specific isotope of an element ...
Types of Measurement
... Periodic Trend - The atomic radius increases as one moves down the group. The atomic radius decreases as one moves across a period. ...
... Periodic Trend - The atomic radius increases as one moves down the group. The atomic radius decreases as one moves across a period. ...
Copyright © 2014 Edmentum - All rights reserved. Chemistry Matter
... E. the number of known compounds 11. Which of these processes separates a mixture according to the chemical properties rather than the physical properties of the components of the mixture? A. Passing a magnet through a mixture of cork pieces and iron filings. B. Cutting away the fat and bone from a ...
... E. the number of known compounds 11. Which of these processes separates a mixture according to the chemical properties rather than the physical properties of the components of the mixture? A. Passing a magnet through a mixture of cork pieces and iron filings. B. Cutting away the fat and bone from a ...
- Chapter 7 - Periodic Properties of the Elements
... Zeff = Z − S where Z is the atomic number and S is a screening constant, usually close to the number of inner electrons. ...
... Zeff = Z − S where Z is the atomic number and S is a screening constant, usually close to the number of inner electrons. ...
The parts of Dalton`s theory Matter is composed of small, chemically
... - The AVERAGE MASS of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. Example: Hydrogen has an atomic weight of 1.008 "atomic mass units" (Naturally-occurring hydrogen is almost all Hydrogen-1!) ...
... - The AVERAGE MASS of all naturally occurring isotopes of an element. Example: Hydrogen has an atomic weight of 1.008 "atomic mass units" (Naturally-occurring hydrogen is almost all Hydrogen-1!) ...
Bohr – Rutherford Diagrams
... draw a circle around the nucleus. This represents the first energy level; draw one small dot on the first energy level line for each electron calculated in step 1 (up to a maximum of 2 dots). Each dot represents 1 electron; if the atom contains more than 2 electrons, draw a second circle around the ...
... draw a circle around the nucleus. This represents the first energy level; draw one small dot on the first energy level line for each electron calculated in step 1 (up to a maximum of 2 dots). Each dot represents 1 electron; if the atom contains more than 2 electrons, draw a second circle around the ...
SB Vocab list Word document
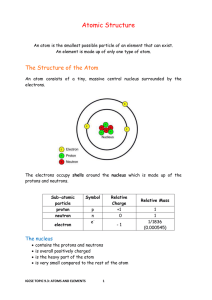
... Vocabulary Sheet Atomic Number (Proton number) The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom or ion. Covalent bond Sharing of a pair of electrons between non-metals Electron A negatively charged particle found in the shells of an atom. Its mass is approximately 1/2000 that of a proton or neutron. ...
... Vocabulary Sheet Atomic Number (Proton number) The number of protons in the nucleus of an atom or ion. Covalent bond Sharing of a pair of electrons between non-metals Electron A negatively charged particle found in the shells of an atom. Its mass is approximately 1/2000 that of a proton or neutron. ...
A Guided Tour of the Periodic Table
... • Later on, the discovery of protons and neutrons were discovered in the nucleus. • And it was later concluded that all atoms are neutral in charge. • The number of protons and electrons in any atom are always equal. ...
... • Later on, the discovery of protons and neutrons were discovered in the nucleus. • And it was later concluded that all atoms are neutral in charge. • The number of protons and electrons in any atom are always equal. ...
Review: theory vs law the atomic theory contributions of early scientists
... Neutral Inside the Neutron Heavy (similar to nucleus protons) Oct 711:36 AM ...
... Neutral Inside the Neutron Heavy (similar to nucleus protons) Oct 711:36 AM ...
2nd Semester Review
... 2. Chemical bonds occur when electrons are _____________________ or ________________________. 3. The combining ability of an atom is called the ______________________________number. 4. Describe each bond and draw a diagram to show what is happening with the valence electrons. COVALENT ...
... 2. Chemical bonds occur when electrons are _____________________ or ________________________. 3. The combining ability of an atom is called the ______________________________number. 4. Describe each bond and draw a diagram to show what is happening with the valence electrons. COVALENT ...
Periodic table
The periodic table is a tabular arrangement of the chemical elements, ordered by their atomic number (number of protons in the nucleus), electron configurations, and recurring chemical properties. The table also shows four rectangular blocks: s-, p- d- and f-block. In general, within one row (period) the elements are metals on the lefthand side, and non-metals on the righthand side.The rows of the table are called periods; the columns are called groups. Six groups (columns) have names as well as numbers: for example, group 17 elements are the halogens; and group 18, the noble gases. The periodic table can be used to derive relationships between the properties of the elements, and predict the properties of new elements yet to be discovered or synthesized. The periodic table provides a useful framework for analyzing chemical behavior, and is widely used in chemistry and other sciences.Although precursors exist, Dmitri Mendeleev is generally credited with the publication, in 1869, of the first widely recognized periodic table. He developed his table to illustrate periodic trends in the properties of the then-known elements. Mendeleev also predicted some properties of then-unknown elements that would be expected to fill gaps in this table. Most of his predictions were proved correct when the elements in question were subsequently discovered. Mendeleev's periodic table has since been expanded and refined with the discovery or synthesis of further new elements and the development of new theoretical models to explain chemical behavior.All elements from atomic numbers 1 (hydrogen) to 118 (ununoctium) have been discovered or reportedly synthesized, with elements 113, 115, 117, and 118 having yet to be confirmed. The first 94 elements exist naturally, although some are found only in trace amounts and were synthesized in laboratories before being found in nature. Elements with atomic numbers from 95 to 118 have only been synthesized in laboratories. It has been shown that einsteinium and fermium once occurred in nature but currently do not. Synthesis of elements having higher atomic numbers is being pursued. Numerous synthetic radionuclides of naturally occurring elements have also been produced in laboratories.