Intro overview
... talents, penchants, tendencies, abilities, vocations, and race of his ancestors."(Watson, 1930) ...
... talents, penchants, tendencies, abilities, vocations, and race of his ancestors."(Watson, 1930) ...
Function
... The cerebral peduncle - everything in the mesencephalon except the tectum. The region includes: ...
... The cerebral peduncle - everything in the mesencephalon except the tectum. The region includes: ...
Classical Conditioning
... naturally and automatically (salivation) • Conditioned Stimulus (CR)- an ordinarily neutral event, after training leads to a response (sound of bell leads to salivation) • Neutral Stimulus (NS)- has nothing to do with the response ...
... naturally and automatically (salivation) • Conditioned Stimulus (CR)- an ordinarily neutral event, after training leads to a response (sound of bell leads to salivation) • Neutral Stimulus (NS)- has nothing to do with the response ...
Central Nervous System (CNS)
... • The paired C-shaped lateral ventricles • The third ventricle found in the diencephalon • The fourth ventricle found in the hindbrain dorsal to the pons ...
... • The paired C-shaped lateral ventricles • The third ventricle found in the diencephalon • The fourth ventricle found in the hindbrain dorsal to the pons ...
Learning
... The process of pairing a conditioned stimulus with a stimulus that elicits a response that is incompatible with an unwanted conditioned response. Another child’s fear of rabbits was removed by pairing the stimulus which elicited fear with a stimulus that elicited happiness. ...
... The process of pairing a conditioned stimulus with a stimulus that elicits a response that is incompatible with an unwanted conditioned response. Another child’s fear of rabbits was removed by pairing the stimulus which elicited fear with a stimulus that elicited happiness. ...
Exam
... c. demyelination in the right side of the basilar pons (pontine protuberance) d. axonal degeneration in the pyramids of the medulla on the left side e. axonal degeneration in spinal nerves on the left side ...
... c. demyelination in the right side of the basilar pons (pontine protuberance) d. axonal degeneration in the pyramids of the medulla on the left side e. axonal degeneration in spinal nerves on the left side ...
lec4 vision 01142010
... removal of an inhibitory (hyperpolarizing) influence – as a result, the bipolar cell depolarizes ‘OFF’ bipolars – ‘inactivation’ (hyperpolarization) in response to light – these cells are depolarized in response to the neurotransmitter glutamate – light causes photoreceptors to hyperpolarize and rel ...
... removal of an inhibitory (hyperpolarizing) influence – as a result, the bipolar cell depolarizes ‘OFF’ bipolars – ‘inactivation’ (hyperpolarization) in response to light – these cells are depolarized in response to the neurotransmitter glutamate – light causes photoreceptors to hyperpolarize and rel ...
Chapter 15 - Austin Community College
... • The BBB is absent in some places of the 3rd and 4th ventricles at patches called circumventricular organs where some substances may pass into the brain tissue. ...
... • The BBB is absent in some places of the 3rd and 4th ventricles at patches called circumventricular organs where some substances may pass into the brain tissue. ...
Thalamus Notes
... mechanical distortion of deep tissues, or joint rotation, but not to more than one of these. These informations are then integrated in the cortex into perceptions of form, size and texture. The cortical cytoarchitectonic subdivisions of area 3,1,2 differ with regard to the kinds of receptor from whi ...
... mechanical distortion of deep tissues, or joint rotation, but not to more than one of these. These informations are then integrated in the cortex into perceptions of form, size and texture. The cortical cytoarchitectonic subdivisions of area 3,1,2 differ with regard to the kinds of receptor from whi ...
Learning_ Unit 6 PP-pdf 2015-16
... • Stimulus contiguity = occurring together in time and space Presenting the CS no more than 2 to 3 seconds before an US/UCS will result in most effective learning ...
... • Stimulus contiguity = occurring together in time and space Presenting the CS no more than 2 to 3 seconds before an US/UCS will result in most effective learning ...
Operant Conditioning - Everglades High School
... • Stimulus contiguity = occurring together in time and space Presenting the CS no more than 2 to 3 seconds before an US/UCS will result in most effective learning ...
... • Stimulus contiguity = occurring together in time and space Presenting the CS no more than 2 to 3 seconds before an US/UCS will result in most effective learning ...
Social Cognitive Learning Theory PowerPoint
... • Individuals learn through imitating others who receive rewards and punishments. Learning a behavior and performing it are not the same thing • Tenet 1: Response consequences (such as rewards or punishments) influence the likelihood that a person will perform a particular behavior again • Tenet 2: ...
... • Individuals learn through imitating others who receive rewards and punishments. Learning a behavior and performing it are not the same thing • Tenet 1: Response consequences (such as rewards or punishments) influence the likelihood that a person will perform a particular behavior again • Tenet 2: ...
5-5-cognitive_learning
... • Individuals learn through imitating others who receive rewards and punishments. Learning a behavior and performing it are not the same thing • Tenet 1: Response consequences (such as rewards or punishments) influence the likelihood that a person will perform a particular behavior again • Tenet 2: ...
... • Individuals learn through imitating others who receive rewards and punishments. Learning a behavior and performing it are not the same thing • Tenet 1: Response consequences (such as rewards or punishments) influence the likelihood that a person will perform a particular behavior again • Tenet 2: ...
Cognition and Operant Conditioning
... Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning organism comes to associate two stimuli a neutral stimulus that signals an unconditioned stimulus begins to produce a response that anticipates and prepares for the unconditioned stimulus ...
... Classical Conditioning Classical Conditioning organism comes to associate two stimuli a neutral stimulus that signals an unconditioned stimulus begins to produce a response that anticipates and prepares for the unconditioned stimulus ...
Slides 6
... In 2000, the six major organiztions listed below provided a joint statement to congress on the effects of media violence, including the excerpts quoted below. “At this time, well over 1000 studies point overwhelmingly to a causal connection between media violence and aggressive behavior in some chil ...
... In 2000, the six major organiztions listed below provided a joint statement to congress on the effects of media violence, including the excerpts quoted below. “At this time, well over 1000 studies point overwhelmingly to a causal connection between media violence and aggressive behavior in some chil ...
Myers Update 2011
... This design came as a result of other attempted experiments, but this one has the most control. This device gave more accurate results and proved his hypothesis ...
... This design came as a result of other attempted experiments, but this one has the most control. This device gave more accurate results and proved his hypothesis ...
Learning - Gordon State College
... response to a stimulus Unconditioned stimulus (UCS): naturally and automatically elicits a response Conditioned response (CR): learned response to a previously neutral stimulus Conditioned stimulus (CS): after repeated pairings with UCS, elicits the same response ...
... response to a stimulus Unconditioned stimulus (UCS): naturally and automatically elicits a response Conditioned response (CR): learned response to a previously neutral stimulus Conditioned stimulus (CS): after repeated pairings with UCS, elicits the same response ...
Slide ()
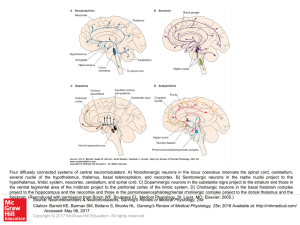
... several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamus, limbic system, neocortex, cerebellum, and spinal cord. C) Dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra project to the striatum and those in the v ...
... several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamus, limbic system, neocortex, cerebellum, and spinal cord. C) Dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra project to the striatum and those in the v ...
Neural Plasticity in Auditory Cortex
... ‘neural plasticity’ refers to systematic long-term (minutes to months) changes in the responses of neurons to the same physical stimulus (e.g., a tone), due to experience. Neural plasticity in the auditory cortex is interesting not only in itself but also as a case study in the intersection of two s ...
... ‘neural plasticity’ refers to systematic long-term (minutes to months) changes in the responses of neurons to the same physical stimulus (e.g., a tone), due to experience. Neural plasticity in the auditory cortex is interesting not only in itself but also as a case study in the intersection of two s ...
Unit 6: Learning (Conditioning)
... The lessening of a CR due to no longer pairing the US and CS ...
... The lessening of a CR due to no longer pairing the US and CS ...
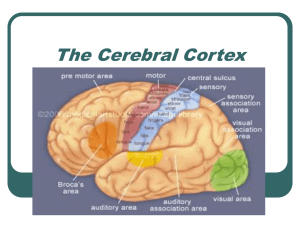
The Cerebral Cortex
... Fingers & mouth occupy the greatest amount of motor cortical space b/c they require precise control (Foerster & Penfield) 2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural prosthetics with paralyzed humans ...
... Fingers & mouth occupy the greatest amount of motor cortical space b/c they require precise control (Foerster & Penfield) 2004, USDA approved 1st clinical trial of neural prosthetics with paralyzed humans ...
Psychology312-2_002 - Northwestern University
... interval. Not = .5 sec. Garcia showed that the response system determined the optimal CS-UCS interval, and that Spence’s putative learning law was not general. Physiological explanations based on .5sec would be wrong. ...
... interval. Not = .5 sec. Garcia showed that the response system determined the optimal CS-UCS interval, and that Spence’s putative learning law was not general. Physiological explanations based on .5sec would be wrong. ...
Learning: Test Revision Section A – Multiple choice questions
... B. A spider spinning a web C. A person’s fear of spiders D. Pulling your hand away after touching a hot object ...
... B. A spider spinning a web C. A person’s fear of spiders D. Pulling your hand away after touching a hot object ...