Genetics Introduction:
... o Watson and Crick discovered 3D structure of DNA o Molecular structure of DNA is double helix comprised of a linear sequence of paired nucleotide bases and a sugar phosphate backbone o Nucleotides= building blocks= phosphate + sugar (5C deoxyribose) + base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine) o 2 ...
... o Watson and Crick discovered 3D structure of DNA o Molecular structure of DNA is double helix comprised of a linear sequence of paired nucleotide bases and a sugar phosphate backbone o Nucleotides= building blocks= phosphate + sugar (5C deoxyribose) + base (adenine, thymine, cytosine, guanine) o 2 ...
No Slide Title
... colorblindness) had a child what is the percent chance that the child will be red-green colorblind and what would the sex of the child be? ...
... colorblindness) had a child what is the percent chance that the child will be red-green colorblind and what would the sex of the child be? ...
Ch. 12 Review- pg. 315 1-23 Answers The process by which one
... that affects genetic information. Gene mutations involve a change in one or several nucleotides in a single gene, whereas chromosomal mutations involve changes in the number or structure of the whole chromosome. ...
... that affects genetic information. Gene mutations involve a change in one or several nucleotides in a single gene, whereas chromosomal mutations involve changes in the number or structure of the whole chromosome. ...
Genetics Exam 3
... cell types. ________________________________ A chromosomal mutation in which there is a change in position of chromosome segments to a different location in the genome. ________________________________ A gene present in only one dose. ________________________________ An enzyme that introduces or eli ...
... cell types. ________________________________ A chromosomal mutation in which there is a change in position of chromosome segments to a different location in the genome. ________________________________ A gene present in only one dose. ________________________________ An enzyme that introduces or eli ...
docx Probes and fingerprint matching Card sort or vocab
... with a family history of genetic disorders on the likelihood it could be passed to their children. ...
... with a family history of genetic disorders on the likelihood it could be passed to their children. ...
Electrophoresis literally means “the condition of
... The charge on DNA and the component that gives it that charge ...
... The charge on DNA and the component that gives it that charge ...
DNA Quiz #1 - Houston ISD
... 12. ____________ is complementary to the original DNA strand? 13. The mRNA carries information from the nucleus to a _________. 14. What is the correct base pairing of RNA? ___=___ ___=___ 15. Translation takes place in the ________________. 16. Replication, transcription, and translation are the st ...
... 12. ____________ is complementary to the original DNA strand? 13. The mRNA carries information from the nucleus to a _________. 14. What is the correct base pairing of RNA? ___=___ ___=___ 15. Translation takes place in the ________________. 16. Replication, transcription, and translation are the st ...
Exam Review 2B -- Rodermel
... Attach to single-stranded DNA and prevent secondary structures from forming Unwinds DNA at replication fork ...
... Attach to single-stranded DNA and prevent secondary structures from forming Unwinds DNA at replication fork ...
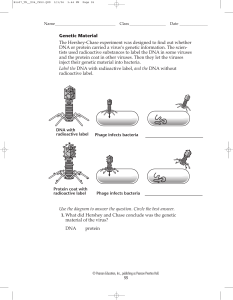
Genetic Material The Hershey-Chase experiment was designed to
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
... 1. What did Hershey and Chase conclude was the genetic material of the virus? DNA ...
Part I, for Exam 1: 1. Based on Chargaff`s rules, which of the
... 6. Describe qualitatively how the tm (melting temperature) for a double-stranded DNA depends upon its ...
... 6. Describe qualitatively how the tm (melting temperature) for a double-stranded DNA depends upon its ...
Central Dogma.pptx
... DNA’s message (gene) is expressed (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
... DNA’s message (gene) is expressed (turned on) by first being transcribed into RNA (mRNA, tRNA or rRNA) mRNA=messenger RNA, carries DNA’s message to be later translated into proteins with the help of tRNA and the ribosome. ...
DNA Replication - The Biology Corner
... 5. The other side is the lagging strand - its moving away from the helicase (in the 5' to 3' direction). Problem: it reaches the replication fork, but the helicase is moving in the opposite direction. It stops, and another polymerase binds farther down the chain. This process creates several fragmen ...
... 5. The other side is the lagging strand - its moving away from the helicase (in the 5' to 3' direction). Problem: it reaches the replication fork, but the helicase is moving in the opposite direction. It stops, and another polymerase binds farther down the chain. This process creates several fragmen ...
BIO I Review Packet Protein Synthesis 2017
... 28. In transcription, does a portion of the DNA unwind, or the entire molecule of DNA? Please explain your answer. ...
... 28. In transcription, does a portion of the DNA unwind, or the entire molecule of DNA? Please explain your answer. ...
DNA, Chromosomes & Genes - Blountstown Middle School
... http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/info=basics/show/gene ...
... http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/info=basics/show/gene ...
Review Questions - effinghamschools.com
... What is NOT true of DNA a) It is located in the nucleus b) It delivers information for making proteins to the ribosome. c) It provides instructions for controling cell activities d) It is found in all living organisms e) All of these are true ...
... What is NOT true of DNA a) It is located in the nucleus b) It delivers information for making proteins to the ribosome. c) It provides instructions for controling cell activities d) It is found in all living organisms e) All of these are true ...
Genetics Objectives 15
... Probe: a piece of genetic material that is complementary to a specific sequence. Normally labeled in some manner so that it can be washed over a large amount of DNA to find a specific sequence Probe use in Southern and Northern blotting: after a gel has been run, the gel is transferred and fixed to ...
... Probe: a piece of genetic material that is complementary to a specific sequence. Normally labeled in some manner so that it can be washed over a large amount of DNA to find a specific sequence Probe use in Southern and Northern blotting: after a gel has been run, the gel is transferred and fixed to ...
2013 DNA, Repl, Trans and Transl Review
... 10. What organelle is made of rRNA? Where is this organelle synthesized, organelle? 11. What bases pair with each other on: a) DNA? b) RNA? 12. Name the 3 types of RNA & tell the function of each. 13. What is the function of DNA helicrase? 14. If the code on DNA is TTAGCCTGA, what will be the code o ...
... 10. What organelle is made of rRNA? Where is this organelle synthesized, organelle? 11. What bases pair with each other on: a) DNA? b) RNA? 12. Name the 3 types of RNA & tell the function of each. 13. What is the function of DNA helicrase? 14. If the code on DNA is TTAGCCTGA, what will be the code o ...
Your name
... 21. What kind of ends are possible with the use of restriction enzymes? Sticky ends and blunt ends 22. What is the end result of the central dogma? proteins 23. What are the most basic units of genetic information? ...
... 21. What kind of ends are possible with the use of restriction enzymes? Sticky ends and blunt ends 22. What is the end result of the central dogma? proteins 23. What are the most basic units of genetic information? ...
Name - Lyndhurst School District
... Each unit of DNA called a nucleotide of DNA consists of 3 parts. Phosphate backbone A sugar (deoxyribose) A nitrogen base attached to the sugar There are four different types of nucleotides found in DNA A is for adenine G is for guanine C is for cytosine T is for thymine A goes w ...
... Each unit of DNA called a nucleotide of DNA consists of 3 parts. Phosphate backbone A sugar (deoxyribose) A nitrogen base attached to the sugar There are four different types of nucleotides found in DNA A is for adenine G is for guanine C is for cytosine T is for thymine A goes w ...
GENETICS
... tRNA has a complementary set of bases called an a specific for the codon on the mRNA Amino acids are attached to tRNA, requires e in the form of ATP Assembly of proteins occurs on the r (or rRNA), rRNA is the w for protein assemble and constitutes approximately 80-90% of RNA in a cell Assemblage of ...
... tRNA has a complementary set of bases called an a specific for the codon on the mRNA Amino acids are attached to tRNA, requires e in the form of ATP Assembly of proteins occurs on the r (or rRNA), rRNA is the w for protein assemble and constitutes approximately 80-90% of RNA in a cell Assemblage of ...
ib biology………………
... Lytic cycle - reproductive cycle of virus. Virus attaches to host cell, injects its hereditary material into the host cell, host cell reproduces new virus particles and host cell bursts releasing new virus particles. Nucleotide - monomer of DNA and RNA. Composed of a five carbon sugar, a phosphate a ...
... Lytic cycle - reproductive cycle of virus. Virus attaches to host cell, injects its hereditary material into the host cell, host cell reproduces new virus particles and host cell bursts releasing new virus particles. Nucleotide - monomer of DNA and RNA. Composed of a five carbon sugar, a phosphate a ...
Jeffreys - OldForensics 2012-2013
... techniques those of which are commonly used today for police and detective work, paternity tests, and immigration issues ...
... techniques those of which are commonly used today for police and detective work, paternity tests, and immigration issues ...
Go to - Net Start Class
... This explore is best when the students can use computers but can be done globally if necessary. ...
... This explore is best when the students can use computers but can be done globally if necessary. ...
DNA

Deoxyribonucleic acid (/diˌɒksiˌraɪbɵ.njuːˌkleɪ.ɨk ˈæsɪd/; DNA) is a molecule that carries most of the genetic instructions used in the development, functioning and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses. DNA is a nucleic acid; alongside proteins and carbohydrates, nucleic acids compose the three major macromolecules essential for all known forms of life. Most DNA molecules consist of two biopolymer strands coiled around each other to form a double helix. The two DNA strands are known as polynucleotides since they are composed of simpler units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is composed of a nitrogen-containing nucleobase—either cytosine (C), guanine (G), adenine (A), or thymine (T)—as well as a monosaccharide sugar called deoxyribose and a phosphate group. The nucleotides are joined to one another in a chain by covalent bonds between the sugar of one nucleotide and the phosphate of the next, resulting in an alternating sugar-phosphate backbone. According to base pairing rules (A with T, and C with G), hydrogen bonds bind the nitrogenous bases of the two separate polynucleotide strands to make double-stranded DNA. The total amount of related DNA base pairs on Earth is estimated at 5.0 x 1037, and weighs 50 billion tonnes. In comparison, the total mass of the biosphere has been estimated to be as much as 4 TtC (trillion tons of carbon).DNA stores biological information. The DNA backbone is resistant to cleavage, and both strands of the double-stranded structure store the same biological information. Biological information is replicated as the two strands are separated. A significant portion of DNA (more than 98% for humans) is non-coding, meaning that these sections do not serve as patterns for protein sequences.The two strands of DNA run in opposite directions to each other and are therefore anti-parallel. Attached to each sugar is one of four types of nucleobases (informally, bases). It is the sequence of these four nucleobases along the backbone that encodes biological information. Under the genetic code, RNA strands are translated to specify the sequence of amino acids within proteins. These RNA strands are initially created using DNA strands as a template in a process called transcription.Within cells, DNA is organized into long structures called chromosomes. During cell division these chromosomes are duplicated in the process of DNA replication, providing each cell its own complete set of chromosomes. Eukaryotic organisms (animals, plants, fungi, and protists) store most of their DNA inside the cell nucleus and some of their DNA in organelles, such as mitochondria or chloroplasts. In contrast, prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea) store their DNA only in the cytoplasm. Within the chromosomes, chromatin proteins such as histones compact and organize DNA. These compact structures guide the interactions between DNA and other proteins, helping control which parts of the DNA are transcribed.First isolated by Friedrich Miescher in 1869 and with its molecular structure first identified by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, DNA is used by researchers as a molecular tool to explore physical laws and theories, such as the ergodic theorem and the theory of elasticity. The unique material properties of DNA have made it an attractive molecule for material scientists and engineers interested in micro- and nano-fabrication. Among notable advances in this field are DNA origami and DNA-based hybrid materials.The obsolete synonym ""desoxyribonucleic acid"" may occasionally be encountered, for example, in pre-1953 genetics.