Extensions of Mendel`s Rules
... and prevent normal CNS development – 1/15,000 births on average – If affected person consumes a diet low in phenylalanine, then they develop normally – *Mere presence of gene DOES NOT determine phenotype ...
... and prevent normal CNS development – 1/15,000 births on average – If affected person consumes a diet low in phenylalanine, then they develop normally – *Mere presence of gene DOES NOT determine phenotype ...
Human Genetics Presentations
... 3.Males determine gender of offspring! a)Except in birds and reptiles where female is XY and male is XX ...
... 3.Males determine gender of offspring! a)Except in birds and reptiles where female is XY and male is XX ...
Alleles segregate during gamete formation, but do they do
... the formation of gametes. • Leads to genetic variation in plants, animals, and other organisms. ...
... the formation of gametes. • Leads to genetic variation in plants, animals, and other organisms. ...
Patterns of Heredity Can Be Complex
... trait – when several genes influence a trait ► The genes for a polygenic trait may be scattered along the same chromosome or located on different chromosomes. ► Determining the effect of any one of these genes is difficult. Due to independent assortment and crossing-over, many combinations appear in ...
... trait – when several genes influence a trait ► The genes for a polygenic trait may be scattered along the same chromosome or located on different chromosomes. ► Determining the effect of any one of these genes is difficult. Due to independent assortment and crossing-over, many combinations appear in ...
Human Genetics - Pleasantville High School
... Which cross could result in all four blood types in the offspring? IA ...
... Which cross could result in all four blood types in the offspring? IA ...
Foundations of Genetics
... Explain Mendel’s principle of dominance. What is the gene that is not expressed called? What do upper and lower case symbolize? What do heterozygous and homozygous mean, in terms of letters? Make a Punnett square showing a cross between 2 heterozygous purple flower pea plants. HINT: Purple is domi ...
... Explain Mendel’s principle of dominance. What is the gene that is not expressed called? What do upper and lower case symbolize? What do heterozygous and homozygous mean, in terms of letters? Make a Punnett square showing a cross between 2 heterozygous purple flower pea plants. HINT: Purple is domi ...
Genetic Disorders in Culture and Art
... we are faced with many personal and social decisions Ethical use of genetic information and biotechnology requires participation by a broad cross section of society We can make informed personal decisions and formulate public policy only if we have a knowledge of genetics and how genetics is use ...
... we are faced with many personal and social decisions Ethical use of genetic information and biotechnology requires participation by a broad cross section of society We can make informed personal decisions and formulate public policy only if we have a knowledge of genetics and how genetics is use ...
A Perspective on Human Genetics
... we are faced with many personal and social decisions Ethical use of genetic information and biotechnology requires participation by a broad cross section of society We can make informed personal decisions and formulate public policy only if we have a knowledge of genetics and how genetics is use ...
... we are faced with many personal and social decisions Ethical use of genetic information and biotechnology requires participation by a broad cross section of society We can make informed personal decisions and formulate public policy only if we have a knowledge of genetics and how genetics is use ...
Introduction to Genetics
... Evident at puberty when secondary sex characteristic do not develop, but breast tissue does. Typically, very passive males. ...
... Evident at puberty when secondary sex characteristic do not develop, but breast tissue does. Typically, very passive males. ...
Technology Review (Cambridge, Mass
... how these concepts together with the principles of mathematical probability make it possible to predict ratios of observable traits expected in offspring. Solve simple genetics problems using Mendel’s principles and the laws of probability. Use a Punnett square in solving genetic problems. ■ Disting ...
... how these concepts together with the principles of mathematical probability make it possible to predict ratios of observable traits expected in offspring. Solve simple genetics problems using Mendel’s principles and the laws of probability. Use a Punnett square in solving genetic problems. ■ Disting ...
17 Greenough-Behavior Genetics 2006
... Sources of evidence regarding genetic components • Pedigree - family tree (good for single-gene disorders--pattern of inheritance can be evident) • Relatedness and risk (degree of relationship; first ...
... Sources of evidence regarding genetic components • Pedigree - family tree (good for single-gene disorders--pattern of inheritance can be evident) • Relatedness and risk (degree of relationship; first ...
Chapter 4: Modification of Mendelian Ratios Incomplete or Partial
... *Wild-type allele *Mutant allele Conventional symbols for alleles: recessive allele- initial letter of the name of the recessive trait, lowercased and italicized dominant allele- same letter in uppercase Genetic nomenclature is extremely diverse! ...
... *Wild-type allele *Mutant allele Conventional symbols for alleles: recessive allele- initial letter of the name of the recessive trait, lowercased and italicized dominant allele- same letter in uppercase Genetic nomenclature is extremely diverse! ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER 5 TEST: HEREDITY
... 4. purebred: organism that produces same traits in offspring 5. cross pollinate: pollinate a flower or plant with pollen from another flower or plant 6. self pollinate: self-fertilized; fertilized by its own pollen 7. dominant: the form of a trait that appears to dominate or mask another form of the ...
... 4. purebred: organism that produces same traits in offspring 5. cross pollinate: pollinate a flower or plant with pollen from another flower or plant 6. self pollinate: self-fertilized; fertilized by its own pollen 7. dominant: the form of a trait that appears to dominate or mask another form of the ...
Non-Mendelian Inheritance: Multifactoril, …
... weight head circumference and … are compared with the weight, normal expected measurements for a child’s sex and age Normal range of a quantitative trait is consider between the two standard deviation above and below the population mean ...
... weight head circumference and … are compared with the weight, normal expected measurements for a child’s sex and age Normal range of a quantitative trait is consider between the two standard deviation above and below the population mean ...
Evolutionary Psychology
... • Tobacco addiction: (188890) • Alcoholism: (103780) • Homosexuality: (306995) ...
... • Tobacco addiction: (188890) • Alcoholism: (103780) • Homosexuality: (306995) ...
Interplay of Nature versus nurture
... appearance, but also in genetic structure. Fraternal twins (dizygotic twins) are formed when the female produces two separate eggs that are fertilized by two different sperm cells from the father. These twins are not genetically identical. These twins share about 50% of their genetics. Scientists li ...
... appearance, but also in genetic structure. Fraternal twins (dizygotic twins) are formed when the female produces two separate eggs that are fertilized by two different sperm cells from the father. These twins are not genetically identical. These twins share about 50% of their genetics. Scientists li ...
Document
... Genetic Engineering- manipulating genes for practical purposes Examples 1. Medicine Many medicines, such as the ones used to treat burns, are produced by genetic engineering techniques. 2. Vaccines A person vaccinated with a genetically engineered vaccine will make antibodies against the virus. The ...
... Genetic Engineering- manipulating genes for practical purposes Examples 1. Medicine Many medicines, such as the ones used to treat burns, are produced by genetic engineering techniques. 2. Vaccines A person vaccinated with a genetically engineered vaccine will make antibodies against the virus. The ...
Document
... • The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called heredity. • traits are the result of interactions of the genes of both parents. • 1. Inherited characteristics are controlled by factors called genes • 2. One gene masks the effects of another. Principle of dominance • 3. A pair of factors ...
... • The passing of traits from parents to offspring is called heredity. • traits are the result of interactions of the genes of both parents. • 1. Inherited characteristics are controlled by factors called genes • 2. One gene masks the effects of another. Principle of dominance • 3. A pair of factors ...
Fill-in Handout - Liberty Union High School District
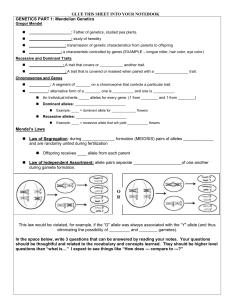
... and are randomly united during fertilization Offspring receives ____ allele from each parent Law of Independent Assortment: allele pairs separate _____________________of one another during gamete formation. ...
... and are randomly united during fertilization Offspring receives ____ allele from each parent Law of Independent Assortment: allele pairs separate _____________________of one another during gamete formation. ...
Pregnancy
... • Life begins with joining of two separate cells one from the male and one from the ...
... • Life begins with joining of two separate cells one from the male and one from the ...
FAQ092 -- Having Twins
... of oxygen and nutrients. As a result, the fetuses may not grow as much as they should. It also can damage your heart, liver, kidneys, and brain. In severe cases, preeclampsia may cause seizures and threaten your life. The babies may need to be delivered early if your blood pressure becomes too high. ...
... of oxygen and nutrients. As a result, the fetuses may not grow as much as they should. It also can damage your heart, liver, kidneys, and brain. In severe cases, preeclampsia may cause seizures and threaten your life. The babies may need to be delivered early if your blood pressure becomes too high. ...
Variation Lecture
... of genetic variation, reproduction and inheritance, and natural selection and time. ...
... of genetic variation, reproduction and inheritance, and natural selection and time. ...
Twin study

Twin studies reveal the absolute and relative importance of environmental and genetic influences on individuals in a sample. Twin research is considered a key tool in behavioral genetics and in content fields, from biology to psychology. Twin studies are part of the methods used in behavior genetics, which includes all data that are genetically informative – siblings, adoptees, pedigree data etc.Twins are a valuable source for observation because they allow the study of varying family environments (across pairs) and widely differing genetic makeup: ""identical"" or monozygotic (MZ) twins share nearly 100% of their genes, which means that most differences between the twins (such as height, susceptibility to boredom, intelligence, depression, etc.) is due to experiences that one twin has but not the other twin. ""Fraternal"" or dizygotic (DZ) twins share only about 50% of their genes. Thus powerful tests of the effects of genes can be made. Twins share many aspects of their environment (e.g., uterine environment, parenting style, education, wealth, culture, community) by virtue of being born in the same time and place. The presence of a given genetic trait in only one member of a pair of identical twins (called discordance) provides a powerful window into environmental effects.The classical twin design compares the similarity of monozygotic (identical) and dizygotic (fraternal) twins. If identical twins are considerably more similar than fraternal twins (which is found for most traits), this implicates that genes play an important role in these traits. By comparing many hundreds of families of twins, researchers can then understand more about the roles of genetic effects, shared environment, and unique environment in shaping behavior.Modern twin studies have shown that almost all traits are in part influenced by genetic differences, with some characteristics showing a strong influence (e.g. height), others an intermediate level (e.g. personality traits) and some more complex heritabilities, with evidence for different genes affecting different aspects of the trait — as in the case of autism.