Introduction to Plants
... • critical to other life on this planet because they form the basis of all food webs • Most plants are autotrophic • earliest fossils found have been aged at 3.8 billion years • scientific study of plants, known as botany • identified about 350,000 extant (living) species of plants – ~258,650 are fl ...
... • critical to other life on this planet because they form the basis of all food webs • Most plants are autotrophic • earliest fossils found have been aged at 3.8 billion years • scientific study of plants, known as botany • identified about 350,000 extant (living) species of plants – ~258,650 are fl ...
Taxonomy Notes - Warren County Schools
... from penicillin mold (fungi). Antiseptic - agent that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms on the external surfaces of the body. Plaque is the accumulation of bacteria and microorganisms on a tooth. Tartar is dental plaque that has mineralized. Tartar can form when plaque is not remo ...
... from penicillin mold (fungi). Antiseptic - agent that kills or inhibits the growth of microorganisms on the external surfaces of the body. Plaque is the accumulation of bacteria and microorganisms on a tooth. Tartar is dental plaque that has mineralized. Tartar can form when plaque is not remo ...
The Enemy: Western sticktight (Lappula occidenstalis) Strategy: This
... blunt on the tips. It prefers compact soil such as roadways, pathways, and trails. The plant produces very small blue flowers with 4 nutlets of which have margins with a small single row of spear-like spines, thus allowing it to stick onto everything. The small flower dries into a charcoal grey seed ...
... blunt on the tips. It prefers compact soil such as roadways, pathways, and trails. The plant produces very small blue flowers with 4 nutlets of which have margins with a small single row of spear-like spines, thus allowing it to stick onto everything. The small flower dries into a charcoal grey seed ...
PDF
... stays small, 15 to 30 centimetres high. The flowers are bright-orange to red and will be in bloom the whole year round. The Nematanthus strigillosus is sold by Araflora for decoration only not for consumption. Height: 10 cm ...
... stays small, 15 to 30 centimetres high. The flowers are bright-orange to red and will be in bloom the whole year round. The Nematanthus strigillosus is sold by Araflora for decoration only not for consumption. Height: 10 cm ...
canada thistle - Clallam County
... It is a perennial and can reproduce by seed. Reproduction is mainly by horizontal roots which have buds that sprout and develop into new plants. Roots need not be attached to the parent plant; root fragments as small as half an inch can grow into new plants. ...
... It is a perennial and can reproduce by seed. Reproduction is mainly by horizontal roots which have buds that sprout and develop into new plants. Roots need not be attached to the parent plant; root fragments as small as half an inch can grow into new plants. ...
Effect of naturally occurring amino acid stimulants on the growth and
... around 3350 t of fresh chilli will be required in order to meet 70% sufficiency in chilli production by 2015. A large acreage of land (additional of 310 Ha) would be required to meet this production target. Land being a limited resource in Mauritius, the use of naturally occurring plant bioregulator ...
... around 3350 t of fresh chilli will be required in order to meet 70% sufficiency in chilli production by 2015. A large acreage of land (additional of 310 Ha) would be required to meet this production target. Land being a limited resource in Mauritius, the use of naturally occurring plant bioregulator ...
Plant Diversity
... Microspores develop into pollen grains, which are the male gametophytes, while megaspores form an ovule that contains the female gametophytes. ...
... Microspores develop into pollen grains, which are the male gametophytes, while megaspores form an ovule that contains the female gametophytes. ...
Life: The Science of Biology, 8e
... elongation in wild-type plants. These inhibitors are used in greenhouses to prevent plants from becoming tall and spindly. Also used to prevent “bolting” (producing a tall stem that flowers) in plants such as cabbage. ...
... elongation in wild-type plants. These inhibitors are used in greenhouses to prevent plants from becoming tall and spindly. Also used to prevent “bolting” (producing a tall stem that flowers) in plants such as cabbage. ...
Slide 1
... Symptoms: Yellowing and browning of old foliage precedes fading and death of twigs and branches. Sunken, long cankers with a reddish tinge develop at wounds on bark, bark is darkened and resin exudes from margins of cankers. Infection can occur on any part of the plant and stage of the tree. Infecte ...
... Symptoms: Yellowing and browning of old foliage precedes fading and death of twigs and branches. Sunken, long cankers with a reddish tinge develop at wounds on bark, bark is darkened and resin exudes from margins of cankers. Infection can occur on any part of the plant and stage of the tree. Infecte ...
Gardening Tips: Using Fragrance as a Landscape Tool
... many others offer noteworthy fragrance. To take advantage of the fragrance offered by these plants, it is best to place them in areas where there fragrance can be most appreciated. When possible, these plants should be situated near entrances, walkways or outdoor activity areas such as porches or de ...
... many others offer noteworthy fragrance. To take advantage of the fragrance offered by these plants, it is best to place them in areas where there fragrance can be most appreciated. When possible, these plants should be situated near entrances, walkways or outdoor activity areas such as porches or de ...
Classifying Living Things vocab and notes
... Invertebrates are animals that do not have backbones. This group accounts for about 97% of the animal kingdom. Examples include: arthropods like insects, spiders, and crabs; mollusks like snails, oysters, and squid; echinoderms like sea stars and sea urchins; cnidarians like jellyfish, corals, and s ...
... Invertebrates are animals that do not have backbones. This group accounts for about 97% of the animal kingdom. Examples include: arthropods like insects, spiders, and crabs; mollusks like snails, oysters, and squid; echinoderms like sea stars and sea urchins; cnidarians like jellyfish, corals, and s ...
Evolution of developmental mechanisms in plants
... Land plants evolved from green algae in the mid-Ordovician, over 450 million years ago [1]. Phylogenetic analyses based on both morphological and molecular data suggest that within the green algae, charophytes in the order Charales are the sister group to the land plants [2]. The cellular innovation ...
... Land plants evolved from green algae in the mid-Ordovician, over 450 million years ago [1]. Phylogenetic analyses based on both morphological and molecular data suggest that within the green algae, charophytes in the order Charales are the sister group to the land plants [2]. The cellular innovation ...
Himalayan balsam - Greater Lincolnshire Nature Partnership
... to avoid re-growth. Plants can easily be pulled by hand as the roots are shallow (above left). Cut or pulled plants can be safely left on site to decompose if they have not produced seed heads, though this must be done in a dry open area. Make sure you carry on checking for re-growth after rem ...
... to avoid re-growth. Plants can easily be pulled by hand as the roots are shallow (above left). Cut or pulled plants can be safely left on site to decompose if they have not produced seed heads, though this must be done in a dry open area. Make sure you carry on checking for re-growth after rem ...
Sulphur Cinquefoil (Poten lla recta)
... Erect, long-lived perennial 0.3 to 0.8 metres tall. Older plants o!en form a ringshaped clump as old roots die in the center and new shoots grow on the outside edges. Na"ve to Eurasia. ...
... Erect, long-lived perennial 0.3 to 0.8 metres tall. Older plants o!en form a ringshaped clump as old roots die in the center and new shoots grow on the outside edges. Na"ve to Eurasia. ...
Courtesy of Wm. C. Brown Publishers
... Support (hold up leaves) Store (food and water) Protect (thorns) Reproduction (stolons) ...
... Support (hold up leaves) Store (food and water) Protect (thorns) Reproduction (stolons) ...
Filicinae, Gymnospermae, Angiospermae
... conifers as the dominant trees only around 60-100 million years ago The earliest known macrofossil confidently identified as an ...
... conifers as the dominant trees only around 60-100 million years ago The earliest known macrofossil confidently identified as an ...
Ch30 PowerPoint LN
... Coevolution: the influence two different species have on each other’s evolution through their interactions and thus affecting the selected adaptations of each organism. • insects were favored to evolve with those plants that kept their reproductive parts off of the ground. ...
... Coevolution: the influence two different species have on each other’s evolution through their interactions and thus affecting the selected adaptations of each organism. • insects were favored to evolve with those plants that kept their reproductive parts off of the ground. ...
Explain why Photosynthesis is the most important chemical reaction
... Where does most of photosynthesis take place? A.Flower B.Xylem C.Leaves D.Roots ...
... Where does most of photosynthesis take place? A.Flower B.Xylem C.Leaves D.Roots ...
PLANTS - SharpSchool
... Layers of dead cells that make up bundles of tissue that transport water and minerals from the roots, through the stems, and to the leaves of a plant is called? A) B) C) D) ...
... Layers of dead cells that make up bundles of tissue that transport water and minerals from the roots, through the stems, and to the leaves of a plant is called? A) B) C) D) ...
20.1 Origins of Plant Life
... Plant life began in the water and became adapted to land. Land plants evolved from green algae. • Plants and green algae have many common traits: –photosynthetic eukaryotes –have the same types of chlorophyll –use starch as a storage product –have cell walls with cellulose ...
... Plant life began in the water and became adapted to land. Land plants evolved from green algae. • Plants and green algae have many common traits: –photosynthetic eukaryotes –have the same types of chlorophyll –use starch as a storage product –have cell walls with cellulose ...
Virtual Plant Diversity lab
... 10. List the four groups of gymnosperms and give an example of each. 11. Gymnosperms were the first widely distributed plant group; what major animal group are gymnosperms linked to? 12. What is the “main plant” of gymnosperms? 13. What are cones? 14. In pine trees which is larger, the male or femal ...
... 10. List the four groups of gymnosperms and give an example of each. 11. Gymnosperms were the first widely distributed plant group; what major animal group are gymnosperms linked to? 12. What is the “main plant” of gymnosperms? 13. What are cones? 14. In pine trees which is larger, the male or femal ...
Chapter 24 - Jamestown Public Schools
... Ovule female sex cells of a seed plant Pollination transfer of pollen grains from male reproductive structures to female reproductive structure ...
... Ovule female sex cells of a seed plant Pollination transfer of pollen grains from male reproductive structures to female reproductive structure ...
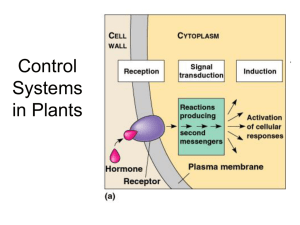
Control Systems in Plants
... Functions of Plant Hormones • Control plant growth and development by affecting division, elongation, and cell differentiation • Effect depends on size of action, stage of plant growth and hormone concentration • Hormonal signal is amplified by gene ...
... Functions of Plant Hormones • Control plant growth and development by affecting division, elongation, and cell differentiation • Effect depends on size of action, stage of plant growth and hormone concentration • Hormonal signal is amplified by gene ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.