View PDF
... After several days, the tips of the stems start to bend toward the window. What happens if you turn the plant around so that those stems reach into the room? The stems will bend as they continue to grow, turning back toward the light. Plants respond to light with the help of a hormone. A hormone is ...
... After several days, the tips of the stems start to bend toward the window. What happens if you turn the plant around so that those stems reach into the room? The stems will bend as they continue to grow, turning back toward the light. Plants respond to light with the help of a hormone. A hormone is ...
Chapter Outline
... a. The plant is small so many hundreds of plants can grow in a small amount of space. ...
... a. The plant is small so many hundreds of plants can grow in a small amount of space. ...
Plants are producers.
... After several days, the tips of the stems start to bend toward the window. What happens if you turn the plant around so that those stems reach into the room? The stems will bend as they continue to grow, turning back toward the light. Plants respond to light with the help of a hormone. A hormone is ...
... After several days, the tips of the stems start to bend toward the window. What happens if you turn the plant around so that those stems reach into the room? The stems will bend as they continue to grow, turning back toward the light. Plants respond to light with the help of a hormone. A hormone is ...
Male Sex Organs
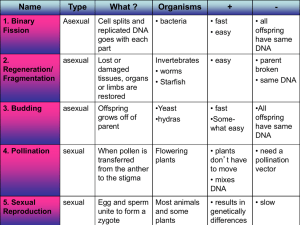
... Cloning Cloning is the process of forming identical genetic offspring from a single cell. It is a natural process that happens daily in nature when organisms produce exact duplicates of themselves by asexual reproduction (binary fission, budding…). Cloning is referred to as asexual reproduction bec ...
... Cloning Cloning is the process of forming identical genetic offspring from a single cell. It is a natural process that happens daily in nature when organisms produce exact duplicates of themselves by asexual reproduction (binary fission, budding…). Cloning is referred to as asexual reproduction bec ...
Science – Grade2
... Know that some seeds are very small while others are List a few examples to prove that size of a big. Name a few small seeds. Name a few big seeds. plant need not depend on size of the seed. Realise that size of a plant need not depend on size of the seed. Realise that some plants don’t grow from se ...
... Know that some seeds are very small while others are List a few examples to prove that size of a big. Name a few small seeds. Name a few big seeds. plant need not depend on size of the seed. Realise that size of a plant need not depend on size of the seed. Realise that some plants don’t grow from se ...
Sedum (Sedum) - Garden Basics
... between thorough waterings; for plants that become semidormant during the winter, such as showy stonecrop and October plant, water only enough to keep the leaves from shriveling during this period. Feed established plants three times a year--in very early spring, late spring and late summer, using a ...
... between thorough waterings; for plants that become semidormant during the winter, such as showy stonecrop and October plant, water only enough to keep the leaves from shriveling during this period. Feed established plants three times a year--in very early spring, late spring and late summer, using a ...
Winter - Reynolda Gardens
... In winter, the shapes of deciduous trees are more apparent than in other seasons, when their trunks and branches are obscured by leaves. Sometimes the growth patterns seem very odd, until we understand how they developed. Like all living things, trees respond to environmental forces that surround th ...
... In winter, the shapes of deciduous trees are more apparent than in other seasons, when their trunks and branches are obscured by leaves. Sometimes the growth patterns seem very odd, until we understand how they developed. Like all living things, trees respond to environmental forces that surround th ...
Mader/Biology, 11/e – Chapter Outline
... a. A species of acacia, Pseudomyrmex ferruginea, has swollen thorns with a hollow interior and ants will live and feed (without harming) off the acacia. In turn, the ants protect the plant by attacking and stinging herbivores. H. Arabidopsis Is a Model Organism (Nature of Science reading) 1. To stud ...
... a. A species of acacia, Pseudomyrmex ferruginea, has swollen thorns with a hollow interior and ants will live and feed (without harming) off the acacia. In turn, the ants protect the plant by attacking and stinging herbivores. H. Arabidopsis Is a Model Organism (Nature of Science reading) 1. To stud ...
How Do Plants Grow? - Macmillan Publishers
... Plants get water from soil. But plants need more than just water to grow. Plants get food from the soil. This food is called nutrients. If a plant cannot get the nutrients it needs, it will not grow well. It may die. These potatoes used nutrients in soil to help them grow. ...
... Plants get water from soil. But plants need more than just water to grow. Plants get food from the soil. This food is called nutrients. If a plant cannot get the nutrients it needs, it will not grow well. It may die. These potatoes used nutrients in soil to help them grow. ...
Ch44a-Plant_reproduction
... two genetically identical cells. • Meiosis: reduction division, which produces four haploid reproductive cells. ...
... two genetically identical cells. • Meiosis: reduction division, which produces four haploid reproductive cells. ...
FA-3
... In some desert plants like cactus, leaves are reduced to spines so as to reduce loss of water through transpiration. These spines are also called as thorns. Thorns protect these plants from grazing animals. In some insectivorous plants, leaves are modified into pitchers where they are used to trap i ...
... In some desert plants like cactus, leaves are reduced to spines so as to reduce loss of water through transpiration. These spines are also called as thorns. Thorns protect these plants from grazing animals. In some insectivorous plants, leaves are modified into pitchers where they are used to trap i ...
Created with Sketch. Growing new plants
... sexually (by seeds) as well as asexually through vegetative reproduction – via side stems called stolons or underground stems called rhizomes. Tubers and bulbs grow underground and can be split to make more plants. We also grow new plants by taking cuttings from a parent plant or by grafting – inser ...
... sexually (by seeds) as well as asexually through vegetative reproduction – via side stems called stolons or underground stems called rhizomes. Tubers and bulbs grow underground and can be split to make more plants. We also grow new plants by taking cuttings from a parent plant or by grafting – inser ...
Thyme Leaved Savory
... Surface sow seed in April in a greenhouse. Do not allow the compost to dry out. Germination can be slow and erratic but usually takes place within a month. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots as soon as they are large enough to handle. It is usually possible to plant out into their permanen ...
... Surface sow seed in April in a greenhouse. Do not allow the compost to dry out. Germination can be slow and erratic but usually takes place within a month. Prick out the seedlings into individual pots as soon as they are large enough to handle. It is usually possible to plant out into their permanen ...
Plant Lab
... Identify and draw the male and female cones? What plant phylum does the cone bearing plants belong to and what do the flowering plants belong to? ...
... Identify and draw the male and female cones? What plant phylum does the cone bearing plants belong to and what do the flowering plants belong to? ...
Classification and Naming of Plants - UNL, Go URL
... ily communicate with each other and with others across the world without being confused by common names (Figure 1). ...
... ily communicate with each other and with others across the world without being confused by common names (Figure 1). ...
Plant Review | Part I | KEY
... 2 Pollen grains are released from male cones and sticks to female ovule. 5 Diploid embryo develops. 3 Pollen tube grows from male spore (pollen) 4 Two nuclei travel down tube to female spore and one fertilizes the egg. ...
... 2 Pollen grains are released from male cones and sticks to female ovule. 5 Diploid embryo develops. 3 Pollen tube grows from male spore (pollen) 4 Two nuclei travel down tube to female spore and one fertilizes the egg. ...
Plants (powerpoint view)
... 1 cotyledon, petals in multiples of 3, parallel veins, 1 pore in pollen, scattered phloem & xylem, fibrous root Dicot: 2 cotyledons, petals in multiples of 4 or 5, netlike veins, 3 pores in pollen, phloem and xylem in a ring, taproot ...
... 1 cotyledon, petals in multiples of 3, parallel veins, 1 pore in pollen, scattered phloem & xylem, fibrous root Dicot: 2 cotyledons, petals in multiples of 4 or 5, netlike veins, 3 pores in pollen, phloem and xylem in a ring, taproot ...
basic_botany
... Terminology Binomial nomenclature: all plants are given two names. These make up the scientific name and include the genus and species. Cornus florida - flowering dogwood cultivar - Fragrant cloud ...
... Terminology Binomial nomenclature: all plants are given two names. These make up the scientific name and include the genus and species. Cornus florida - flowering dogwood cultivar - Fragrant cloud ...
Plant Life Observation Journal
... Web Quest. Then, use the information that you learn to answer the questions on this page. Remember to be neat and complete. 1. Why are plants always at the bottom of the food chain? __________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ ...
... Web Quest. Then, use the information that you learn to answer the questions on this page. Remember to be neat and complete. 1. Why are plants always at the bottom of the food chain? __________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ ...
File
... Web Quest. Then, use the information that you learn to answer the questions on this page. Remember to be neat and complete. 1. Why are plants always at the bottom of the food chain? __________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ ...
... Web Quest. Then, use the information that you learn to answer the questions on this page. Remember to be neat and complete. 1. Why are plants always at the bottom of the food chain? __________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________ ...
Plant Evolution & Diversity – Ch. 22-25
... • Organisms in this Kingdom don’t fit clearly into what we call plant, animal, or fungi. • Most diverse eukaryotic Kingdom (>60,000 species). • We are interested in this Kingdom because of the Chlorophytes & Charophyceans - green algae. ...
... • Organisms in this Kingdom don’t fit clearly into what we call plant, animal, or fungi. • Most diverse eukaryotic Kingdom (>60,000 species). • We are interested in this Kingdom because of the Chlorophytes & Charophyceans - green algae. ...
Botany

Botany, also called plant science(s) or plant biology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist or plant scientist is a scientist who specializes in this field of study. The term ""botany"" comes from the Ancient Greek word βοτάνη (botanē) meaning ""pasture"", ""grass"", or ""fodder""; βοτάνη is in turn derived from βόσκειν (boskein), ""to feed"" or ""to graze"". Traditionally, botany has also included the study of fungi and algae by mycologists and phycologists respectively, with the study of these three groups of organisms remaining within the sphere of interest of the International Botanical Congress. Nowadays, botanists study approximately 400,000 species of living organisms of which some 260,000 species are vascular plants and about 248,000 are flowering plants.Botany originated in prehistory as herbalism with the efforts of early humans to identify – and later cultivate – edible, medicinal and poisonous plants, making it one of the oldest branches of science. Medieval physic gardens, often attached to monasteries, contained plants of medical importance. They were forerunners of the first botanical gardens attached to universities, founded from the 1540s onwards. One of the earliest was the Padua botanical garden. These gardens facilitated the academic study of plants. Efforts to catalogue and describe their collections were the beginnings of plant taxonomy, and led in 1753 to the binomial system of Carl Linnaeus that remains in use to this day.In the 19th and 20th centuries, new techniques were developed for the study of plants, including methods of optical microscopy and live cell imaging, electron microscopy, analysis of chromosome number, plant chemistry and the structure and function of enzymes and other proteins. In the last two decades of the 20th century, botanists exploited the techniques of molecular genetic analysis, including genomics and proteomics and DNA sequences to classify plants more accurately.Modern botany is a broad, multidisciplinary subject with inputs from most other areas of science and technology. Research topics include the study of plant structure, growth and differentiation, reproduction, biochemistry and primary metabolism, chemical products, development, diseases, evolutionary relationships, systematics, and plant taxonomy. Dominant themes in 21st century plant science are molecular genetics and epigenetics, which are the mechanisms and control of gene expression during differentiation of plant cells and tissues. Botanical research has diverse applications in providing staple foods and textiles, in modern horticulture, agriculture and forestry, plant propagation, breeding and genetic modification, in the synthesis of chemicals and raw materials for construction and energy production, in environmental management, and the maintenance of biodiversity.