* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Plant Review | Part I | KEY
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Historia Plantarum (Theophrastus) wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Sustainable landscaping wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
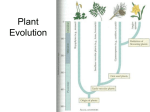
Name: ___________________________________________ Date: _______________________ Period: _________ Plant Review | Part I | KEY Plant Evolution/Origin of Plants 1. Land plants evolved from green algae. 2. List the similarities between land plants and their ancestor: • Same type of chlorophyll • Both store energy as starch • Smiliar DNA squences 3. In order to adapt to life on land, plants had to adapt and overcome challenges. Match the following adaptive structures with the appropriate function: _D_ Allows for taller growth by hardening the cell wall‐ giving wood its strength. _C_ Allows for taller growth by transporting a. Cuticle nutrients to all areas of the plant. _B_ Retains moisture by opening and closing b. Stomata pores to exchange gasses like O2, CO2, and H2O vapor. c. Vascular system _A_ Retains moisture by producing a waxy‐ like outer coating. d. Lignin _F_ Allows for reproduction on dry land e. Seeds (carried by wind or animals). _E_ Allows for reproduction on dry land by f. Pollen supplying the plant embryo with a food source, and by supplying a tough outer coating to protect the embryo. 4. List 3 adaptations plants have that defend themselves from herbivores: a. Spines b. Thorns c. Chemicals d. What type of evolution are these interactions? Co‐evolutionary interactions 5. Instead of water, plants rely on pollination for reproduction. 6. Explain an example of a mutualistic relationship between plants and another organism (you can use words, draw a picture, or both). Plants provide living space for bacteria and bacteria help plant get necessary nutrients. Plants provide food for organisms and organisms help in pollination. Classification of Plants 7. Fill in the following table: Plant Category Seedless, nonvascular Examples of plants Dominant Phase? Mosses Liverworts Hornworts No seeds, no vascular system, grows low to ground, needs water to reproduce, no true leaves Ferns, horsetails, club mosses No seeds, vascular system, grows off the ground, needs water to reproduce Sporophyte Seed producing (cones) Gymnosperms Conifers Cycads Ginkos Has seeds, has vascular system, DOES NOT need water to reproduce, seeds partially protected by cones, cone is reproductive structure Sporophyte Seed producing (flowers) Angiosperms Lillies, apple trees, orange trees, daisies, etc (anything with flower/fruit) Has seeds, vascular system, does not need H20 to reproduce, seeds protect and nourish embryo, flower is reproductive structure Seedless, vascular Defining characteristics Gametophyte Sporophyte Plant life cycles 8. Fill in (label) the alternation of generations diagram below: a. Sporophyte b. Zygote c. Sporophyte d. Fertilization e. Gametophyte f. Meiosis g. Gametes (Egg/Sperm) h. Spores i. Gametophyte For the following statements choose either mitosis or meiosis: 9. The process that produces haploid spores Meiosis 10. The process where a cell grows & divides, but chromosome number doesn’t change Mitosis 11. The process that takes place between letters “b” and “a” Mitosis 12. The process that begins the gametophyte stage Meiosis 13. The process that reduces the chromosome number by half Meiosis For the following statements state whether this happens during the sporophyte or gametophyte phase: 14. Division of zygote sporophyte 15. Production of spores sporophyte 16. Fertilization sporophyte 17. Creation of germ cells gametophyte 18. Place the steps of the moss life cycle in order, from the step started for you: 1 Spores land. 5 Diploid sporophyte will grow from zygote. 3 Through water, sperm swim from antheridium (male gametophyte) to archegonium (female gametophyte). 2 Moss gametophytes grow near the ground. 6 Sporophyte will create and release spores. 4 Fertilization occurs. 19. Place the steps of the fern life cycle in order, from the step started for you: 1 Spores land on soil. 6 Sporophyte creates and releases spores. 3 Through water, sperm swim from antheridium to archegonium on prothallus. 2 from the spores, a prothallus grows. 4 Fertilization occurs. 5 Diploid sporophyte grows from the prothallus, where zygote is. 20. Place the steps of the conifer life cycle in order, from the step started for you: 1 Male and female cones grow into mature sporophytes. 7 Seeds land and the seedling grows into sporophyte (cycle repeats). 6 After seeds harden, cone opens and seeds are released. 2 Pollen grains are released from male cones and sticks to female ovule. 5 Diploid embryo develops. 3 Pollen tube grows from male spore (pollen) 4 Two nuclei travel down tube to female spore and one fertilizes the egg.