Seed Plants: Gymnosperms and Angiosperms
... 24. Explain the difference between annuals, biennials, and perennials. Give two examples of each. ...
... 24. Explain the difference between annuals, biennials, and perennials. Give two examples of each. ...
PlantReproduction
... 4. Fragmentation – when a piece of the parent organism breaks off and is dispersed. Each section is able to form a new organism. • Example - House plants formed from cuttings ...
... 4. Fragmentation – when a piece of the parent organism breaks off and is dispersed. Each section is able to form a new organism. • Example - House plants formed from cuttings ...
Chapter 24 - S3 amazonaws com
... 1. Like all plants, the life cycles of mosses, ferns, and conifers include alternation of generations. 2. Flowers are the reproductive structures of anthophytes. 3. In anthophytes, seeds and fruits can develop from flowers after fertilization. I. Reproduction in Plants A. Asexual reproduction 1. veg ...
... 1. Like all plants, the life cycles of mosses, ferns, and conifers include alternation of generations. 2. Flowers are the reproductive structures of anthophytes. 3. In anthophytes, seeds and fruits can develop from flowers after fertilization. I. Reproduction in Plants A. Asexual reproduction 1. veg ...
plant kingdom - introduction and classification
... Plants with vascular tissues (Tracheophytes) are more advanced over others. Reproduction ...
... Plants with vascular tissues (Tracheophytes) are more advanced over others. Reproduction ...
Reproduction a process whereby living things produce more living
... Reproduction a process whereby living things produce more living things All living organisms need to do it!! ...
... Reproduction a process whereby living things produce more living things All living organisms need to do it!! ...
Plant fungi study guide
... Know the Female and male structure of flowers. Where are pollen and ova formed, etc. ...
... Know the Female and male structure of flowers. Where are pollen and ova formed, etc. ...
File
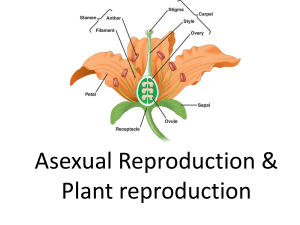
... SKILL: Drawing of half-views of animal-pollinated flowers. Sepals – Anthers – Filaments – Pollen – Carpel – Stigma – Style – Ovary – Ovule – ...
... SKILL: Drawing of half-views of animal-pollinated flowers. Sepals – Anthers – Filaments – Pollen – Carpel – Stigma – Style – Ovary – Ovule – ...
Section 3
... • Some germinate and some can stay in resting stage for hundreds of years • Seeds only germinate when conditions are right ...
... • Some germinate and some can stay in resting stage for hundreds of years • Seeds only germinate when conditions are right ...
Learn About Plants
... •Traps insects in its leaves and digests them for nutrients •Is called a carnivorous (meat eating) plant •Grows in wet, damp bogs •Can reach 1 foot in heighth Let's see other plants ...
... •Traps insects in its leaves and digests them for nutrients •Is called a carnivorous (meat eating) plant •Grows in wet, damp bogs •Can reach 1 foot in heighth Let's see other plants ...
PLANT EVOLUTION DISPLAY Handout Welcome to UCSC
... gametophyte. When this gametophyte is mature, the gametophyte will produce gametes. The gametes (egg and sperm) will fuse to form a zygote that grows into a mature diploid (2n) organism called a sporophyte. The sporophyte will undergo meiosis in some region of the plant and (1n) spores will be produ ...
... gametophyte. When this gametophyte is mature, the gametophyte will produce gametes. The gametes (egg and sperm) will fuse to form a zygote that grows into a mature diploid (2n) organism called a sporophyte. The sporophyte will undergo meiosis in some region of the plant and (1n) spores will be produ ...
BIO101 Unit 4
... a group of gymnosperms that have needle-like leaves and stay green during all seasons. gametophyte the haploid generation of alternation of generations life cycle of plants; produces the gametes that unite to form a diploid zygote which develops into the sporophyte generation. gymnosperms a type of ...
... a group of gymnosperms that have needle-like leaves and stay green during all seasons. gametophyte the haploid generation of alternation of generations life cycle of plants; produces the gametes that unite to form a diploid zygote which develops into the sporophyte generation. gymnosperms a type of ...
Plant/Flower Study Guide
... Plants are “producers”. This means they have the ability to make their own food. The process is called PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Photosynthesis takes place in the plant’s leaves. The plant uses chlorophyll (found in chloroplast) along with water, carbon dioxide, and energy from the sun to produce food. Dur ...
... Plants are “producers”. This means they have the ability to make their own food. The process is called PHOTOSYNTHESIS. Photosynthesis takes place in the plant’s leaves. The plant uses chlorophyll (found in chloroplast) along with water, carbon dioxide, and energy from the sun to produce food. Dur ...
How Plants Colonized onto Land
... Structure specialized for reproduction. Fruit is the mature ovary. ...
... Structure specialized for reproduction. Fruit is the mature ovary. ...
VOCABULARY FOR UNIT B CHAPTER 2 MOSS – a very short
... the word means “naked seed” in Greek. The seeds are not surrounded by a container. Conifers are one kind of gymnosperm. 6. CONIFER – “cone-bearer” ; a type of gymnosperm that bears cones. The cones are the reproductive structures that produce seed. 7. POLLEN – powder-like male spores that develop in ...
... the word means “naked seed” in Greek. The seeds are not surrounded by a container. Conifers are one kind of gymnosperm. 6. CONIFER – “cone-bearer” ; a type of gymnosperm that bears cones. The cones are the reproductive structures that produce seed. 7. POLLEN – powder-like male spores that develop in ...
Ferns, Club Mosses, and Horsetails Guided Reading
... 16.Germination is the sprouting of the embryo out of a seed. 17.b, d 18.a.Anchor plants in the ground; b.Absorb water and minerals from the soil; c.Store food 19.Fibrous roots, Taproot 20.b 21.d 22.a 23.c 24.d 25.a.Carry substances between the leaves and roots; b.Support the plant and hold up the le ...
... 16.Germination is the sprouting of the embryo out of a seed. 17.b, d 18.a.Anchor plants in the ground; b.Absorb water and minerals from the soil; c.Store food 19.Fibrous roots, Taproot 20.b 21.d 22.a 23.c 24.d 25.a.Carry substances between the leaves and roots; b.Support the plant and hold up the le ...
Name Date ______ Hour_______ Table ____ Wonderful World of
... 4. The ___________ is the middle part of the pistil. 5. Since they have just one set of chromosomes, gametophytes are said to be ___________. ...
... 4. The ___________ is the middle part of the pistil. 5. Since they have just one set of chromosomes, gametophytes are said to be ___________. ...
6 th Grade Science Ms. Koennecke Growing and
... 1. Petals – leaf-like colorful part of a flower used to attract insects and birds 2. Sepals – modified leafs protect the bud of a young flower 3. Receptacle – the section where the reproductive parts of a plant are attached ...
... 1. Petals – leaf-like colorful part of a flower used to attract insects and birds 2. Sepals – modified leafs protect the bud of a young flower 3. Receptacle – the section where the reproductive parts of a plant are attached ...
An increase in the Aplectrum hyemale population in Hougham
... population biology of these orchids has been studied for three years. The population remained stable for two years but increased in size in 2014, from 305 in 2012 to 363 in 2014. Additionally, only one plant flowered in 2012 and none flowered in 2013, but in 2014, 42 plants bloomed with an average o ...
... population biology of these orchids has been studied for three years. The population remained stable for two years but increased in size in 2014, from 305 in 2012 to 363 in 2014. Additionally, only one plant flowered in 2012 and none flowered in 2013, but in 2014, 42 plants bloomed with an average o ...
Explain what xylem and phloem are used for
... and oxygen and water out of the leaves. Stomata are open during the daytime, when photosynthesis can take place. They close at night because photosynthesis can not take place and to conserve water. How is reproduction different in angiosperms and gymnosperms? Angiosperms reproduce by producing flowe ...
... and oxygen and water out of the leaves. Stomata are open during the daytime, when photosynthesis can take place. They close at night because photosynthesis can not take place and to conserve water. How is reproduction different in angiosperms and gymnosperms? Angiosperms reproduce by producing flowe ...
Plantae - phsgirard.org
... Form new plants Release heat through stomata The Flower Sexual reproduction unit Produces and houses gametes (sex cells) Attract pollinators Plants utilize many agents for transporting pollen from one flower to another Wind, Water, Insects, Birds, Bats ...
... Form new plants Release heat through stomata The Flower Sexual reproduction unit Produces and houses gametes (sex cells) Attract pollinators Plants utilize many agents for transporting pollen from one flower to another Wind, Water, Insects, Birds, Bats ...
Notes Chapter 30
... -microspore mother cells each produce four haploid microspores -each microspore undergoes mitosis to produce two haploid cells that do not separate (pollen grain) -the larger of the two cells is the tube cell (forms pollen tube) - the smaller of the two cells is the generative cell, which will divid ...
... -microspore mother cells each produce four haploid microspores -each microspore undergoes mitosis to produce two haploid cells that do not separate (pollen grain) -the larger of the two cells is the tube cell (forms pollen tube) - the smaller of the two cells is the generative cell, which will divid ...
Pollination - GaryTurnerScience
... food, beverages, fibers, spices, and medicines need to be pollinated by animals in order to produce the goods on which we depend. Foods and beverages produced with the help of pollinators include: apples, bananas, blueberries, chocolate, coffee, melons, peaches, potatoes, pumpkins, vanilla, almonds. ...
... food, beverages, fibers, spices, and medicines need to be pollinated by animals in order to produce the goods on which we depend. Foods and beverages produced with the help of pollinators include: apples, bananas, blueberries, chocolate, coffee, melons, peaches, potatoes, pumpkins, vanilla, almonds. ...
Alternation of generations: a review
... This undergoes cytokinesis, forming cell membranes and walls and thus becoming multicellular: Endosperm is rich in nutrients, which it provides to the developing embryo In most monocots, endosperm stocks nutrients that can be used by the seedling after germination In many dicots, food reserves of th ...
... This undergoes cytokinesis, forming cell membranes and walls and thus becoming multicellular: Endosperm is rich in nutrients, which it provides to the developing embryo In most monocots, endosperm stocks nutrients that can be used by the seedling after germination In many dicots, food reserves of th ...
Plant reproduction

Plant reproduction is the production of new individuals or offspring in plants, which can be accomplished by sexual or asexual reproduction. Sexual reproduction produces offspring by the fusion of gametes, resulting in offspring genetically different from the parent or parents. Asexual reproduction produces new individuals without the fusion of gametes, genetically identical to the parent plants and each other, except when mutations occur. In seed plants, the offspring can be packaged in a protective seed, which is used as an agent of dispersal.