Chapter_20_Heart_Review
... 3. Left ventricle has the thickest wall due to work load 4. Chambers of the heart, atria and ventricle 5. Heart separations – septums and conary sulcus 6. Cardiac circulation – coronary artery and coronary sinus 7. Valves of the heart – tricuspid, bicuspid (mitral), pulmonary, aortic 8. Blood flow t ...
... 3. Left ventricle has the thickest wall due to work load 4. Chambers of the heart, atria and ventricle 5. Heart separations – septums and conary sulcus 6. Cardiac circulation – coronary artery and coronary sinus 7. Valves of the heart – tricuspid, bicuspid (mitral), pulmonary, aortic 8. Blood flow t ...
Interferences to Oxygen: congenital anomalies and cardiovascular
... L atrium during systole. Usually benign in nature but may progress to pronounced mitral regurgitation. Most are asymptomatic Most common in women between 20 and 54 years of age Genetic Auscultation of midsystolic click with late systolic murmur audible at apex. ...
... L atrium during systole. Usually benign in nature but may progress to pronounced mitral regurgitation. Most are asymptomatic Most common in women between 20 and 54 years of age Genetic Auscultation of midsystolic click with late systolic murmur audible at apex. ...
1- Dilated cardiomyopathy
... - is the common reason for heart transplantation - is so dangerous because: - often goes unrecognized and untreated - frequently affects younger people - Cardiomyopathy: is a group of diseases that primarily involve the myocardium and produce myocardial dysfunction - usually present with heart failu ...
... - is the common reason for heart transplantation - is so dangerous because: - often goes unrecognized and untreated - frequently affects younger people - Cardiomyopathy: is a group of diseases that primarily involve the myocardium and produce myocardial dysfunction - usually present with heart failu ...
File - Developing Anaesthesia
... Management consists of medical and surgical strategies to relieve this dynamic outflow tract obstruction, as well as controlling secondary complications such as arrhythmias and heart failure. It is an important condition to recognize, as it is one of the causes of sudden cardiac death in the young. ...
... Management consists of medical and surgical strategies to relieve this dynamic outflow tract obstruction, as well as controlling secondary complications such as arrhythmias and heart failure. It is an important condition to recognize, as it is one of the causes of sudden cardiac death in the young. ...
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy What Is Hypertrophic
... are predisposed to the disease, the domestic short hair (regular house cat) is most commonly diagnosed with HCM. Cats are usually middle aged to older; however, it can be diagnosed at any age. No viral or nutritional causes of HCM have been identified in cats. ...
... are predisposed to the disease, the domestic short hair (regular house cat) is most commonly diagnosed with HCM. Cats are usually middle aged to older; however, it can be diagnosed at any age. No viral or nutritional causes of HCM have been identified in cats. ...
Cardiac Biomarkers
... heart rate and titrate the dose accordingly. Many cardiologists would repeat an echocardiogram in 6 –12 months. Chest radiographs would be indicated if the cat were to develop clinical signs of congestive heart failure (e.g., tachypnea, dyspnea, coughing or syncope). Currently, the value of monitori ...
... heart rate and titrate the dose accordingly. Many cardiologists would repeat an echocardiogram in 6 –12 months. Chest radiographs would be indicated if the cat were to develop clinical signs of congestive heart failure (e.g., tachypnea, dyspnea, coughing or syncope). Currently, the value of monitori ...
Diseases of The Myocardium
... ,dynamic out flow obstruction ,exersional angina & shortness of breath ,arrythmias and sudden death.The condition is inherited as autosomal dominant. ...
... ,dynamic out flow obstruction ,exersional angina & shortness of breath ,arrythmias and sudden death.The condition is inherited as autosomal dominant. ...
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
... - complications: mortality <1-2%, complete heart block (10-30%), VSD, AR, ventricular fibrillation, myocardial infarction of a larger territory ...
... - complications: mortality <1-2%, complete heart block (10-30%), VSD, AR, ventricular fibrillation, myocardial infarction of a larger territory ...
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)
... All first degree relatives of an individual who has HCM should undergo routine cardiac evaluation. This includes parents, brothers, sisters, and children. If a gene mutation causing HCM in an individual is known, screening is recommended for those family members proven to also carry the gene mutatio ...
... All first degree relatives of an individual who has HCM should undergo routine cardiac evaluation. This includes parents, brothers, sisters, and children. If a gene mutation causing HCM in an individual is known, screening is recommended for those family members proven to also carry the gene mutatio ...
Slide () - AccessAnesthesiology
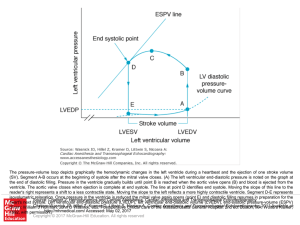
... The pressure-volume loop depicts graphically the hemodynamic changes in the left ventricle during a heartbeat and the ejection of one stroke volume (SV). Segment A-B occurs at the beginning of systole after the mitral valve closes. (A) The left ventricular end-diastolic pressure is noted on the grap ...
... The pressure-volume loop depicts graphically the hemodynamic changes in the left ventricle during a heartbeat and the ejection of one stroke volume (SV). Segment A-B occurs at the beginning of systole after the mitral valve closes. (A) The left ventricular end-diastolic pressure is noted on the grap ...
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
... The enlarged ventricular septum may obstruct the outlets to the aorta and/or pulmonary artery (PA), causing a heart murmur. This is known as Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Many patients experience no symptoms except during periods of exertion, when chest pain and shortness of breath may oc ...
... The enlarged ventricular septum may obstruct the outlets to the aorta and/or pulmonary artery (PA), causing a heart murmur. This is known as Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy. Many patients experience no symptoms except during periods of exertion, when chest pain and shortness of breath may oc ...
Document
... ventricle, and is most evident in subaortic region. • Asymmetric septal hypertrophy is often associated with functional ventricular outflow obstruction during systole (25%) which is caused by abnormal anterior motion of the mitral valve leaflet during systole. • This motion lead to recurrent, forcef ...
... ventricle, and is most evident in subaortic region. • Asymmetric septal hypertrophy is often associated with functional ventricular outflow obstruction during systole (25%) which is caused by abnormal anterior motion of the mitral valve leaflet during systole. • This motion lead to recurrent, forcef ...
Ventricular Remodeling
... radius of the LV ventricular curvature is located at the basal septum, a septal bulge develops early in the hypertensive process. This may be particular prominent in the elderly, which is typically sigmoidal in shape-this shape is less common in the hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM) pop ...
... radius of the LV ventricular curvature is located at the basal septum, a septal bulge develops early in the hypertensive process. This may be particular prominent in the elderly, which is typically sigmoidal in shape-this shape is less common in the hypertrophic obstructive cardiomyopathy (HOCM) pop ...
Cardiovascular Study Guide
... b. Arteries/veins c. Capillaries/arterioles/venules d. Circuits a. Pulmonary b. Systemic ...
... b. Arteries/veins c. Capillaries/arterioles/venules d. Circuits a. Pulmonary b. Systemic ...
Slide ()
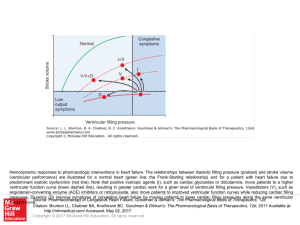
... Hemodynamic responses to pharmacologic interventions in heart failure. The relationships between diastolic filling pressure (preload) and stroke volume (ventricular performance) are illustrated for a normal heart (green line; the Frank-Starling relationship) and for a patient with heart failure due ...
... Hemodynamic responses to pharmacologic interventions in heart failure. The relationships between diastolic filling pressure (preload) and stroke volume (ventricular performance) are illustrated for a normal heart (green line; the Frank-Starling relationship) and for a patient with heart failure due ...
Sudden Cardiac Death in Three Generations of the Same Family: A
... (VF), and electromechanical dissociation (EMD).2,5 It occurs more in young asymptomatic or less symptomatic patients.2 Though our patient was symptomatic but strong family history and history of arrhythmia put him in danger zone for SCD. ...
... (VF), and electromechanical dissociation (EMD).2,5 It occurs more in young asymptomatic or less symptomatic patients.2 Though our patient was symptomatic but strong family history and history of arrhythmia put him in danger zone for SCD. ...
Slide 1
... individuals will be at risk of inheriting the gene and developing the disease. The offspring of unaffected family members carry no risk of inheriting the gene and developing the disease. In any one family with FHCM, all affected members have the same mutation. ...
... individuals will be at risk of inheriting the gene and developing the disease. The offspring of unaffected family members carry no risk of inheriting the gene and developing the disease. In any one family with FHCM, all affected members have the same mutation. ...
Good Drugs for a Bad Heart
... With hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), the most common feline cardiac disease, most cats progress to develop dynamic obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT). Beta blockers, particularly atenolol, are the standard drugs used to decrease LVOT obstruction in cats because of their nega ...
... With hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM), the most common feline cardiac disease, most cats progress to develop dynamic obstruction of the left ventricular outflow tract (LVOT). Beta blockers, particularly atenolol, are the standard drugs used to decrease LVOT obstruction in cats because of their nega ...
(HCM), idiopathic hypertrophic
... FriendsThis week’s FMEA deals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) patients. This is not the acquired form of hypertrophy or dilated cardiomyopathy. Rather it is a congenital form of HCM seen mostly in children and young adults. In the city where I live it probably accounts for the death of at lea ...
... FriendsThis week’s FMEA deals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) patients. This is not the acquired form of hypertrophy or dilated cardiomyopathy. Rather it is a congenital form of HCM seen mostly in children and young adults. In the city where I live it probably accounts for the death of at lea ...
cardiomyopathies
... LV cavity small, systolic function normal or hyperdynamic early on. Diastolic dysfunction common Obstructive and non-obstructive forms ...
... LV cavity small, systolic function normal or hyperdynamic early on. Diastolic dysfunction common Obstructive and non-obstructive forms ...
echocardiography in chd
... Doctors should arrange for people with suspected heart failure to be offered the appropriate investigations (e.G. Electrocardiography, echocardiography) that will confirm or refute the diagnosis. For those in whom heart failure is confirmed, its cause should be identified. The treatments most ...
... Doctors should arrange for people with suspected heart failure to be offered the appropriate investigations (e.G. Electrocardiography, echocardiography) that will confirm or refute the diagnosis. For those in whom heart failure is confirmed, its cause should be identified. The treatments most ...
Go For Red - Jump Start Your Heart, Inc.
... The joint recommendations of the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association are published online in Circulation: Journal of the American Heart Association and Journal of the American College of Cardiology. ―HCM is widely misperceived as a fatal condition, but a diag ...
... The joint recommendations of the American College of Cardiology Foundation and the American Heart Association are published online in Circulation: Journal of the American Heart Association and Journal of the American College of Cardiology. ―HCM is widely misperceived as a fatal condition, but a diag ...
4 - Pass the FracP
... drugs may limit the increase in the gradient that occurs during exercise. It is not known whether -adrenergic blockers offer any protection against sudden death. Amiodarone appears to be effective in reducing the frequency of supraventricular as well as life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, and ...
... drugs may limit the increase in the gradient that occurs during exercise. It is not known whether -adrenergic blockers offer any protection against sudden death. Amiodarone appears to be effective in reducing the frequency of supraventricular as well as life-threatening ventricular arrhythmias, and ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.