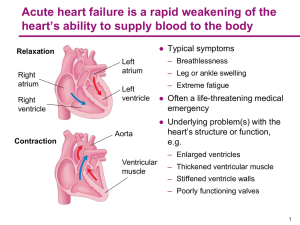
60 Cardiovascular Formulary for the Hypertensive
... to reduce and prevent elevations in LVEDP, to lower systolic pressure gradients and myocardial oxygen requirements, to prevent stress-induced tachycardia and reduce resting heart rate, and for its antiarrhythmic effects. When arrhythmias are present, this drug may be initiated earlier in the diseas ...
... to reduce and prevent elevations in LVEDP, to lower systolic pressure gradients and myocardial oxygen requirements, to prevent stress-induced tachycardia and reduce resting heart rate, and for its antiarrhythmic effects. When arrhythmias are present, this drug may be initiated earlier in the diseas ...
Cardiomyopathy - Lock Haven University
... Skin deposits leads to bronze discoloration that results from increased melanin production. Hyperpigmentation Remember: liver, pancreas, heart ...
... Skin deposits leads to bronze discoloration that results from increased melanin production. Hyperpigmentation Remember: liver, pancreas, heart ...
100 faces of hypertrophy
... and quantify the systolic and diastolic function. New techniques in echocardiography have provided insight into regional myocardial motion and deformation. Tissue Doppler imaging, as well as grayscale 2D speckle tracking, provides more sensitive markers of early myocardial dysfunction compared with ...
... and quantify the systolic and diastolic function. New techniques in echocardiography have provided insight into regional myocardial motion and deformation. Tissue Doppler imaging, as well as grayscale 2D speckle tracking, provides more sensitive markers of early myocardial dysfunction compared with ...
Lab/ECG/Xray Rounds - Calgary Emergency Medicine
... 30 yo male with 20 min of lightheadedness running to bus ...
... 30 yo male with 20 min of lightheadedness running to bus ...
MP3-15 Familial WPW and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy caused by
... Familial WPW and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy caused by PRKAG2 mutations: cardiac MRI and electrophysiology findings Hiippala A. (1), Holmström M. (2), Pöyhönen P. (2), Kivistö S. (2), Happonen J-M. (1) Department of Pediatric Cardiology (1) and Department of Radiology (2), Helsinki University Hospit ...
... Familial WPW and hypertrophic cardiomyopathy caused by PRKAG2 mutations: cardiac MRI and electrophysiology findings Hiippala A. (1), Holmström M. (2), Pöyhönen P. (2), Kivistö S. (2), Happonen J-M. (1) Department of Pediatric Cardiology (1) and Department of Radiology (2), Helsinki University Hospit ...
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy diagnosis and management
... CMR - Poor Prognostic factors • Markedly elevated LV mass index (men > 91 g/m2; women > 69 g/m2) was sensitive (100%) • Maximal wall thickness of more than 30 mm was specific (91%) for cardiac deaths • Right ventricular (RV) hypertrophy • Myocardial edema by T2-weighted imaging • LGE has been assoc ...
... CMR - Poor Prognostic factors • Markedly elevated LV mass index (men > 91 g/m2; women > 69 g/m2) was sensitive (100%) • Maximal wall thickness of more than 30 mm was specific (91%) for cardiac deaths • Right ventricular (RV) hypertrophy • Myocardial edema by T2-weighted imaging • LGE has been assoc ...
CT IMAGING OF A CASE WITH BIVENTRICULAR HYPERTROPHIC
... HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) Most common inherited cardiovascular disease, which manifests as diffuse or segmental left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy with a nondilated and hyperdynamic chamber. HCM is an autosomal dominant disease caused by mutations in genes encoding sarcomere proteins. ...
... HYPERTROPHIC CARDIOMYOPATHY (HCM) Most common inherited cardiovascular disease, which manifests as diffuse or segmental left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy with a nondilated and hyperdynamic chamber. HCM is an autosomal dominant disease caused by mutations in genes encoding sarcomere proteins. ...
HOCM DR SREEJITH
... useful in the assessment of peak velocities • SAM of the mitral valve is clearly seen on cardiac MRI • Improvement in obstruction after septal ablation or myomectomy can be demonstrated, as can the location and size of the associated infarction, which are useful for planning repeat procedures • Card ...
... useful in the assessment of peak velocities • SAM of the mitral valve is clearly seen on cardiac MRI • Improvement in obstruction after septal ablation or myomectomy can be demonstrated, as can the location and size of the associated infarction, which are useful for planning repeat procedures • Card ...
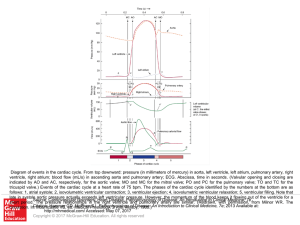
Slide ()
... Diagram of events in the cardiac cycle. From top downward: pressure (in millimeters of mercury) in aorta, left ventricle, left atrium, pulmonary artery, right ventricle, right atrium; blood flow (mL/s) in ascending aorta and pulmonary artery; ECG. Abscissa, time in seconds. (Valvular opening and clo ...
... Diagram of events in the cardiac cycle. From top downward: pressure (in millimeters of mercury) in aorta, left ventricle, left atrium, pulmonary artery, right ventricle, right atrium; blood flow (mL/s) in ascending aorta and pulmonary artery; ECG. Abscissa, time in seconds. (Valvular opening and clo ...
Teare D. Asymmetrical hypertrophy of the heart in young adults. Brit
... clinical manifestations. It is now accepted that hypertrophy in the affected segment of myocardium develops in the first two decades of life, and there is no indication from echocardiographic4studies of spread to involve the rest of the ventricle. As a corollary there will be cases with the disease ...
... clinical manifestations. It is now accepted that hypertrophy in the affected segment of myocardium develops in the first two decades of life, and there is no indication from echocardiographic4studies of spread to involve the rest of the ventricle. As a corollary there will be cases with the disease ...
A1989CB63500002
... clinical manifestations. It is now accepted that hypertrophy in the affected segment of myocardium develops in the first two decades of life, and there is no indication from echocardiographic4studies of spread to involve the rest of the ventricle. As a corollary there will be cases with the disease ...
... clinical manifestations. It is now accepted that hypertrophy in the affected segment of myocardium develops in the first two decades of life, and there is no indication from echocardiographic4studies of spread to involve the rest of the ventricle. As a corollary there will be cases with the disease ...
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM)
... others in the family can and should be tested to see if they are at risk of developing the disease. The other problem is that individuals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may not have any symptoms, or symptoms may be non-specific. However symptoms, such as shortness of breath, chest pain or discomfo ...
... others in the family can and should be tested to see if they are at risk of developing the disease. The other problem is that individuals with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy may not have any symptoms, or symptoms may be non-specific. However symptoms, such as shortness of breath, chest pain or discomfo ...
Implications of Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Transmitted by
... JAMA. 2009;302(15):1681-1684. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1507 ...
... JAMA. 2009;302(15):1681-1684. doi:10.1001/jama.2009.1507 ...
ACVIM Fact Sheet: Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy in Cats
... binding protein C. This disease is usually diagnosed in middle-aged cats. However, there is also a juvenile form affecting young cats (usually Ragdolls). The impact of the thickening of the ventricular wall on the heart function is quite variable because they are many different forms of hypertrophy ...
... binding protein C. This disease is usually diagnosed in middle-aged cats. However, there is also a juvenile form affecting young cats (usually Ragdolls). The impact of the thickening of the ventricular wall on the heart function is quite variable because they are many different forms of hypertrophy ...
Clinical and electrocardiographic features
... HCM has a reported prevalence of 1:500 and is a substantial contributor to sudden cardiac death in young athletes. Diagnosis of HCM is made by echocardiography and defined as septal wall thickness > 15 mm in the absence of history of hypertension or other explanatory etiologies, according to Dr. Hau ...
... HCM has a reported prevalence of 1:500 and is a substantial contributor to sudden cardiac death in young athletes. Diagnosis of HCM is made by echocardiography and defined as septal wall thickness > 15 mm in the absence of history of hypertension or other explanatory etiologies, according to Dr. Hau ...
Cardiomyopathy
... 25% associated with subaortic obstruction and/or systolic anterior motion of mitral valve 70% associated with gene mutations Inheritance: Autosomal dominant (50% are sporadic) Screening relatives: Helpful preventative measures, but life insurance problems Symptoms Often no Dyspnoea (PND) Exert ...
... 25% associated with subaortic obstruction and/or systolic anterior motion of mitral valve 70% associated with gene mutations Inheritance: Autosomal dominant (50% are sporadic) Screening relatives: Helpful preventative measures, but life insurance problems Symptoms Often no Dyspnoea (PND) Exert ...
Is prevention of sudden cardiac death feasible?
... sudden death has long been an aspiration in HCM. Early experiences with pharmacologic strategies demonstrated that drugs (e.g., amiodarone) are not absolutely protective against sudden death. Based on recent substantial experience, the ICD has now proved to be a safe and the only effective therapeut ...
... sudden death has long been an aspiration in HCM. Early experiences with pharmacologic strategies demonstrated that drugs (e.g., amiodarone) are not absolutely protective against sudden death. Based on recent substantial experience, the ICD has now proved to be a safe and the only effective therapeut ...
Sudden Cardiac Death
... Approximately 25% of patients with HCM have a dynamic systolic pressure gradient in the left ventricular outflow tract caused by contact between the mitral valve leaflet(s) and the interventricular septum under resting conditions Outflow tract gradient in excess of 30 mmHg is an important cause of s ...
... Approximately 25% of patients with HCM have a dynamic systolic pressure gradient in the left ventricular outflow tract caused by contact between the mitral valve leaflet(s) and the interventricular septum under resting conditions Outflow tract gradient in excess of 30 mmHg is an important cause of s ...
HPI - iupui
... Echocardiography has been used extensively both as an aid to diagnosis and for research into the pathophysiology of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM). It is characterized by an abnormal arrangement of the myocardial cells, which instead of lying in parallel rows, form whorl-like patterns. It most ...
... Echocardiography has been used extensively both as an aid to diagnosis and for research into the pathophysiology of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HOCM). It is characterized by an abnormal arrangement of the myocardial cells, which instead of lying in parallel rows, form whorl-like patterns. It most ...
Cardiomyopaties
... Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis) or HOCMP (Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy) features. There is no pressure gradient at left ventricle outflow(LVOT) tract in 1/3 of patient. (Rest or provocated gradient). HCMP prevalance: 1/500. HCMP is the most prevalant genetic cardiovascular disease. Nearl ...
... Hypertrophic Subaortic Stenosis) or HOCMP (Hypertrophic Obstructive Cardiomyopathy) features. There is no pressure gradient at left ventricle outflow(LVOT) tract in 1/3 of patient. (Rest or provocated gradient). HCMP prevalance: 1/500. HCMP is the most prevalant genetic cardiovascular disease. Nearl ...
Document
... • Beta blockers (slows heart rate, reduce force of LV contraction, augments ventricular filling and relaxation, decreases myocardial O2 demand, blunts outflow gradient triggered by sympathetic activity) • Verapamil (improves LV relaxation and filling) • Disopyramide • End stage failure –ACE ,ARBs, I ...
... • Beta blockers (slows heart rate, reduce force of LV contraction, augments ventricular filling and relaxation, decreases myocardial O2 demand, blunts outflow gradient triggered by sympathetic activity) • Verapamil (improves LV relaxation and filling) • Disopyramide • End stage failure –ACE ,ARBs, I ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.