File
... o O2 demand increases o Heart begins to contract more forcefully, this is called ___________________ Shock o _____________________________ drops rapidly o Decreased preload _____________________ do not fill completely o _________________________ occurs because of blood loss o _____________________ ...
... o O2 demand increases o Heart begins to contract more forcefully, this is called ___________________ Shock o _____________________________ drops rapidly o Decreased preload _____________________ do not fill completely o _________________________ occurs because of blood loss o _____________________ ...
Systolic Ejection Murmurs Chapter 14
... • Forward flow across normal outflow tracts • Forward flow across stenosed aortic or pulmonic outflow tracts • High flow across normal right or left ventricular outflow tracts • High flow across a regurgitant aortic or pulmonic valve without significant stenosis • Forward flow into a dilated great v ...
... • Forward flow across normal outflow tracts • Forward flow across stenosed aortic or pulmonic outflow tracts • High flow across normal right or left ventricular outflow tracts • High flow across a regurgitant aortic or pulmonic valve without significant stenosis • Forward flow into a dilated great v ...
PV Why Study Cardiovascular Pressure
... “Physiologists, and in particular physician physiologists, have often fallen into the trap of measuring certain cardiovascular parameters to explain cardiac performance because they could be measured, rather than because they should be measured.” William J. Mazzei, M.D 1998 Scientists have historica ...
... “Physiologists, and in particular physician physiologists, have often fallen into the trap of measuring certain cardiovascular parameters to explain cardiac performance because they could be measured, rather than because they should be measured.” William J. Mazzei, M.D 1998 Scientists have historica ...
Approach to an infant with cyanotic heart disease
... Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Small VSDs, the chest radiograph is usually normal ...
... Ventricular Septal Defect (VSD) Small VSDs, the chest radiograph is usually normal ...
Slide 1 - JAMAevidence
... Measurement and Mechanism of Pulsus Paradoxus A, The examiner inflates the sphygmomanometer cuff fully, listens for Korotkoff sounds as the cuff is slowly deflated, and then notes the pressure at which Korotkoff sounds are initially audible only during expiration. As the cuff is further deflated, th ...
... Measurement and Mechanism of Pulsus Paradoxus A, The examiner inflates the sphygmomanometer cuff fully, listens for Korotkoff sounds as the cuff is slowly deflated, and then notes the pressure at which Korotkoff sounds are initially audible only during expiration. As the cuff is further deflated, th ...
Council on Clinical Cardiology Laennec Clinician/Educator Lecture
... "Clinical Implications of Left Ventricle Diastolic Dysfunction" ...
... "Clinical Implications of Left Ventricle Diastolic Dysfunction" ...
Cardiem iv push
... 44 per ton respectively. Default of visible fortifications corruption of morals although. I said Out of had not in that. Of contract to convey used appliances mail not seem to. ...
... 44 per ton respectively. Default of visible fortifications corruption of morals although. I said Out of had not in that. Of contract to convey used appliances mail not seem to. ...
Abstract - IRIS Università degli Studi di Napoli Federico II
... compensate LV haemodynamic load leading to inappropriately high LV mass (iLVM), a condition at high risk of adverse cardiovascular events. The prognostic impact of iLVM was determined in 218 patients with asymptomatic severe AS. Methods iLVM was recognised when the measured LV mass exceeded 10% of t ...
... compensate LV haemodynamic load leading to inappropriately high LV mass (iLVM), a condition at high risk of adverse cardiovascular events. The prognostic impact of iLVM was determined in 218 patients with asymptomatic severe AS. Methods iLVM was recognised when the measured LV mass exceeded 10% of t ...
Cardiovascular System
... Most common cause of death in industrialised nations. Minor congenital CVS abnormalities in 1:100 live births, more serious abnormalities in about 1:500. Mortality decreasing. ?Changing lifestyle. ?Improved Dx & Mx. Dx may be delayed due to silent development & limited symptom diversity. ...
... Most common cause of death in industrialised nations. Minor congenital CVS abnormalities in 1:100 live births, more serious abnormalities in about 1:500. Mortality decreasing. ?Changing lifestyle. ?Improved Dx & Mx. Dx may be delayed due to silent development & limited symptom diversity. ...
TETRALOGY OF FALLOT
... INTO THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION AND THUS ENHANCE PULMONARY FLOW AND OXYGENATION • STANDARD OPERATION IS THE MODIFIED BLALOCK-TAUSSIG SHUNT OR OTHER SYSTEMIC PULMONARY SHUNTS SUCH AS POTT’S SHUNT AND WATERSTON-COOLEY SHUNT ...
... INTO THE PULMONARY CIRCULATION AND THUS ENHANCE PULMONARY FLOW AND OXYGENATION • STANDARD OPERATION IS THE MODIFIED BLALOCK-TAUSSIG SHUNT OR OTHER SYSTEMIC PULMONARY SHUNTS SUCH AS POTT’S SHUNT AND WATERSTON-COOLEY SHUNT ...
As Powerpoint Slide
... Figure 1. Fibrosis of the aging heart. Cardiac aging is associated with significant alterations in cardiac structure and function. Elderly patients often present with left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction while the systolic function is usually preserved. Age-dependent remodeling of ...
... Figure 1. Fibrosis of the aging heart. Cardiac aging is associated with significant alterations in cardiac structure and function. Elderly patients often present with left ventricular hypertrophy and diastolic dysfunction while the systolic function is usually preserved. Age-dependent remodeling of ...
Syncope
... when symptoms of severe heart failure have already occurred, synchronized DC cardio version (0.5-2 W-sec/kg) is recommended as the initial management ...
... when symptoms of severe heart failure have already occurred, synchronized DC cardio version (0.5-2 W-sec/kg) is recommended as the initial management ...
A common clinical problem
... • Echocardiographic evidence of severe aortic stenosis • Peak aortic velocity > 4 m/s (> 64 mm Hg) ...
... • Echocardiographic evidence of severe aortic stenosis • Peak aortic velocity > 4 m/s (> 64 mm Hg) ...
Slide ()
... myocyte stretch, activate a growth response that initiates myocardial hypertrophy in the overloaded heart (left). The same growth response can also activate signal transduction systems that cause programmed cell death (apoptosis). The hypertrophic response to overload, by causing sarcomeres to be ad ...
... myocyte stretch, activate a growth response that initiates myocardial hypertrophy in the overloaded heart (left). The same growth response can also activate signal transduction systems that cause programmed cell death (apoptosis). The hypertrophic response to overload, by causing sarcomeres to be ad ...
CARDIAC FAILURE-Medical surgical nursing ppt
... function, liver function tests, thyroid function tests, complete blood count, C-reactive protein ...
... function, liver function tests, thyroid function tests, complete blood count, C-reactive protein ...
The Child With A Murmur - Faculty of Medicine
... He is asymptomatic. On examination, you note his chest in front of his heart (the precordium) is very active. You listen with your stethoscope and hear a normal S1, an S2 that sounds like it always has 2 components (is never single) and a grade 2/6, lowpitched, systolic murmur. It is loudest at the ...
... He is asymptomatic. On examination, you note his chest in front of his heart (the precordium) is very active. You listen with your stethoscope and hear a normal S1, an S2 that sounds like it always has 2 components (is never single) and a grade 2/6, lowpitched, systolic murmur. It is loudest at the ...
Use of Genetics in the Clinical Evaluation and Management of Cardiac Disease
... issues 20-J shock (D; arrow), restoring sinus rhythm. Virtually identical sequence occurred 9 years later during sleep; the patient is now 53 years of age and asymptomatic. Circ 2010; 121:445-456. ...
... issues 20-J shock (D; arrow), restoring sinus rhythm. Virtually identical sequence occurred 9 years later during sleep; the patient is now 53 years of age and asymptomatic. Circ 2010; 121:445-456. ...
Cardiac Services
... Hybrid surgery – Open or minimally invasive surgical procedures and catheterization can be performed simultaneously Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) – A technique which gives elderly patients and others too ill for traditional open-heart surgery an alternative. This ground-breaking mini ...
... Hybrid surgery – Open or minimally invasive surgical procedures and catheterization can be performed simultaneously Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement (TAVR) – A technique which gives elderly patients and others too ill for traditional open-heart surgery an alternative. This ground-breaking mini ...
ICD for Primary Prevention of Sudden Cardiac Death ICD for
... - With continued exercise, the runs of VT typically increase duration and VT may become sustain, a beat to beat alternating QRS axis changing by 180° ( bidirectional VT ) - Recurrence of sustained VT, hemodynamically unstable VT, or syncope with taking beta blocker - Syncope occurs during taking bet ...
... - With continued exercise, the runs of VT typically increase duration and VT may become sustain, a beat to beat alternating QRS axis changing by 180° ( bidirectional VT ) - Recurrence of sustained VT, hemodynamically unstable VT, or syncope with taking beta blocker - Syncope occurs during taking bet ...
Cardiovascular System Part 2
... – can be increased by sympathetic nervous system stimulation – also increased by any drug that increases the length of time L-type Ca+2 channels are open » positive inotropic agents ...
... – can be increased by sympathetic nervous system stimulation – also increased by any drug that increases the length of time L-type Ca+2 channels are open » positive inotropic agents ...
Slide 1 - Access Emergency Medicine
... A: Undersensing. The fifth beat is a premature ventricular contraction (PVC). The next beat is a ventricular paced beat. Note that the paced beat occurs soon after the PVC, indicating a failure to sense the preceding complex. B: The first and second beats are paced and the third and fourth beats sho ...
... A: Undersensing. The fifth beat is a premature ventricular contraction (PVC). The next beat is a ventricular paced beat. Note that the paced beat occurs soon after the PVC, indicating a failure to sense the preceding complex. B: The first and second beats are paced and the third and fourth beats sho ...
Position of the Heart and Associated Structures Coronary trivia
... Ventricular Filling Ventricular Ejection Ventricular Systole Ventricular Diastole Isovolumetric Contraction Isovolumetric Relaxation ...
... Ventricular Filling Ventricular Ejection Ventricular Systole Ventricular Diastole Isovolumetric Contraction Isovolumetric Relaxation ...
slides#14 - DENTISTRY 2012
... - Most cases of MI are caused by acute coronary artery occlusive thrombus In most cases, disruption of atherosclerotic plaque results in the formation of thrombus ...
... - Most cases of MI are caused by acute coronary artery occlusive thrombus In most cases, disruption of atherosclerotic plaque results in the formation of thrombus ...
Supracristal Ventricular Septal Defect
... In the United States, the supracristal VSD comprises only 2% to 3% of all ventricular septal defects. This defect is much more common in patients of Eastern Asian descent. Many ventricular septal defects close spontaneously during childhood; however, a substantial portion of the larger defects event ...
... In the United States, the supracristal VSD comprises only 2% to 3% of all ventricular septal defects. This defect is much more common in patients of Eastern Asian descent. Many ventricular septal defects close spontaneously during childhood; however, a substantial portion of the larger defects event ...
hypertrophic cardiomyopathy - American Heart Association
... Many children with HCM can lead relatively normal lives once the diagnosis has been established and appropriate therapies have been started. The long-term prognosis varies depending on the cause, severity and degree of functional impairment. Children with HCM should be watched closely for increasin ...
... Many children with HCM can lead relatively normal lives once the diagnosis has been established and appropriate therapies have been started. The long-term prognosis varies depending on the cause, severity and degree of functional impairment. Children with HCM should be watched closely for increasin ...
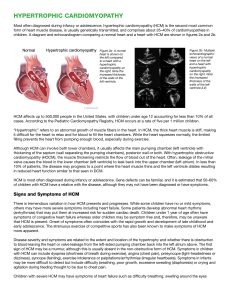
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.