* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Slide 1 - JAMAevidence
Remote ischemic conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac contractility modulation wikipedia , lookup
Coronary artery disease wikipedia , lookup
Heart failure wikipedia , lookup
Cardiac surgery wikipedia , lookup
Electrocardiography wikipedia , lookup
Lutembacher's syndrome wikipedia , lookup
Myocardial infarction wikipedia , lookup
Antihypertensive drug wikipedia , lookup
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy wikipedia , lookup
Mitral insufficiency wikipedia , lookup
Jatene procedure wikipedia , lookup
Atrial septal defect wikipedia , lookup
Dextro-Transposition of the great arteries wikipedia , lookup
Arrhythmogenic right ventricular dysplasia wikipedia , lookup
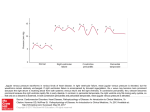
Measurement and Mechanism of Pulsus Paradoxus A, The examiner inflates the sphygmomanometer cuff fully, listens for Korotkoff sounds as the cuff is slowly deflated, and then notes the pressure at which Korotkoff sounds are initially audible only during expiration. As the cuff is further deflated, the examiner notes the pressure at which Korotkoff sounds become audible during expiration and inspiration. The difference between these 2 pressures is the pulsus paradoxus. In cardiac tamponade, the pulsus paradoxus measures greater than 10 mm Hg. Inspiratory diminution in the pulse wave amplitude seen on this arterial tracing demonstrates pulsus paradoxus. A similar phenomenon may be observed on a pulse oximeter waveform. B, During inspiration in the normal heart, negative intrapleural pressures increase venous return to the right ventricle and decrease pulmonary venous return to the left ventricle by Source: Cardiac Tamponade, The Rational Clinical Examination: Evidence-Based Clinical Diagnosis increasing pulmonary reservoir for blood. As a result of increased right ventricular distention, the interventricular septum bows slightly to the left, and the Simel DL,volume RennieofD.the The Examination: Evidence-Based Clinical Diagnosis; 2016 Available distensibility,Citation: filling, and stroke leftRational ventricleClinical are mildly reduced. In expiration, these changes are reciprocal, resultingat: in http://mhmedical.com/ the septum bowing to Accessed: May 07, 2017 the right and a mild reduction in right ventricular filling. In the presence of cardiac tamponade, the reciprocal changes seen in the normal heart are 2017 McGraw-Hill Education. rights reserved exaggerated Copyright when the © pericardial sac is filled with fluid,Allthus limiting distensibility of the entire heart. This results in a more dramatic reduction in filling of the left ventricle during inspiration, exacerbating the normal inspiratory decrease in stroke volume and blood pressure.