cardiomyopathy - WordPress.com
... Case History Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM ) • A 52- year old female presented with a 10 year history of HCM , increasing dyspnea and chest discomfort on exertion, palpitation, postural light headedness and functional limitation of less than one flight of stairs. • Symptoms were init ...
... Case History Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (HCM ) • A 52- year old female presented with a 10 year history of HCM , increasing dyspnea and chest discomfort on exertion, palpitation, postural light headedness and functional limitation of less than one flight of stairs. • Symptoms were init ...
Defibrillators
... • The irregular, unsynchronized contraction of the muscle fibers. • In the heart ventricular fibrillation is a condition which can lead to asystole. • It is usually preceded by ventricular tachycardia (fast heart rhythm). ...
... • The irregular, unsynchronized contraction of the muscle fibers. • In the heart ventricular fibrillation is a condition which can lead to asystole. • It is usually preceded by ventricular tachycardia (fast heart rhythm). ...
Cardio Review 4 Quince [CAPT],Joan,Juliet
... pressure is 120 mm Hg and the diastolic blood pressure is 80 mm Hg ...
... pressure is 120 mm Hg and the diastolic blood pressure is 80 mm Hg ...
Slide 1
... infinterventricular groove to supply blood to the inf lv wall and inf 1/3 of interventricular septum and plv supply blood for post lvwhich is right dominant.10% left dominant and PDA PLV from lcx,5%codominant RCA gives PDA and LCX gives PLV ...
... infinterventricular groove to supply blood to the inf lv wall and inf 1/3 of interventricular septum and plv supply blood for post lvwhich is right dominant.10% left dominant and PDA PLV from lcx,5%codominant RCA gives PDA and LCX gives PLV ...
Cardiovascular System
... – Depolarizes every .8 sec. At rest – Depolarizes due to change in permeability – Pacemaker ...
... – Depolarizes every .8 sec. At rest – Depolarizes due to change in permeability – Pacemaker ...
Size: 2 MB - diastolic dysfunction mgmc
... of active myocardial relaxation and passive ventricular filling. • Condition that includes classic CHF findings and abnormal diastolic and normal systolic function at rest ...
... of active myocardial relaxation and passive ventricular filling. • Condition that includes classic CHF findings and abnormal diastolic and normal systolic function at rest ...
What is the cardiac cycle?
... the heart rate – the number of times the heart beats per minute. A typical value for an adult at rest is 70 bpm. cardiac output = stroke volume × heart rate ...
... the heart rate – the number of times the heart beats per minute. A typical value for an adult at rest is 70 bpm. cardiac output = stroke volume × heart rate ...
Apical Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy: The Ace-of
... mmHg, with a regular heart rate of 63 beats per minute, no superimposed heart sounds or murmurs and no resting dyspnea. The 12-lead electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with a rate of 56 beats per minute, with flattened T waves in the limb leads and a strain pattern (ST segment depression of 1.5-2 ...
... mmHg, with a regular heart rate of 63 beats per minute, no superimposed heart sounds or murmurs and no resting dyspnea. The 12-lead electrocardiogram showed sinus rhythm with a rate of 56 beats per minute, with flattened T waves in the limb leads and a strain pattern (ST segment depression of 1.5-2 ...
Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Explained - New
... If parts of the clot become dislodged they can travel in the bloodstream and become lodged in smaller vessels. The most common place for them to lodge is at the bottom of the aorta, obstructing blood supply to the back legs. This is usually very painful and the back legs become paralysed and cold to ...
... If parts of the clot become dislodged they can travel in the bloodstream and become lodged in smaller vessels. The most common place for them to lodge is at the bottom of the aorta, obstructing blood supply to the back legs. This is usually very painful and the back legs become paralysed and cold to ...
Full Text-1 - African Index Medicus
... identification of HCM remains confined to those patients with a loud heart murmur associated with the outflow gradient. Between June 1998 and October 2002, 134 patients were studied at Hindu Mandal Hospital, 67.9% were male and 32.1% were female. Their mean age was 54.8 + 14.2 years. The presenting ...
... identification of HCM remains confined to those patients with a loud heart murmur associated with the outflow gradient. Between June 1998 and October 2002, 134 patients were studied at Hindu Mandal Hospital, 67.9% were male and 32.1% were female. Their mean age was 54.8 + 14.2 years. The presenting ...
Present and Future trends in Paediatric Cardiology Dr Oliver
... outcome at the lowest morbidity and mortality. The diagnosis of congenital heart disease is shifting towards the antenatal period with routine screening programs being implemented before 20 weeks gestation. Detection rates still vary considerably throughout the UK and Europe. However, in the context ...
... outcome at the lowest morbidity and mortality. The diagnosis of congenital heart disease is shifting towards the antenatal period with routine screening programs being implemented before 20 weeks gestation. Detection rates still vary considerably throughout the UK and Europe. However, in the context ...
Components of S2 - University Health
... • The pressure & its rate of development across the closed semilunar valves – The greater the rate of development of the pressure gradient (rapid ventricular relaxation), the more rapid the velocity of valve vibration and the louder the sound produced ...
... • The pressure & its rate of development across the closed semilunar valves – The greater the rate of development of the pressure gradient (rapid ventricular relaxation), the more rapid the velocity of valve vibration and the louder the sound produced ...
The Structural Heart Disease Program your partners for advanced
... CATH LAB EXPERTS Catheter-based treatment of structural heart disease is rapidly evolving. As technology advances, and new treatment options become available, one thing remains the same: the need for interventionalists, cardiac surgeons, general cardiologists and cardiac imaging specialists to colla ...
... CATH LAB EXPERTS Catheter-based treatment of structural heart disease is rapidly evolving. As technology advances, and new treatment options become available, one thing remains the same: the need for interventionalists, cardiac surgeons, general cardiologists and cardiac imaging specialists to colla ...
Update on Feline Cardiomyopathy: Diagnosis, Treatment and
... Treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is directed at decreasing the heart rate to allow for maximum filling time, decreasing the left ventricular outflow tract gradient if SAM is present, and controlling CHF, if present. The optimal therapy for asymptomatic cats is uncertain. In general, mildly a ...
... Treatment of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is directed at decreasing the heart rate to allow for maximum filling time, decreasing the left ventricular outflow tract gradient if SAM is present, and controlling CHF, if present. The optimal therapy for asymptomatic cats is uncertain. In general, mildly a ...
Echocardiographic Evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function
... Background: Mitral stenosis is frequent valvular complication of rheumatic heart disease, leading to reduced LV filling during diastole, causing diastolic dysfunction. The aim of this study is 2D Echocardiographic Evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function after closed mitral valvotomy in rhe ...
... Background: Mitral stenosis is frequent valvular complication of rheumatic heart disease, leading to reduced LV filling during diastole, causing diastolic dysfunction. The aim of this study is 2D Echocardiographic Evaluation of left ventricular diastolic function after closed mitral valvotomy in rhe ...
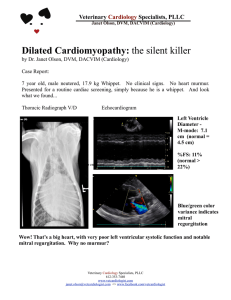
Dilated Cardiomyopathy: the silent killer
... ventricular dilation. As the annulus pulls apart, the mitral valve leaflets can no longer coaptate and create a tight seal when the heart contracts. This allows blood to leak across the valve. So, mitral regurgiation occurs in advanced dilated cardiomyopathy. This is in direct opposition to the mitr ...
... ventricular dilation. As the annulus pulls apart, the mitral valve leaflets can no longer coaptate and create a tight seal when the heart contracts. This allows blood to leak across the valve. So, mitral regurgiation occurs in advanced dilated cardiomyopathy. This is in direct opposition to the mitr ...
Rheumatic heart disease
... • Increased heart rate –decreased transvalvular gradient ----increased LAP • Lv diastolic pressure in normal in ms • Co is normal at rest ---at exercise –decreased ...
... • Increased heart rate –decreased transvalvular gradient ----increased LAP • Lv diastolic pressure in normal in ms • Co is normal at rest ---at exercise –decreased ...
Heart Sounds Worksheet
... Why/when does left atrial pressure and pulmonary pressures increase in response to aortic regurgitation & stenosis? What causes pulmonary edema in the various valvular disorders discussed? ...
... Why/when does left atrial pressure and pulmonary pressures increase in response to aortic regurgitation & stenosis? What causes pulmonary edema in the various valvular disorders discussed? ...
North American Society for Cardiac Imaging 2012
... mutations within sarcomere genes. HCM is characterized histopathologically by myocyte hypertrophy and disarray and interstitial fibrosis. Coronary arteriole dysplasia is also often present. Histological criteria for diagnosis require at least 5-10% of myocytes within the interventricular septum to s ...
... mutations within sarcomere genes. HCM is characterized histopathologically by myocyte hypertrophy and disarray and interstitial fibrosis. Coronary arteriole dysplasia is also often present. Histological criteria for diagnosis require at least 5-10% of myocytes within the interventricular septum to s ...
The Second Heart Sound (S2) Chapter 8
... filling when the atria contract and before the first heart sound • Fourth heart sounds seldom occur in normal hearts • Pathological S4 is a low-frequency, dull or thudding sound resulting from the sudden movement of stiff ventricular wall as they respond to the force delivered through the AV valves ...
... filling when the atria contract and before the first heart sound • Fourth heart sounds seldom occur in normal hearts • Pathological S4 is a low-frequency, dull or thudding sound resulting from the sudden movement of stiff ventricular wall as they respond to the force delivered through the AV valves ...
An usual cardiac manifestation of a very common
... A 69 year old lady presents to the primary percutaneous ...
... A 69 year old lady presents to the primary percutaneous ...
Mechanical Complications of Acute Myocardial Infarction: Review
... infarct frequently require IV inotropic agents (eg, dopamine, dobutamine); however, these agents should be used when volume loading fails. In addition, dobutamine has been shown to be superior to other agents in improving cardiac index and RV ejection fraction.3 An IABP may be useful, but it is not ...
... infarct frequently require IV inotropic agents (eg, dopamine, dobutamine); however, these agents should be used when volume loading fails. In addition, dobutamine has been shown to be superior to other agents in improving cardiac index and RV ejection fraction.3 An IABP may be useful, but it is not ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.

![Cardio Review 4 Quince [CAPT],Joan,Juliet](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008476689_1-582bb2f244943679cde904e2d5670e20-300x300.png)