Skipping the Beat The “Beatless” Heart
... • Blood pushes through each of the heart's four chambers • The pulse or “beat” allows for blood to circulate through the body efficiently Rather than using a “beating” mechanism that would mimic the body’s heart, Dr. Cohn and Dr. Frazier devised a system ...
... • Blood pushes through each of the heart's four chambers • The pulse or “beat” allows for blood to circulate through the body efficiently Rather than using a “beating” mechanism that would mimic the body’s heart, Dr. Cohn and Dr. Frazier devised a system ...
Ethical Scenario - My Surgery Website
... commissioning consortium. Within a few weeks of starting the job you are required to make a high profile budget decision. The local hospital trust has increased it’s spending on 2 significant areas within cardiology – ICD implantation and cardiac ablation. ICD implantation has been proven to prolong ...
... commissioning consortium. Within a few weeks of starting the job you are required to make a high profile budget decision. The local hospital trust has increased it’s spending on 2 significant areas within cardiology – ICD implantation and cardiac ablation. ICD implantation has been proven to prolong ...
Podstawy patofizjologii chorób serca
... Systole – ventricular systole induces increased pressure in the left and right ventricles. Ventricular pressure exceeds atrial pressure, thus closing the tricuspid and mitral valves (first heart sound). Ventricular pressure continues to rise isovolumic ventricular contraction (semilunar valves close ...
... Systole – ventricular systole induces increased pressure in the left and right ventricles. Ventricular pressure exceeds atrial pressure, thus closing the tricuspid and mitral valves (first heart sound). Ventricular pressure continues to rise isovolumic ventricular contraction (semilunar valves close ...
Morte cardiaca improvvisa - Informazioni
... are often few warning signs. More than 95% of sufferers die before they ever reach the hospital. 1 Sudden cardiac death (SCD) claims more than 350,000 lives per year in Europe 2 and it is the predominant risk of death for patients with heart failure. 3 Each additional year, the risk increases for pa ...
... are often few warning signs. More than 95% of sufferers die before they ever reach the hospital. 1 Sudden cardiac death (SCD) claims more than 350,000 lives per year in Europe 2 and it is the predominant risk of death for patients with heart failure. 3 Each additional year, the risk increases for pa ...
Plötzlicher Herztod - Hintergrundinformationen
... are often few warning signs. More than 95% of sufferers die before they ever reach the hospital. 1 Sudden cardiac death (SCD) claims more than 350,000 lives per year in Europe 2 and it is the predominant risk of death for patients with heart failure. 3 Each additional year, the risk increases for pa ...
... are often few warning signs. More than 95% of sufferers die before they ever reach the hospital. 1 Sudden cardiac death (SCD) claims more than 350,000 lives per year in Europe 2 and it is the predominant risk of death for patients with heart failure. 3 Each additional year, the risk increases for pa ...
Protocol of investigation of sudden cardiac death at post
... Third degree of certainty • Coronary artery narrowing • No acute or healed infarct • Did the narrowing cause death? ...
... Third degree of certainty • Coronary artery narrowing • No acute or healed infarct • Did the narrowing cause death? ...
athlete`s heart
... • If an athlete is identified as being at risk for coronary artery disease or if symptoms suggest ischemia, an exercise stress test should be performed. • Stress testing is also recommended in males older than 40 years of age or females older than 50 years of age on the presence of at least two risk ...
... • If an athlete is identified as being at risk for coronary artery disease or if symptoms suggest ischemia, an exercise stress test should be performed. • Stress testing is also recommended in males older than 40 years of age or females older than 50 years of age on the presence of at least two risk ...
summation gallop
... occupying the area of 0.5-2 cm and lasting about 2/3 of systole • Lateral and inferior displacement together with larger area of pulsation indicate left ventricular enlargement or hypertrophy ...
... occupying the area of 0.5-2 cm and lasting about 2/3 of systole • Lateral and inferior displacement together with larger area of pulsation indicate left ventricular enlargement or hypertrophy ...
isovolumic ventricular contraction
... Ventricular Filling phase. • In Reduced Ventricular Filling (diastasis) phase, atrium and ventricle are both fully relaxed. • Arterial pressure continues to fall as blood flows into capillary beds. • This phase typically disappears when HR increases. ...
... Ventricular Filling phase. • In Reduced Ventricular Filling (diastasis) phase, atrium and ventricle are both fully relaxed. • Arterial pressure continues to fall as blood flows into capillary beds. • This phase typically disappears when HR increases. ...
Slide ()
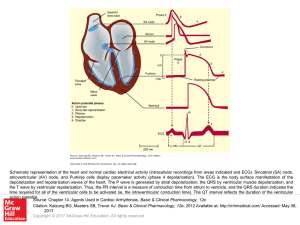
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
... Schematic representation of the heart and normal cardiac electrical activity (intracellular recordings from areas indicated and ECG). Sinoatrial (SA) node, atrioventricular (AV) node, and Purkinje cells display pacemaker activity (phase 4 depolarization). The ECG is the body surface manifestation of ...
a sudden death following cardiomyopathy in a child
... There was no amyloid or iron deposition, granulomas or tissue eosinophilia. The lungs and the liver showed vascular congestion. Other organs were unremarkable. The cause of death was ascertained as acute cardiac failure following cardiomyopathy. DISCUSSION Cardiomyopathy is a clinically heterogeneou ...
... There was no amyloid or iron deposition, granulomas or tissue eosinophilia. The lungs and the liver showed vascular congestion. Other organs were unremarkable. The cause of death was ascertained as acute cardiac failure following cardiomyopathy. DISCUSSION Cardiomyopathy is a clinically heterogeneou ...
Slide 1 - AccessCardiology
... Left. Wide physiologic splitting of the second heart sound (S2) is seen in a patient with complete right bundle-branch block (RBBB). Audible expiratory splitting, which widens normally with inspiration, is present. Note also the wide splitting of the first heart sound into its mitral (M1) and tricus ...
... Left. Wide physiologic splitting of the second heart sound (S2) is seen in a patient with complete right bundle-branch block (RBBB). Audible expiratory splitting, which widens normally with inspiration, is present. Note also the wide splitting of the first heart sound into its mitral (M1) and tricus ...
Is Your Patient HuFfing and PuEFing? (HFPEF)
... dilated left atrium etc. HFPEF is often only finally diagnosed ...
... dilated left atrium etc. HFPEF is often only finally diagnosed ...
Genetic Testing in Cardiomyopathies
... • It is characterized by hypokinetic areas involving the free wall of the right ventricle, with fibrofatty replacement of the right ventricular myocardium, with associated arrhythmias originating in the right ventricle • ARVD is caused by genetic defects of the parts of myocardium known as desmosome ...
... • It is characterized by hypokinetic areas involving the free wall of the right ventricle, with fibrofatty replacement of the right ventricular myocardium, with associated arrhythmias originating in the right ventricle • ARVD is caused by genetic defects of the parts of myocardium known as desmosome ...
ECHOCARDIOGRAPHY IN NORMAL PREGNANCY: THE MAYO
... (L/min) increased from 5.0 to 6.7 to 7.6 (Spearman’s r=0.53, p<0.05) and mitral atrial filling “a” velocity (m/s) rose from 0.4 to 0.56 to 0.7 (Spearman’s r=0.72, p<0.01).There was no statistically significant change in stroke volume, blood pressures, left ventricular ejection fraction, left atrial ...
... (L/min) increased from 5.0 to 6.7 to 7.6 (Spearman’s r=0.53, p<0.05) and mitral atrial filling “a” velocity (m/s) rose from 0.4 to 0.56 to 0.7 (Spearman’s r=0.72, p<0.01).There was no statistically significant change in stroke volume, blood pressures, left ventricular ejection fraction, left atrial ...
Heart Intro
... II. Pericardial Cavity – space between parietal and visceral layers to reduce friction. ...
... II. Pericardial Cavity – space between parietal and visceral layers to reduce friction. ...
Cardiac Failure Protocol
... To confirm the diagnosis of heart failure by electrocardiography where possible. To consider all possible treatment options to improve the quality of life. To promote the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors Identification of target population Cardiac failure is a clinical syndrome ...
... To confirm the diagnosis of heart failure by electrocardiography where possible. To consider all possible treatment options to improve the quality of life. To promote the use of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors Identification of target population Cardiac failure is a clinical syndrome ...
Grade 11 Biology Worksheet -2 ( Circulatory system) a)Give one
... 1) SA node is called the pacemaker of heart. 2) The atrial systole normally precedes the ventricular systole. 3) Ventricle relaxes as a closed chamber in the early phase of its diastole. 4) You can palpate the pulse on an artery in each heart beat. 5) There is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenate ...
... 1) SA node is called the pacemaker of heart. 2) The atrial systole normally precedes the ventricular systole. 3) Ventricle relaxes as a closed chamber in the early phase of its diastole. 4) You can palpate the pulse on an artery in each heart beat. 5) There is no mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenate ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy: A clinical and genetic update
... Copyright © 2013 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. ...
... Copyright © 2013 Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. Unauthorized reproduction of this article is prohibited. ...
Slide ()
... Schematic of cardiac morphogenesis. Oblique views of whole embryo and frontal views of cardiac precursors during human cardiac development are shown. Day 15: First heart field cells form a crescent shape in the anterior embryo with second heart field cells medial to the first heart field. Day 21: Se ...
... Schematic of cardiac morphogenesis. Oblique views of whole embryo and frontal views of cardiac precursors during human cardiac development are shown. Day 15: First heart field cells form a crescent shape in the anterior embryo with second heart field cells medial to the first heart field. Day 21: Se ...
Levosimendan - Wellington ICU
... prospects” Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology, 21:78–84 PY Mindmaps ...
... prospects” Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology, 21:78–84 PY Mindmaps ...
A1982PS35000001
... hypertension, or sedentary habits distinguished the individual prone to sudden death. “Our hypothesis was that the occurrence of ventricular premature beats (VPB5) is associated with sudden death. This was a wild but not illogical conjecture. VPB5 were ubiquitous and demonstrable among nearly 90 per ...
... hypertension, or sedentary habits distinguished the individual prone to sudden death. “Our hypothesis was that the occurrence of ventricular premature beats (VPB5) is associated with sudden death. This was a wild but not illogical conjecture. VPB5 were ubiquitous and demonstrable among nearly 90 per ...
Sudden Cardiac Death - LeadER Animal Specialty Hospital
... Unfortunately, some dogs and cats may experience sudden cardiac death (SCD). This often unexpected event can lead to a lot of unanswered questions and frustration for many grieving pet owners. When a pet is otherwise not apparently ill or obviously exposed to a toxin of some kind, the heart is usual ...
... Unfortunately, some dogs and cats may experience sudden cardiac death (SCD). This often unexpected event can lead to a lot of unanswered questions and frustration for many grieving pet owners. When a pet is otherwise not apparently ill or obviously exposed to a toxin of some kind, the heart is usual ...
Cardiomyopathies
... • Failure of the LV causes an increase in end-diastolic volume, which results in increase in LA, pulmonary venous and pulmonary capillary pressure. Mitral valve regurgitation may result from papillary muscle dysfunction or severe dilatation of the valve annulus. ...
... • Failure of the LV causes an increase in end-diastolic volume, which results in increase in LA, pulmonary venous and pulmonary capillary pressure. Mitral valve regurgitation may result from papillary muscle dysfunction or severe dilatation of the valve annulus. ...
Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy

Hypertrophic cardiomyopathy (HCM) is a primary disease of the myocardium (the muscle of the heart) in which a portion of the myocardium is hypertrophied (thickened) without any obvious cause, creating functional impairment of the cardiac muscle. It is a leading cause of sudden cardiac death in young athletes.The occurrence of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy is a significant cause of sudden unexpected cardiac death in any age group and as a cause of disabling cardiac symptoms. Younger people are likely to have a more severe form of hypertrophic cardiomyopathy.HCM is frequently asymptomatic until sudden cardiac death, and for this reason some suggest routinely screening certain populations for this disease.A cardiomyopathy is a disease that affects the muscle of the heart. With HCM, the myocytes (cardiac contractile cells) in the heart increase in size, which results in the thickening of the heart muscle. In addition, the normal alignment of muscle cells is disrupted, a phenomenon known as myocardial disarray. HCM also causes disruptions of the electrical functions of the heart. HCM is most commonly due to a mutation in one of nine sarcomeric genes that results in a mutated protein in the sarcomere, the primary component of the myocyte (the muscle cell of the heart). These are predominantly single-point missense mutations in the genes for beta-myosin heavy chain (MHC), myosin-binding protein C, cardiac troponinT, or tropomyosin. These mutations cause myofibril and myocyte structural abnormalities and possible deficiencies in force generation. Not to be confused with dilated cardiomyopathy or any other cardiomyopathy.While most literature so far focuses on European, American, and Japanese populations, HCM appears in all ethnic groups. The prevalence of HCM is about 0.2% to 0.5% of the general population.