Ch. 1 Scope of Microbiology
... – the branch of biology that studies microorganisms and their effects on humans. – The study of organisms that are usually too small to be seen with the naked eye- requires a microscope – Includes bacteria, algae, protozoan, fungi, parasitic worms, viruses ...
... – the branch of biology that studies microorganisms and their effects on humans. – The study of organisms that are usually too small to be seen with the naked eye- requires a microscope – Includes bacteria, algae, protozoan, fungi, parasitic worms, viruses ...
the evolution of the cell
... the scene. With a population of increasingly diverse bacterial life, the stage was set for some amazing things to happen. ...
... the scene. With a population of increasingly diverse bacterial life, the stage was set for some amazing things to happen. ...
Document
... The study of organisms too small to be seen individually with the naked eye during part or all of their life cycle. ...
... The study of organisms too small to be seen individually with the naked eye during part or all of their life cycle. ...
METX 119 - UCSC Summer Session
... Ecosystems can be modeled in Winogradsky columns. Many microbes grow as biofilms –aggregated on surfaces in nature and are profoundly affected by nutrient limitations and other adverse factors. Cell-to cell communication can occur within microbial populations in biofilms. Bacteria use chemical signa ...
... Ecosystems can be modeled in Winogradsky columns. Many microbes grow as biofilms –aggregated on surfaces in nature and are profoundly affected by nutrient limitations and other adverse factors. Cell-to cell communication can occur within microbial populations in biofilms. Bacteria use chemical signa ...
Bacteria in your life HW
... 8. The textbook mentions that many bacteria that produce toxins are able to produce thick walls around their cells. What are these called and why is this a helpful adaptation for the bacteria? ...
... 8. The textbook mentions that many bacteria that produce toxins are able to produce thick walls around their cells. What are these called and why is this a helpful adaptation for the bacteria? ...
Tiktaalik
... appendix serves to aid digestion of plant material. • It is still unclear what function, if any, the appendix serves in humans. ...
... appendix serves to aid digestion of plant material. • It is still unclear what function, if any, the appendix serves in humans. ...
Pathogens – Bacteria & Viruses
... Viruses are Obligate Intracellular Parasites Obligate like an obligation – can only replicate inside other cells Must live within a specific host cell – example: cats don’t get chicken pox Use the host cell for replication, metabolism, etc. ...
... Viruses are Obligate Intracellular Parasites Obligate like an obligation – can only replicate inside other cells Must live within a specific host cell – example: cats don’t get chicken pox Use the host cell for replication, metabolism, etc. ...
Small, smaller, smallest
... • Exposure to sick people resulted in disease • Something was being spread (didn’t know what) • Lepers: had to wear a bell and live away from town – People understood immunity • Chinese exposed themselves to mild smallpox virus to build up protection against the often fatal major smallpox virus. ...
... • Exposure to sick people resulted in disease • Something was being spread (didn’t know what) • Lepers: had to wear a bell and live away from town – People understood immunity • Chinese exposed themselves to mild smallpox virus to build up protection against the often fatal major smallpox virus. ...
Anthropogenic factors: loss of predators, changes in habitat
... 5. Importance of Genetic Diversity - Monocultures have more frequent diseases; - Strong selection for diversity - Mixtures of species and genotypes more stable (agriculture, forestry) - Evolution of microbial organisms is rapid - Mortality rate generally higher if transmitted from relative - This m ...
... 5. Importance of Genetic Diversity - Monocultures have more frequent diseases; - Strong selection for diversity - Mixtures of species and genotypes more stable (agriculture, forestry) - Evolution of microbial organisms is rapid - Mortality rate generally higher if transmitted from relative - This m ...
PowerPoint
... • Bacillus thuringiensis produces a toxin (BT toxin) that is toxic to certain types of insect larvae that feed on plants. • Drawback only occur in sporulating cells. • Genes were transferred to Pseudomonas and are produced all the time. • Work is underway to increase the range of these toxins and to ...
... • Bacillus thuringiensis produces a toxin (BT toxin) that is toxic to certain types of insect larvae that feed on plants. • Drawback only occur in sporulating cells. • Genes were transferred to Pseudomonas and are produced all the time. • Work is underway to increase the range of these toxins and to ...
Title - Iowa State University
... o Parasitism: a parasite eats the tissues or fluids of its host, which harms the host Archaea 1. Name the three types of extremophiles, and describe their living conditions/preferences: Halophiles Either tolerate or prefer highly saline environments. ...
... o Parasitism: a parasite eats the tissues or fluids of its host, which harms the host Archaea 1. Name the three types of extremophiles, and describe their living conditions/preferences: Halophiles Either tolerate or prefer highly saline environments. ...
Practice Exam 1
... c. infer the structure of a bacterial cell wall and bacterial response to antibiotics d. count bacteria in medical or environmental samples e. do all of the above 8. Cyanobacteria play what ecological role? a. producers b. consumers c. decomposers d. parasites e. none of the listed choices 9. By mea ...
... c. infer the structure of a bacterial cell wall and bacterial response to antibiotics d. count bacteria in medical or environmental samples e. do all of the above 8. Cyanobacteria play what ecological role? a. producers b. consumers c. decomposers d. parasites e. none of the listed choices 9. By mea ...
Host Defense Against Bacterial Toxins: Mechanisms and Therapies
... Host Defense Against Bacterial Toxins: Mechanisms and Therapies Pore-forming toxins are the largest single class of proteinaceous bacterial toxins produced by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial species. Many pore-forming toxins have been proven to be key virulence factors in major pathog ...
... Host Defense Against Bacterial Toxins: Mechanisms and Therapies Pore-forming toxins are the largest single class of proteinaceous bacterial toxins produced by both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial species. Many pore-forming toxins have been proven to be key virulence factors in major pathog ...
Microbial Biotechnology
... What are some other characteristics of prokaryotes? (no nucleus, cell wall (gram stain), binary fission, 20 minute growth rate, conjugation (transfer of DNA by cytoplasmic bridge), transduction (DNA is packaged in a virus and infects recipient bacterial cells ...
... What are some other characteristics of prokaryotes? (no nucleus, cell wall (gram stain), binary fission, 20 minute growth rate, conjugation (transfer of DNA by cytoplasmic bridge), transduction (DNA is packaged in a virus and infects recipient bacterial cells ...
What Are Microbes?
... visible sometimes only with a microscope. It is too tiny to be seen with the naked eye. Microbes are the oldest form of life on Earth. Some types have existed for billions of years. They may live as individuals or cluster together in communities. Microbes live in the water you drink, the food you ea ...
... visible sometimes only with a microscope. It is too tiny to be seen with the naked eye. Microbes are the oldest form of life on Earth. Some types have existed for billions of years. They may live as individuals or cluster together in communities. Microbes live in the water you drink, the food you ea ...
Gardnerella vaginalis by jonel matheson
... secret spy in that I isolate myself without any signs or symptoms of infection making it very hard for me to be detected. I have a Gram-positive cell wall that is so thin it can appear either Gram-positive or its brother Gram-negative under the key eye of a microscope. My friends are clue cells, whi ...
... secret spy in that I isolate myself without any signs or symptoms of infection making it very hard for me to be detected. I have a Gram-positive cell wall that is so thin it can appear either Gram-positive or its brother Gram-negative under the key eye of a microscope. My friends are clue cells, whi ...
10. Genetic engineering and bacteria
... – Inserting gene for beta-carotene production into rice so that the molecule is present in the edible part of the rice plant. Beta-carotene can be converted into vitamin A in people who eat it. ...
... – Inserting gene for beta-carotene production into rice so that the molecule is present in the edible part of the rice plant. Beta-carotene can be converted into vitamin A in people who eat it. ...
Think big! - Division of Archaea Biology and Ecogenomics
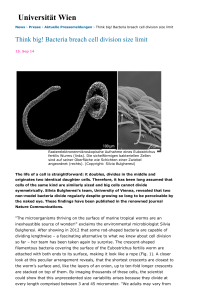
... the scientific paper together with PhD student Nika Pende. But what about the tiny little friends of the closely related E. dianeae worm? Here, the filamentous bacteria are attached to the worm host with only one end, as if to form a fur (Fig. 2). How long can one bacterium, that is a fur hair be? O ...
... the scientific paper together with PhD student Nika Pende. But what about the tiny little friends of the closely related E. dianeae worm? Here, the filamentous bacteria are attached to the worm host with only one end, as if to form a fur (Fig. 2). How long can one bacterium, that is a fur hair be? O ...
Diseases - Ms. Alger
... • The growth of bacterial pathogens disrupts the body’s normal functions • Louis Pasteur (French chemist) was the first person to show that bacteria causes diseases • Established the Germ Theory ...
... • The growth of bacterial pathogens disrupts the body’s normal functions • Louis Pasteur (French chemist) was the first person to show that bacteria causes diseases • Established the Germ Theory ...
Host Tissues May Actively Respond to Beneficial Microbes
... the biochemical and genetic environment of the individual hosts with which they are associated. Such adaptations may not always be beneficial to the host and could contribute to common diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease and periodontitis, conditions that include both human and microbial gen ...
... the biochemical and genetic environment of the individual hosts with which they are associated. Such adaptations may not always be beneficial to the host and could contribute to common diseases such as inflammatory bowel disease and periodontitis, conditions that include both human and microbial gen ...
study outline chart
... tuberculosis, can result in a LATENT INFECTION that can turn deadly in the lungs or other parts of the body. HIV DISEASE and AIDS are usually caused by the human immunodeficiency ...
... tuberculosis, can result in a LATENT INFECTION that can turn deadly in the lungs or other parts of the body. HIV DISEASE and AIDS are usually caused by the human immunodeficiency ...
Introduction to microbial world
... function of the specific protein coded by that gene, and they determined the exact way in which genetic information is translated into a protein. Molecular biology combines aspects of biochemistry, cell biology, and genetics to explain cell function at the molecular level. It is particularly concern ...
... function of the specific protein coded by that gene, and they determined the exact way in which genetic information is translated into a protein. Molecular biology combines aspects of biochemistry, cell biology, and genetics to explain cell function at the molecular level. It is particularly concern ...
Environmental Health for Microbial Agents
... Colonization and the Normal Flora of the Body • Microbes colonize and inhabit the environment as well as humans and other living things. • -So-called "normal flora" colonize the skin, the oral cavity, the gastrointestinal tract, the upper respiratory tract (throat, nasal passages and nasopharynx), a ...
... Colonization and the Normal Flora of the Body • Microbes colonize and inhabit the environment as well as humans and other living things. • -So-called "normal flora" colonize the skin, the oral cavity, the gastrointestinal tract, the upper respiratory tract (throat, nasal passages and nasopharynx), a ...
Human microbiota

The human microbiota is the aggregate of microorganisms, a microbiome that resides on the surface and in deep layers of skin (including in mammary glands), in the saliva and oral mucosa, in the conjunctiva, and in the gastrointestinal tracts. They include bacteria, fungi, and archaea. Micro-animals which live on the human body are excluded. The human microbiome refer to their genomes.One study indicated they outnumber human cells 10 to 1. Some of these organisms perform tasks that are useful for the human host. However, the majority have been too poorly researched for us to understand the role they play, however communities of microflora have been shown to change their behavior in diseased individuals. Those that are expected to be present, and that under normal circumstances do not cause disease, but instead participate in maintaining health, are deemed members of the normal flora. Though widely known as microflora, this is a misnomer in technical terms, since the word root flora pertains to plants, and biota refers to the total collection of organisms in a particular ecosystem. Recently, the more appropriate term microbiota is applied, though its use has not eclipsed the entrenched use and recognition of flora with regard to bacteria and other microorganisms. Both terms are being used in different literature.Studies in 2009 questioned whether the decline in biota (including microfauna) as a result of human intervention might impede human health.Most of the microbes associated with humans appear to be not harmful at all, but rather assist in maintaining processes necessary for a healthy body. A surprising finding was that at specific sites on the body, a different set of microbes may perform the same function for different people. For example, on the tongues of two people, two entirely different sets of organisms will break down sugars in the same way. This suggests that medical science may be forced to abandon the ""one only"" microbe model of infectious disease, and rather pay attention to functions of groups of microbes that have somehow gone awry.