The Greek City
... to ignore the growing power of Macedonia, an oversight that cost the Greeks their freedom. ...
... to ignore the growing power of Macedonia, an oversight that cost the Greeks their freedom. ...
SAC Worksheet - Story, storey, istor
... "Our constitution favors the many instead of the few. This is why it is called a democracy. If we look to the laws, they afford (give) equal justice to all people. Advancement in public life falls to one’s reputation for good work. Social class (whether someone is rich or poor) is not allowed to int ...
... "Our constitution favors the many instead of the few. This is why it is called a democracy. If we look to the laws, they afford (give) equal justice to all people. Advancement in public life falls to one’s reputation for good work. Social class (whether someone is rich or poor) is not allowed to int ...
Athens
... from each of the ten tribes, who served for one year. More important than any other function of the Council was its role in preparing the agenda for meetings of the Assembly, where all Athenian citizens gathered to discuss and vote on decrees. Athens had law courts with trial by jury. The People’s C ...
... from each of the ten tribes, who served for one year. More important than any other function of the Council was its role in preparing the agenda for meetings of the Assembly, where all Athenian citizens gathered to discuss and vote on decrees. Athens had law courts with trial by jury. The People’s C ...
Athenian Democracy - Get Well Kathleen Davey
... very small percentage of the American population gets more politically involved than that.) In comparison, an estimated 40% of Athenian male citizen population was directly involved on a more or less regular basis in Athenian government. Moreover, the system of pay for service allowed the poor to pa ...
... very small percentage of the American population gets more politically involved than that.) In comparison, an estimated 40% of Athenian male citizen population was directly involved on a more or less regular basis in Athenian government. Moreover, the system of pay for service allowed the poor to pa ...
GOVERNMENT OF ANCIENT ATHENS
... They were divided into three structures: The People’s Assembly (Ecclesia), The Council of 500, and The People’s Court. The Ecclesia, who were the central structure of Athenian government, can have all citizens to speak, however, adult male citizens can only participate. 5,000 to 7,000 out of ...
... They were divided into three structures: The People’s Assembly (Ecclesia), The Council of 500, and The People’s Court. The Ecclesia, who were the central structure of Athenian government, can have all citizens to speak, however, adult male citizens can only participate. 5,000 to 7,000 out of ...
Athens` Age of Glory
... If Athenians living in 500 BC could somehow have traveled 65 years into the future, they would have been amazed by what they saw. In the city’s harbor many ships would be tied at a long dock leading straight to a huge trading area. People could buy a wide range of goods, from Egyptian papyrus to Ita ...
... If Athenians living in 500 BC could somehow have traveled 65 years into the future, they would have been amazed by what they saw. In the city’s harbor many ships would be tied at a long dock leading straight to a huge trading area. People could buy a wide range of goods, from Egyptian papyrus to Ita ...
What is the definition of Citizenship: Courtesy of Grolier`s New Book
... provided citizens a greater role in government and reorganized how citizens might participate. To have political power in Athens at that time meant being a landowner. However, there were many people who were wealthier than landowners, like merchants, who could not participate in government. Solon di ...
... provided citizens a greater role in government and reorganized how citizens might participate. To have political power in Athens at that time meant being a landowner. However, there were many people who were wealthier than landowners, like merchants, who could not participate in government. Solon di ...
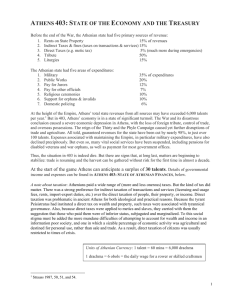
Athens 403: State of Athenian Finances
... With trade beginning to rebound, this amount can be expected to grow 10%+/year for the next few years, more if pro-trade policies are enacted, and much, much more if the Empire can be reestablished: in 413 BCE over 30,000 talents of shipping moved through the Piraeus annually. Taxed at 5%, this prod ...
... With trade beginning to rebound, this amount can be expected to grow 10%+/year for the next few years, more if pro-trade policies are enacted, and much, much more if the Empire can be reestablished: in 413 BCE over 30,000 talents of shipping moved through the Piraeus annually. Taxed at 5%, this prod ...
Athens City
... A. Classical Athens developed the most democratic system of government the world had ever seen, although not everyone could participate in decision making. 1. It became a foundation of modern democracies. B. Early Athens was ruled by a monarchy or king. ...
... A. Classical Athens developed the most democratic system of government the world had ever seen, although not everyone could participate in decision making. 1. It became a foundation of modern democracies. B. Early Athens was ruled by a monarchy or king. ...
warring city-states
... (Draco’s code gave a person accused of murder the right to be tried. The accused have to be proven guilty before being punished)-positive ( He helped to develop a government based on written laws) -positive (His laws were said to be written not in ink but in blood.)- negative ...
... (Draco’s code gave a person accused of murder the right to be tried. The accused have to be proven guilty before being punished)-positive ( He helped to develop a government based on written laws) -positive (His laws were said to be written not in ink but in blood.)- negative ...
DBQ
... implements destroyed as well as growing vines and olive trees . . . In Athens, as many as fifty thousand people had probably died of the plague . . . War casualties seem to have included at least five thousand . . . soldiers and twelve thousand sailors . . . Probably the number of adult male citizen ...
... implements destroyed as well as growing vines and olive trees . . . In Athens, as many as fifty thousand people had probably died of the plague . . . War casualties seem to have included at least five thousand . . . soldiers and twelve thousand sailors . . . Probably the number of adult male citizen ...
Sparta vs. Athens - Franklin County Public Schools
... the military. After the first year, they were given a sword and a shield with the state's emblem on it. Although they served only two years, they could be called at any moment up to age sixty. The army consisted of horsemen and hoplites (footsoldiers.) They were armed with swords, shields, and ext ...
... the military. After the first year, they were given a sword and a shield with the state's emblem on it. Although they served only two years, they could be called at any moment up to age sixty. The army consisted of horsemen and hoplites (footsoldiers.) They were armed with swords, shields, and ext ...
File - Mr. C at Hamilton
... At the same time, Athens greatly increased its own power; a number of its formerly independent allies were reduced, over the course of the century, to the status of tributepaying subject states of the Delian League. This tribute was used to support a powerful fleet and, after the middle of the centu ...
... At the same time, Athens greatly increased its own power; a number of its formerly independent allies were reduced, over the course of the century, to the status of tributepaying subject states of the Delian League. This tribute was used to support a powerful fleet and, after the middle of the centu ...
Citizens of Athens
... equal under the law, laws were written down to prevent the wealthy from manipulating the law against the poor Draco’s Code also set out harsh punishments for crimes, (draconian) and supported the practice of debt slavery (making someone a slave until their debts were paid off) ...
... equal under the law, laws were written down to prevent the wealthy from manipulating the law against the poor Draco’s Code also set out harsh punishments for crimes, (draconian) and supported the practice of debt slavery (making someone a slave until their debts were paid off) ...
APPARTS athens
... from freedom and freedom comes from courage; never decline the dangers of war.” ...
... from freedom and freedom comes from courage; never decline the dangers of war.” ...
Archaic Age - Way of living – polis revolved around market place
... Way of living – polis revolved around market place (agora), which was a centre of trade Acropolis - place of defense in a high position or a hill (most known Athens) Types of government Monarchy – rule by one – total control by king with some of support of counsel Aristocracy – rule by an elit ...
... Way of living – polis revolved around market place (agora), which was a centre of trade Acropolis - place of defense in a high position or a hill (most known Athens) Types of government Monarchy – rule by one – total control by king with some of support of counsel Aristocracy – rule by an elit ...
Athens - Prep World History I
... sold into slavery abroad back to Athens. In addition, he encouraged the development of olive and wine production, so that by the end of the century, most of Athenian land was dedicated to these lucrative crops. The original sense of “tyrant,” from the Greek tyrannos means one who has taken power by ...
... sold into slavery abroad back to Athens. In addition, he encouraged the development of olive and wine production, so that by the end of the century, most of Athenian land was dedicated to these lucrative crops. The original sense of “tyrant,” from the Greek tyrannos means one who has taken power by ...
Ancient Greece PPT
... (city-states) Created because geography prevented it from uniting Population varied: HundredSeveral thousand ...
... (city-states) Created because geography prevented it from uniting Population varied: HundredSeveral thousand ...
File
... commands or in the cavalry commands, for the poor realize that they reap greater benefit by not having these offices in their own hands, but by allowing men of standing to hold them. All those offices, however, whose end is pay and family benefits the poor do seek to hold. Secondly, some people are ...
... commands or in the cavalry commands, for the poor realize that they reap greater benefit by not having these offices in their own hands, but by allowing men of standing to hold them. All those offices, however, whose end is pay and family benefits the poor do seek to hold. Secondly, some people are ...
Liturgy (ancient Greece)
The liturgy (Greek: λειτουργία or λῃτουργία, leitourgia, from λαός / Laos, ""the people"" and the root ἔργο / ergon, ""work"" ) was in ancient Greece a public service established by the city-state whereby its richest members (whether citizens or resident aliens), more or less voluntarily, financed the State with their personal wealth. It took its legitimacy from the idea that ""personal wealth is possessed only through delegation from the city"". The liturgical system dates back to the early days of Athenian democracy, but gradually fell into disuse by the end of the 4th century BC, eclipsed by the development of Euergetism in the Hellenistic period.