March 20 - Axis determination in frog embryos
... formation in embryos from UVirradiated embryos (32-64 cell stage) ...
... formation in embryos from UVirradiated embryos (32-64 cell stage) ...
Congenital Malformation & Hydrocephalus
... destined for the cerebral cortex. Disruption of normal neuronal migration and differentiation during development can lead to a disruption of the normal gyration and six-layered neocortical ...
... destined for the cerebral cortex. Disruption of normal neuronal migration and differentiation during development can lead to a disruption of the normal gyration and six-layered neocortical ...
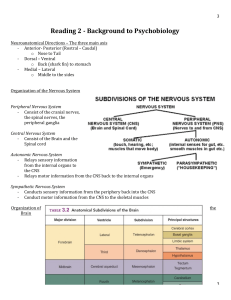
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... o You can think of the brain as many servers that are interconnected (subcortical and cerebral cortex/different areas) o Called white matter because those axons are covered with Myelin - The Lateral Fissure – Separates the temporal lobe - Central Sulcus – Separates the frontal and parietal lob ...
... o You can think of the brain as many servers that are interconnected (subcortical and cerebral cortex/different areas) o Called white matter because those axons are covered with Myelin - The Lateral Fissure – Separates the temporal lobe - Central Sulcus – Separates the frontal and parietal lob ...
Anatomy and Physiology 121: The Nervous System General
... ~ 100,000 presynaptic terminals lie on dendrites of a cell Synaptic Transmission ...
... ~ 100,000 presynaptic terminals lie on dendrites of a cell Synaptic Transmission ...
Drugs Hanson 4
... • Inhibitory synapse diminishes likelihood of an impulse in the receiving neuron or reduces the activity in other target cells. ...
... • Inhibitory synapse diminishes likelihood of an impulse in the receiving neuron or reduces the activity in other target cells. ...
lecture - McLoon Lab - University of Minnesota
... Star-shaped glial cells in the CNS Most abundant cell type of the brain and spinal cord Surround most synaspes Functions of astrocytes: Contribute to the cellular scaffolding Secrete extracellular matrix molecules Provide trophic support for neurons Form external limiting membrane of b ...
... Star-shaped glial cells in the CNS Most abundant cell type of the brain and spinal cord Surround most synaspes Functions of astrocytes: Contribute to the cellular scaffolding Secrete extracellular matrix molecules Provide trophic support for neurons Form external limiting membrane of b ...
Neuron Teacher Key 5-17-16
... 13. What is a synapse? Identify where synapse junctions may occur in the body. A synapse is the junction where a neuron communicates with another cell across a ...
... 13. What is a synapse? Identify where synapse junctions may occur in the body. A synapse is the junction where a neuron communicates with another cell across a ...
COMPUTATIONAL INTELLIGENCE Medical Diagnostic Systems
... The typical neuron of a vertebrate animal can carry time impulses for a considerable distance. The neuron depicted here, with its various parts drawn to scale, is enlarged 250 times. The nerve impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches ...
... The typical neuron of a vertebrate animal can carry time impulses for a considerable distance. The neuron depicted here, with its various parts drawn to scale, is enlarged 250 times. The nerve impulses originate in the cell body, and are propagated along the axon, which may have one or more branches ...
The Emerging Nervous System
... • At four weeks the neural plate folds to form a tube that than becomes the brain and spinal cord • Neurons begin to produce ten weeks after conception • By 28 weeks almost all neurons are produced • Neurons are formed at 4,000 per second ...
... • At four weeks the neural plate folds to form a tube that than becomes the brain and spinal cord • Neurons begin to produce ten weeks after conception • By 28 weeks almost all neurons are produced • Neurons are formed at 4,000 per second ...
Nervous System
... Nerve Impulse- an electrical signal is sent from the dendrite, along the axon, to the terminal. A chemical message, called a neurotransmitter is released from the axon terminals into the synapse, where it travels to the next cell. ...
... Nerve Impulse- an electrical signal is sent from the dendrite, along the axon, to the terminal. A chemical message, called a neurotransmitter is released from the axon terminals into the synapse, where it travels to the next cell. ...
Now!
... b. Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). c. Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. d. Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and functions: — central and peripheral nervous systems; — major brain regions, lo ...
... b. Discuss the influence of drugs on neurotransmitters (e.g., reuptake mechanisms, agonists, antagonists). c. Discuss the effect of the endocrine system on behavior. d. Describe the nervous system and its subdivisions and functions: — central and peripheral nervous systems; — major brain regions, lo ...
Sensory neurons
... Motor Neurons send short pulses which produce a twitch in the body, if these twitches become so fast, they produce smooth movement of the body which is known as Tetanus. Motor Neurons are part of the PNS and are very important in movement, homeostasis and practically every other system in the body f ...
... Motor Neurons send short pulses which produce a twitch in the body, if these twitches become so fast, they produce smooth movement of the body which is known as Tetanus. Motor Neurons are part of the PNS and are very important in movement, homeostasis and practically every other system in the body f ...
Sistemas sensoriales - U
... the posterior parietal cortex. The relationship of S‐I to S‐II and to the posterior parietal cortex is seen best from a lateral perspective of the surface of the cerebral cortex. Bottom: A section shows the four distinct cytoarchitectonic regions of S‐I (Brodmann's areas 3a, 3b, 1, and 2) and th ...
... the posterior parietal cortex. The relationship of S‐I to S‐II and to the posterior parietal cortex is seen best from a lateral perspective of the surface of the cerebral cortex. Bottom: A section shows the four distinct cytoarchitectonic regions of S‐I (Brodmann's areas 3a, 3b, 1, and 2) and th ...
Biology General Knowledge 3 iQuiz
... Nerve cells or neurons that bring messages to muscles are called … ...
... Nerve cells or neurons that bring messages to muscles are called … ...
The Nervous System
... Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” whic ...
... Cells of the Nervous System Neurons/nerve cells: receive stimuli and transmit action potentials (send and receive information) Cell Body: contains the nucleus and two extensions Dendrites: shorter, more numerous, and receives information (Action Potentials) Axons: single, long “fiber” whic ...
Lecture 14 - School of Computing
... molecule that is free to diffuse slowly away from its origin, unhindered by intervening cellular structures. NO secreted by a neuron affects all neurons within range – regardless of circuitry. Such influences go beyond excitation or inhibition. NO has the potential to modulate many aspects of the ne ...
... molecule that is free to diffuse slowly away from its origin, unhindered by intervening cellular structures. NO secreted by a neuron affects all neurons within range – regardless of circuitry. Such influences go beyond excitation or inhibition. NO has the potential to modulate many aspects of the ne ...
File
... CNS (thus, in the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)), or they simply exist within, and contribute to the structure of the CNS itself. -- the action potential (nerve impulse) does NOT diminish in strength as its journey along an axon persists. -- synaptic endings are swellings at the end of an axon. -- ...
... CNS (thus, in the Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)), or they simply exist within, and contribute to the structure of the CNS itself. -- the action potential (nerve impulse) does NOT diminish in strength as its journey along an axon persists. -- synaptic endings are swellings at the end of an axon. -- ...
Other mechanism: MOSAIC development
... – Cells determine fate both by reading their own gene expression, and by reading environmental cues. – Position info in leg and wing must be the same! – Nature often re-uses systems, and genes! ...
... – Cells determine fate both by reading their own gene expression, and by reading environmental cues. – Position info in leg and wing must be the same! – Nature often re-uses systems, and genes! ...
PowerPoint
... gap and attach themselves to SPECIAL RECEPTORS on the membrane of the neuron receiving the impulse. • When the neurotransmitter becomes attached to the cell membrane of the adjacent nerve cell, it changes the permeability of that membrane. • As a result, Na+ ions diffuse through the membrane into th ...
... gap and attach themselves to SPECIAL RECEPTORS on the membrane of the neuron receiving the impulse. • When the neurotransmitter becomes attached to the cell membrane of the adjacent nerve cell, it changes the permeability of that membrane. • As a result, Na+ ions diffuse through the membrane into th ...
Biology 4 Study Guide
... 3. The _______ is a long, thin __________ that makes neurons the _______________ cells in the body. It carries the _______________ __________ away from the cell body, and is what allows signals to be carried ________ _____________. Multiple _______ are bundled together to form “_________”. 4. _____ ...
... 3. The _______ is a long, thin __________ that makes neurons the _______________ cells in the body. It carries the _______________ __________ away from the cell body, and is what allows signals to be carried ________ _____________. Multiple _______ are bundled together to form “_________”. 4. _____ ...