Med Term Chapter 10
... Microglial Cells: as phagocytes protect neurons from inflammation. Oligodendroglial Cells (Oligodendrocytes): form myelin sheath Ependymal Cells: line membranes within the brain and spinal cord where CSF ...
... Microglial Cells: as phagocytes protect neurons from inflammation. Oligodendroglial Cells (Oligodendrocytes): form myelin sheath Ependymal Cells: line membranes within the brain and spinal cord where CSF ...
Developmental Biology 8/e
... gastrulation. (A,B) Human embryo and uterine connections at day 15 of gestation. (A) Sagittal section through the midline. (B) View looking down on the dorsal surface of the embryo. (C) The movements of the epiblast cells through the primitive streak and Hensen’s node and underneath the epiblast are ...
... gastrulation. (A,B) Human embryo and uterine connections at day 15 of gestation. (A) Sagittal section through the midline. (B) View looking down on the dorsal surface of the embryo. (C) The movements of the epiblast cells through the primitive streak and Hensen’s node and underneath the epiblast are ...
Developmental Biology 8/e
... gastrulation. (A,B) Human embryo and uterine connections at day 15 of gestation. (A) Sagittal section through the midline. (B) View looking down on the dorsal surface of the embryo. (C) The movements of the epiblast cells through the primitive streak and Hensen’s node and underneath the epiblast are ...
... gastrulation. (A,B) Human embryo and uterine connections at day 15 of gestation. (A) Sagittal section through the midline. (B) View looking down on the dorsal surface of the embryo. (C) The movements of the epiblast cells through the primitive streak and Hensen’s node and underneath the epiblast are ...
Central Nervous System - Home Page of Ken Jones
... A nerve fiber with thorn like spines that conducts an impulse towards the cell body Substance of Schwann cell composed of lipoprotein Transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within CNS Unmyelinated axon between Schwann cells on neurons of the peripheral nervous system Transmits impulse into b ...
... A nerve fiber with thorn like spines that conducts an impulse towards the cell body Substance of Schwann cell composed of lipoprotein Transmits impulse from sensory to motor neuron within CNS Unmyelinated axon between Schwann cells on neurons of the peripheral nervous system Transmits impulse into b ...
Module 3:Neural conduction and transmission Lecture 13
... signals from other neurons. Axon is the extension carrying signals from cell body to the terminal buttons at the end of the neurons. These terminal buttons contain neurotransmitters which plays important role in conduction at synapse. Synapse is the junction where one neuron ends and the other begin ...
... signals from other neurons. Axon is the extension carrying signals from cell body to the terminal buttons at the end of the neurons. These terminal buttons contain neurotransmitters which plays important role in conduction at synapse. Synapse is the junction where one neuron ends and the other begin ...
NeuroReview1
... Dorsal root axons are sensory unipolar neurons, with their cell bodies grouped just outside the spinal cord forming the dorsal root ganglion. Synaptic terminals are in dorsal horn. Ventral Root Neurons are motor (efferent) multipolar neurons with their cell bodies in the ventral horn. ...
... Dorsal root axons are sensory unipolar neurons, with their cell bodies grouped just outside the spinal cord forming the dorsal root ganglion. Synaptic terminals are in dorsal horn. Ventral Root Neurons are motor (efferent) multipolar neurons with their cell bodies in the ventral horn. ...
Slide ()
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
... The corticospinal and bulbospinal upper motor neuron pathways. Upper motor neurons have their cell bodies in layer V of the primary motor cortex (the precentral gyrus, or Brodmann’s area 4) and in the premotor and supplemental motor cortex (area 6). The upper motor neurons in the primary motor corte ...
Slide 1 - MisterSyracuse.com
... Name _________________________________________ Date ___________________ Period _________ Directions: This test is designed to let your teacher know how much information you have learned over the past few weeks, and to allow you to gauge this as well. Remember to think about your notes and all the e ...
... Name _________________________________________ Date ___________________ Period _________ Directions: This test is designed to let your teacher know how much information you have learned over the past few weeks, and to allow you to gauge this as well. Remember to think about your notes and all the e ...
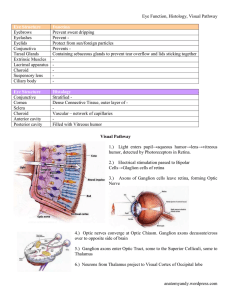
Eye Structure - WordPress.com
... Prevents Containing sebaceous glands to prevent tear overflow and lids sticking together ...
... Prevents Containing sebaceous glands to prevent tear overflow and lids sticking together ...
chapt12 neuron_lecture
... – receptors detect changes in body and external environment – this information is transmitted into brain or spinal cord ...
... – receptors detect changes in body and external environment – this information is transmitted into brain or spinal cord ...
circumference of the egg and is, at first, quite broad. It is
... becomes dilated at its distal end. The dilated end or bulb remains connected with the brain by a stalk. \Vhite particles develop in the bulb, so that it stands out in strong contrast to the dark sUlface of the brain. ...
... becomes dilated at its distal end. The dilated end or bulb remains connected with the brain by a stalk. \Vhite particles develop in the bulb, so that it stands out in strong contrast to the dark sUlface of the brain. ...
Unit III Modules 9 to 13 Test Review
... does not cross the blood-brain barrier), • Thus, a victim of curare poisoning may be aware of what is happening until the very end. • The victim can feel the paralysis progressing but is quickly unable to move, call out or gesture. • If artificial respiration is performed throughout, the victim usua ...
... does not cross the blood-brain barrier), • Thus, a victim of curare poisoning may be aware of what is happening until the very end. • The victim can feel the paralysis progressing but is quickly unable to move, call out or gesture. • If artificial respiration is performed throughout, the victim usua ...
Lecture 12 - Fundamentals of the Nervous System
... Can live for a lifetime (i.e. over 100 years) Do not divide (exception: recent neural stem cells identified) Cannot replace themselves ...
... Can live for a lifetime (i.e. over 100 years) Do not divide (exception: recent neural stem cells identified) Cannot replace themselves ...
4/7
... Neurons are commonly connected to many other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron will do. ...
... Neurons are commonly connected to many other neurons, and the effect of the different incoming signals determines what the neuron will do. ...
Axis formation in Amphibians
... tissue to change fate and form neural tube and dorsal mesodermal tissue (somites) • Can establish a second dorsalventral axis ...
... tissue to change fate and form neural tube and dorsal mesodermal tissue (somites) • Can establish a second dorsalventral axis ...
Bioenergetics - Eastern Michigan University
... Action potential – Occurs when depolarization reaches threshold • Permeability of the membrane changes, allowing Na+ into the cell, making the interior positively ...
... Action potential – Occurs when depolarization reaches threshold • Permeability of the membrane changes, allowing Na+ into the cell, making the interior positively ...
Topic Presentation: Biopsychology
... ii. Different neurotransmitters have different effects iii. Changes in amounts of neurotransmitters can affect our mood, memories, mental abilities, hunger, and more iv. Boosting or diminishing the effects of neurotransmitters 1. Diet 2. Drugs a. Psychoactive drugs cross the blood brain barrier inte ...
... ii. Different neurotransmitters have different effects iii. Changes in amounts of neurotransmitters can affect our mood, memories, mental abilities, hunger, and more iv. Boosting or diminishing the effects of neurotransmitters 1. Diet 2. Drugs a. Psychoactive drugs cross the blood brain barrier inte ...
Ray pavloski
... In spite of its increasing prominence as the focus of both empirical and theoretical investigations, the coexistence of private perceptual experience and familiar objective measures of neural processes has no generally accepted explanation. It is argued that three properties of a perceptual gestalt ...
... In spite of its increasing prominence as the focus of both empirical and theoretical investigations, the coexistence of private perceptual experience and familiar objective measures of neural processes has no generally accepted explanation. It is argued that three properties of a perceptual gestalt ...
The Nervous System: Neural Tissue
... • Anterior, posterior white columns (funiculi) • Anterior white commissure • Lateral white columns ...
... • Anterior, posterior white columns (funiculi) • Anterior white commissure • Lateral white columns ...
Nervous from Cyber
... are called post-synaptic cells. There are two types of synapses: electrical and chemical. An electrical synapse allows the signal to spread directly from the pre-synaptic to the post-synaptic cells. Chemical synapses allows for cells that so not have an electrical connection to spread their messages ...
... are called post-synaptic cells. There are two types of synapses: electrical and chemical. An electrical synapse allows the signal to spread directly from the pre-synaptic to the post-synaptic cells. Chemical synapses allows for cells that so not have an electrical connection to spread their messages ...
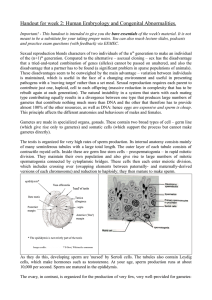
Handout for week 2: Human Embryology and Congenital
... The neural tube, future spinal cord and brain, develops by invagination of the ectoderm, driven by local cell shape changes. The valley produced narrows until its edges meet. An exchange of cell neighbours results in the neural tube dropping free into the embryo and the ectoderm closing over behind ...
... The neural tube, future spinal cord and brain, develops by invagination of the ectoderm, driven by local cell shape changes. The valley produced narrows until its edges meet. An exchange of cell neighbours results in the neural tube dropping free into the embryo and the ectoderm closing over behind ...