Nervous System
... • Constantly interacts with the central nervous system via 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves • Nerves are the bundles axons and dendrites of many neurons • Each spinal nerve has a dorsal root and a ...
... • Constantly interacts with the central nervous system via 12 pairs of cranial nerves and 31 pairs of spinal nerves • Nerves are the bundles axons and dendrites of many neurons • Each spinal nerve has a dorsal root and a ...
Slide - Reza Shadmehr
... How old are the cells in a person’s brain? Carbon dating of DNA The levels of 14C in the atmosphere have been stable over long time periods, with the exception of a large addition of 14C in 1955–1963 as a result of above ground nuclear bomb tests. 14C levels from modern samples are by convention gi ...
... How old are the cells in a person’s brain? Carbon dating of DNA The levels of 14C in the atmosphere have been stable over long time periods, with the exception of a large addition of 14C in 1955–1963 as a result of above ground nuclear bomb tests. 14C levels from modern samples are by convention gi ...
chapt12-nervous system
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. The Synapse Transmission of the nerve ...
... The action potential occurs in each successive portion of an axon. A refractory period ensures that the action potential will not move backwards. In myelinated fibers the action potential only occurs at the nodes of Ranvier. This is called saltatory conduction. The Synapse Transmission of the nerve ...
Neural Anatomy and Images
... npc: nucleus of the posterior commissure npoc: nucleus of the post-optic commissure oc: optic chiasma on: optic nerve pc: posterior commissure poc: post-optic commissure r: rhombomere rb: Rohon-Beard neurons sm: stria medullaris (habenular afferents) sma: spinal motor axons sot: supra-optic tract so ...
... npc: nucleus of the posterior commissure npoc: nucleus of the post-optic commissure oc: optic chiasma on: optic nerve pc: posterior commissure poc: post-optic commissure r: rhombomere rb: Rohon-Beard neurons sm: stria medullaris (habenular afferents) sma: spinal motor axons sot: supra-optic tract so ...
Brain Matters - FirstClass Login
... are released from one neuron at the pre-synaptic nerve terminal. Neurotransmitters then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor. ...
... are released from one neuron at the pre-synaptic nerve terminal. Neurotransmitters then cross the synapse where they may be accepted by the next neuron at a specialized site called a receptor. ...
The Anterolateral System
... reside in the dorsal root ganglia and the trigeminal complex. • This pathway receives input from thermoreceptors, nociceptors, and mechanoreceptors. ...
... reside in the dorsal root ganglia and the trigeminal complex. • This pathway receives input from thermoreceptors, nociceptors, and mechanoreceptors. ...
Neurons and Glia Three basic neurons: ∼ Multipolar: Neurons by
... ∼ Oligodendrocytes ◊ Myelination in CNS ◊ Growth-inhibitory factors ◊ May play a role in ion/neurotransmitter balance in extracellular space ∼ Ependyma: lining of ventricles ∼ Microglia ◊ Activated microglia express a Oligodendryocytes vs. Schwann Cells number of immune-related - CNS - PNS molecules ...
... ∼ Oligodendrocytes ◊ Myelination in CNS ◊ Growth-inhibitory factors ◊ May play a role in ion/neurotransmitter balance in extracellular space ∼ Ependyma: lining of ventricles ∼ Microglia ◊ Activated microglia express a Oligodendryocytes vs. Schwann Cells number of immune-related - CNS - PNS molecules ...
Sending Signals Notes
... • DEPOLARIZED = Inside the membrane becomes more positive than outside. • This causes a THRESHOLD to be REACHED and an impulse (ACTION POTENTIAL) begins in the second cell. • After the neurotransmitter relays it message it is rapidly REMOVED or DESTROYED, thus halting its effect. • The molecules of ...
... • DEPOLARIZED = Inside the membrane becomes more positive than outside. • This causes a THRESHOLD to be REACHED and an impulse (ACTION POTENTIAL) begins in the second cell. • After the neurotransmitter relays it message it is rapidly REMOVED or DESTROYED, thus halting its effect. • The molecules of ...
36.1 The Nervous System Neurons: Basic units of
... Change in this charge moves the impulse down axon. ...
... Change in this charge moves the impulse down axon. ...
Nonlinear Behavior of Neocortical Networks
... Examination of nonlinear components of network activity may provide a powerful link between the understanding of single neuron behavior and the power of the brain as a whole. Determining how the brain establishes and maintains activity states that allow information processing to occur and the role o ...
... Examination of nonlinear components of network activity may provide a powerful link between the understanding of single neuron behavior and the power of the brain as a whole. Determining how the brain establishes and maintains activity states that allow information processing to occur and the role o ...
Unit 8 Review Sheet[1]
... Unit 8 Review Sheet – Sensation and Perception General Terms Sensation: the process by which you detect physical energy from your environment and encode it as neural signals. Perception: the process that organizes sensory input and makes it meaningful. Psychophysics: the study of the relationship be ...
... Unit 8 Review Sheet – Sensation and Perception General Terms Sensation: the process by which you detect physical energy from your environment and encode it as neural signals. Perception: the process that organizes sensory input and makes it meaningful. Psychophysics: the study of the relationship be ...
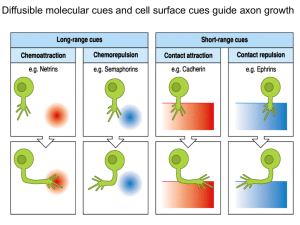
Lecture 18 – Molecular Mechanisms of Neural Induction. 1. During
... 1. During development, embryonic cells signal to each other with secreted diffusible molecules that instruct neighboring cells to change their pattern of gene expression. This signaling event is termed induction. Because the signaling molecule instructs the developmental fate of the recipient cell, ...
... 1. During development, embryonic cells signal to each other with secreted diffusible molecules that instruct neighboring cells to change their pattern of gene expression. This signaling event is termed induction. Because the signaling molecule instructs the developmental fate of the recipient cell, ...
File
... current exceeds the threshold, a neuron will fire. If the depolarizing current fails to exceed the threshold, a neuron will not fire. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...
... current exceeds the threshold, a neuron will fire. If the depolarizing current fails to exceed the threshold, a neuron will not fire. Intensity of an action potential remains the same throughout the length of the axon. ...



















![Unit 8 Review Sheet[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001686639_1-accaddf9a4bef8f1f5e508cc8efafb82-300x300.png)