Tutorial 4: Shapes and Roles of Glial Cells Figure 4: Shapes and
... Receptor sites for neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA have been identified on both astrocytes and Schwann cells. The functional significance of these receptors remains a mystery, but there is some speculation that these receptors allow for identification of neighboring neurons. This identi ...
... Receptor sites for neurotransmitters such as glutamate and GABA have been identified on both astrocytes and Schwann cells. The functional significance of these receptors remains a mystery, but there is some speculation that these receptors allow for identification of neighboring neurons. This identi ...
Ch 48 Nervous System
... – Axons- away from cell body. Long, Myelin sheath- supporting, insulating layer produced by Schwann Cells Schwann cells-PNS support cells; surround axons Axon hillock-Hillock-axon extends from here Synaptic terminals~ neurotransmitter releaser ...
... – Axons- away from cell body. Long, Myelin sheath- supporting, insulating layer produced by Schwann Cells Schwann cells-PNS support cells; surround axons Axon hillock-Hillock-axon extends from here Synaptic terminals~ neurotransmitter releaser ...
Slide ()
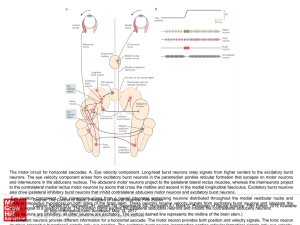
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
... The motor circuit for horizontal saccades. A. Eye velocity component. Long-lead burst neurons relay signals from higher centers to the excitatory burst neurons. The eye velocity component arises from excitatory burst neurons in the paramedian pontine reticular formation that synapse on motor neurons ...
Slide
... 1. Controlled by an interaction between landmarks and idiothetic cues 2. Role of visual landmark (important but not required) 1. rotation of the landmarks -- > an equal rotation of the firing location/ direction of the place cells or head direction cells 2. maintain their location/ direction tuning ...
... 1. Controlled by an interaction between landmarks and idiothetic cues 2. Role of visual landmark (important but not required) 1. rotation of the landmarks -- > an equal rotation of the firing location/ direction of the place cells or head direction cells 2. maintain their location/ direction tuning ...
Slide ()
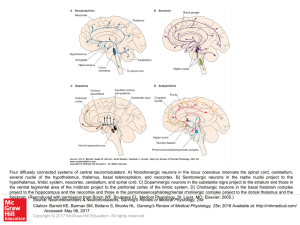
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
... Four diffusely connected systems of central neuromodulators. A) Noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus innervate the spinal cord, cerebellum, several nuclei of the hypothalamus, thalamus, basal telencephalon, and neocortex. B) Serotonergic neurons in the raphe nuclei project to the hypothalamu ...
Modeling the brain
... Neurons are created (under genetic control). Neurons grow axons which are directed towards other neurons (sometimes very long distances; under genetic and ...
... Neurons are created (under genetic control). Neurons grow axons which are directed towards other neurons (sometimes very long distances; under genetic and ...
Nervous System Notes File
... Nervous tissue contains masses of nerve cells called neurons. Specialized to react to physical and chemical changes. Transmit info in the form of electrochemical changes called nerve impulses. Bundles of axons make nerves. Also contains neuroglial cells that provide physical support, ...
... Nervous tissue contains masses of nerve cells called neurons. Specialized to react to physical and chemical changes. Transmit info in the form of electrochemical changes called nerve impulses. Bundles of axons make nerves. Also contains neuroglial cells that provide physical support, ...
2 Guided Notes for PPT 7, Hearing and Sight
... Sensory fibers begin at the bases of the hair cells in the cochlea. Cell bodies form the __________________________ Axons lead away from the cochlea as the ______________________________________________________ This cochlea nerve joins with the ________________________________________________to form ...
... Sensory fibers begin at the bases of the hair cells in the cochlea. Cell bodies form the __________________________ Axons lead away from the cochlea as the ______________________________________________________ This cochlea nerve joins with the ________________________________________________to form ...
The Nervous System
... Functional Unit of the Nervous System—The NEURON Cell body—contains nucleus & organelles Dendrites—short, highly branched processes (extensions) that receive incoming messages from other cells Axons—usually much longer than dendrites, convey outgoing messages from neurons to other cells ...
... Functional Unit of the Nervous System—The NEURON Cell body—contains nucleus & organelles Dendrites—short, highly branched processes (extensions) that receive incoming messages from other cells Axons—usually much longer than dendrites, convey outgoing messages from neurons to other cells ...
Lab 8: Muscle and Nervous Tissue
... images for the microscope work. Go to the HistoWeb Nerve site. (link from “Project Info” on PhysioWeb) 4. Obtain a prepared slide of spinal cord smear. Using low power magnification, search the slide and locate the large, deeply stained cell bodies of motor neurons (multipolar neurons) ...
... images for the microscope work. Go to the HistoWeb Nerve site. (link from “Project Info” on PhysioWeb) 4. Obtain a prepared slide of spinal cord smear. Using low power magnification, search the slide and locate the large, deeply stained cell bodies of motor neurons (multipolar neurons) ...
Exam - McLoon Lab
... C. A strand of mRNA is read by a ribosome and used to determine the sequence in which amino acids are linked together. D. A strand of mRNA is read by a ribosome and used to determine the sequence in which nucleotides are linked together. E. A strand of protein is read by a ribosome and used to deter ...
... C. A strand of mRNA is read by a ribosome and used to determine the sequence in which amino acids are linked together. D. A strand of mRNA is read by a ribosome and used to determine the sequence in which nucleotides are linked together. E. A strand of protein is read by a ribosome and used to deter ...
File
... mesenchymal cells. Mesenchymal cells are able to migrate as individual cells if provided with the proper extracellular environment, and then, differentiate into diverse tissue types. Most mesenchymal cells are from the mesodermal layer, forming primitive connective tissue, muscle, bone, and blood ve ...
... mesenchymal cells. Mesenchymal cells are able to migrate as individual cells if provided with the proper extracellular environment, and then, differentiate into diverse tissue types. Most mesenchymal cells are from the mesodermal layer, forming primitive connective tissue, muscle, bone, and blood ve ...
Spinal Cord
... Soma in ganglion of dorsal root or cranial nerve Synapse with 2nd order neuron 2nd order neurons Soma in dorsal horn or medullary nuclei Extend axons to thalamus or ...
... Soma in ganglion of dorsal root or cranial nerve Synapse with 2nd order neuron 2nd order neurons Soma in dorsal horn or medullary nuclei Extend axons to thalamus or ...
Stereological estimates of neuronal loss in the primary motor cortex
... clinical and pathological diagnosis of MS, evidence suggests mechanisms other than ID may play an important role for the deterioration of function in people with progressive MS (pwPMS) (Trapp & Nave. Annu Rev Neurosci 2008; Kolasinski, et al. Brain 2012). Impaired motor function is one of the most i ...
... clinical and pathological diagnosis of MS, evidence suggests mechanisms other than ID may play an important role for the deterioration of function in people with progressive MS (pwPMS) (Trapp & Nave. Annu Rev Neurosci 2008; Kolasinski, et al. Brain 2012). Impaired motor function is one of the most i ...
Nervous_System_PowerPoint
... Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord White matter: propagates sensory impulses from the periphery to the brain and motor impulses from the brain to the periphery Gray matter: receives and integrates incoming and outgoing info ...
... Internal Anatomy of the Spinal Cord White matter: propagates sensory impulses from the periphery to the brain and motor impulses from the brain to the periphery Gray matter: receives and integrates incoming and outgoing info ...
Social Brains: EEG Hyperconnectivity between operetor pairs whilst actively performing demanding interdependent goal-oriented tasks
... Functional neuroimaging has been a major tool for cognitive neuroscience, experimental psychology, and psychiatry. Noninvasive high-resolution imaging would provide tremendous benefits to better understanding of the brain mechanisms behind mental processes, such as perception, attention, learning, e ...
... Functional neuroimaging has been a major tool for cognitive neuroscience, experimental psychology, and psychiatry. Noninvasive high-resolution imaging would provide tremendous benefits to better understanding of the brain mechanisms behind mental processes, such as perception, attention, learning, e ...
The Nervous System - OCPS TeacherPress
... Charge (polarity) changes – depolarization. A situation called a graded potential (inside more positive) ...
... Charge (polarity) changes – depolarization. A situation called a graded potential (inside more positive) ...
1 NOTES – CHAPTER 9 (Brief) The Nervous System – LECTURE
... a) effectors include muscles or glands 2) Efferent fibers/neurons – nerve fibers that transmit action potentials from the CNS toward the periphery 3) Two subdivisions of Efferent division: a) Somatic Motor Nervous System – transmits impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles b) Autonomic Nervous System ( ...
... a) effectors include muscles or glands 2) Efferent fibers/neurons – nerve fibers that transmit action potentials from the CNS toward the periphery 3) Two subdivisions of Efferent division: a) Somatic Motor Nervous System – transmits impulses from CNS to skeletal muscles b) Autonomic Nervous System ( ...
Nervous System - Downey Unified School District
... PSEUDOUNIPOLAR NEURONS • PSUEDOUNIPOLAR NEURONS IS A SENSORY NEURON IN THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. THE TWO PROCESSES FORM A SINGLE PROCESS. ONE BRANCH IS STRUCTURALLY AN AXON, HOWEVER, FUNCTIONS AS A DENDRITE. • AFFERENT CONDUCTION ORIGINIATING IN A NERVE ENDING. ...
... PSEUDOUNIPOLAR NEURONS • PSUEDOUNIPOLAR NEURONS IS A SENSORY NEURON IN THE PERIPHERAL NERVOUS SYSTEM. THE TWO PROCESSES FORM A SINGLE PROCESS. ONE BRANCH IS STRUCTURALLY AN AXON, HOWEVER, FUNCTIONS AS A DENDRITE. • AFFERENT CONDUCTION ORIGINIATING IN A NERVE ENDING. ...