Single nucleotide polymorphism in the neuroplastin locus
... left and right cerebral hemispheres, neuroimaging measures included cortical thickness for 33 individual regions per hemisphere. These were combined to produce weighted average thickness (weighted for surface at each region) for the four cerebral lobes (that is, frontal, temporal, parietal and occip ...
... left and right cerebral hemispheres, neuroimaging measures included cortical thickness for 33 individual regions per hemisphere. These were combined to produce weighted average thickness (weighted for surface at each region) for the four cerebral lobes (that is, frontal, temporal, parietal and occip ...
Disruption of Target Interactions Prevents the Development of
... like Enk8, are derived from proenkephalin A. With immunocytochemistry, radioimmunoassay, and in situ hybridization, we found a large, transient increase in Enk-IR in the caudal part of the SCG postnatally. The acquisition of Enk-IR and proenkephalin A mRNA could be influenced by a variety of signals ...
... like Enk8, are derived from proenkephalin A. With immunocytochemistry, radioimmunoassay, and in situ hybridization, we found a large, transient increase in Enk-IR in the caudal part of the SCG postnatally. The acquisition of Enk-IR and proenkephalin A mRNA could be influenced by a variety of signals ...
On the Growth in Length of the Prog Embryo.
... blastopore, the embryo grows in length by the proliferation of cells at the spot which formerly formed part of the lips of the blastopore. There is very little doubt that rapid growth at this spot takes place before the final closure of the blastopore ; the question is, when does this growth begin ? ...
... blastopore, the embryo grows in length by the proliferation of cells at the spot which formerly formed part of the lips of the blastopore. There is very little doubt that rapid growth at this spot takes place before the final closure of the blastopore ; the question is, when does this growth begin ? ...
Central Topography of Cranial Motor Nuclei Controlled by
... neurons and are located in highly stereotyped positions. Establishment of this CNS topography is critical to neural circuit assembly. However, little is known of either the cellular or molecular mechanisms that drive nucleus formation during development, a process termed nucleogenesis [2–5]. Brainst ...
... neurons and are located in highly stereotyped positions. Establishment of this CNS topography is critical to neural circuit assembly. However, little is known of either the cellular or molecular mechanisms that drive nucleus formation during development, a process termed nucleogenesis [2–5]. Brainst ...
Zoology 242 Anatomy of Nervous systems Lecture 8
... • Parasympathetic ganglia are located close to or within the organ being controlled. • Sympathetic and parasympathetic are generally antagonistic of each other. Zoology 242 - Lecture 8 ...
... • Parasympathetic ganglia are located close to or within the organ being controlled. • Sympathetic and parasympathetic are generally antagonistic of each other. Zoology 242 - Lecture 8 ...
Cortical interactions underlying the production of speech sounds
... synaptic projections between the sensory error maps and the model’s motor cortex. The learning in this stage is not phoneme- or syllable-specific; rather, the learned sensory– motor transformations will be used for all speech sounds that will be learned later. In the next learning stage, the model i ...
... synaptic projections between the sensory error maps and the model’s motor cortex. The learning in this stage is not phoneme- or syllable-specific; rather, the learned sensory– motor transformations will be used for all speech sounds that will be learned later. In the next learning stage, the model i ...
Emo7onal decision‐making systems and their role in addic7on
... known to have short‐term “reinforcing effects” (but long‐term negative consequences) should be less likely or problematic for individuals scoring higher on tasks that assess this ability. ...
... known to have short‐term “reinforcing effects” (but long‐term negative consequences) should be less likely or problematic for individuals scoring higher on tasks that assess this ability. ...
Lecture VIII. Spinal Cord
... weren’t inhibited to extend the other (contralateral) leg to stand on. ...
... weren’t inhibited to extend the other (contralateral) leg to stand on. ...
Nonlinear brain dynamics as macroscopic manifestation of
... long-range correlation, with the requirement for synaptic renewal at each successive relay. Even the presence of relatively sparse long axons, which provide for high velocity jumps to seed areas over long distances creating small-world effects (Watts and Strogatz, 1998; Kozma et al., 2005), cannot e ...
... long-range correlation, with the requirement for synaptic renewal at each successive relay. Even the presence of relatively sparse long axons, which provide for high velocity jumps to seed areas over long distances creating small-world effects (Watts and Strogatz, 1998; Kozma et al., 2005), cannot e ...
2015 Cosyne Program
... community. Our researchers and computational scientists engage in a wide variety of exciting and technically challenging projects—including exploring applications of systems neuroscience research to machine learning, to enable "smarter" and more efficient computing devices. We help you work smarter, ...
... community. Our researchers and computational scientists engage in a wide variety of exciting and technically challenging projects—including exploring applications of systems neuroscience research to machine learning, to enable "smarter" and more efficient computing devices. We help you work smarter, ...
Localization of Ca2+ Channel Subtypes on Rat Spinal Motor
... anti-C NA1 (diluted 1:15), anti-C NA5 (diluted 1:25), anti-C NA6 (diluted 1:25), anti-C N B2 (diluted 1:15), anti-C NC1 (diluted 1:15), anti-C N D1 (diluted 1:15), anti-C N E2 (diluted 1:15), or anti-synaptotagmin (diluted 1:200) for 36 hr at 4°C. All antibodies were diluted in a solution containing ...
... anti-C NA1 (diluted 1:15), anti-C NA5 (diluted 1:25), anti-C NA6 (diluted 1:25), anti-C N B2 (diluted 1:15), anti-C NC1 (diluted 1:15), anti-C N D1 (diluted 1:15), anti-C N E2 (diluted 1:15), or anti-synaptotagmin (diluted 1:200) for 36 hr at 4°C. All antibodies were diluted in a solution containing ...
Long Term Potentiation
... established (i.e. learned or remembered), may last for a very long time, so, based on our assumptions of a neurological-behavior relationship, there should be some sort of semipermanent changes at the level of the nervous system. In fact, researchers know that, while NMDA receptors are very importan ...
... established (i.e. learned or remembered), may last for a very long time, so, based on our assumptions of a neurological-behavior relationship, there should be some sort of semipermanent changes at the level of the nervous system. In fact, researchers know that, while NMDA receptors are very importan ...
Chapter 29 *Lecture PowerPoint Human Development
... • Gastrulation—multiplying epiblast cells migrate medially toward the primitive groove and down into it – Replace the original hypoblast with a layer called endoderm ...
... • Gastrulation—multiplying epiblast cells migrate medially toward the primitive groove and down into it – Replace the original hypoblast with a layer called endoderm ...
Chapter 29
... • Gastrulation—multiplying epiblast cells migrate medially toward the primitive groove and down into it – Replace the original hypoblast with a layer called endoderm ...
... • Gastrulation—multiplying epiblast cells migrate medially toward the primitive groove and down into it – Replace the original hypoblast with a layer called endoderm ...
Electrical stimulation of neural tissue to evoke behavioral responses
... This review yields numerous conclusions. (1) Both unit recording and behavioral studies find that current activates neurons (i.e., cell bodies and axons) directly according to the square of the distance between the electrode and the neuron, and that the excitability of neurons can vary between 100 a ...
... This review yields numerous conclusions. (1) Both unit recording and behavioral studies find that current activates neurons (i.e., cell bodies and axons) directly according to the square of the distance between the electrode and the neuron, and that the excitability of neurons can vary between 100 a ...
Dopamine`s Actions in Primate Prefrontal Cortex
... association memories that arise from sequence repetitions. In these more classic forms of plasticity, experiences are stored as architectural changes in synapses, e.g., with the formation of new spines or structural changes in existing immature spines, as documented in the sensory cortices, hippocam ...
... association memories that arise from sequence repetitions. In these more classic forms of plasticity, experiences are stored as architectural changes in synapses, e.g., with the formation of new spines or structural changes in existing immature spines, as documented in the sensory cortices, hippocam ...
Clustered Organization of Neurons with Similar Extra
... five different penetrations. The summation indices of all neurons recorded were shown (Figure 3, left panels), together with histological reconstruction of the electrode track through the cortical layers (Figure 3, right panels). Regardless of whether the penetration was tangential, oblique, or norm ...
... five different penetrations. The summation indices of all neurons recorded were shown (Figure 3, left panels), together with histological reconstruction of the electrode track through the cortical layers (Figure 3, right panels). Regardless of whether the penetration was tangential, oblique, or norm ...
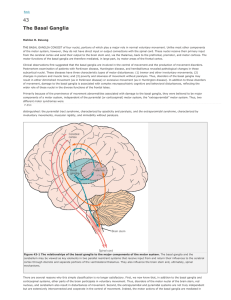
Principles of Neural Science
... THE BASAL GANGLIA CONSIST of four nuclei, portions of which play a major role in normal voluntary movement. Unlike most other components of the motor system, however, they do not have direct input or output connections with the spinal cord. These nuclei receive their primary input from the cerebral ...
... THE BASAL GANGLIA CONSIST of four nuclei, portions of which play a major role in normal voluntary movement. Unlike most other components of the motor system, however, they do not have direct input or output connections with the spinal cord. These nuclei receive their primary input from the cerebral ...
PDF
... 1970; Eaton et al., 1977; Lingenhöhl and Friauf, 1992). These fastconducting cells are invariably located within the brainstem or homologous hindbrain structure and often receive input from multiple sensory modalities including the auditory, visual and somatosensory systems. Even in mammals, who lac ...
... 1970; Eaton et al., 1977; Lingenhöhl and Friauf, 1992). These fastconducting cells are invariably located within the brainstem or homologous hindbrain structure and often receive input from multiple sensory modalities including the auditory, visual and somatosensory systems. Even in mammals, who lac ...
Functional maps within a single neuron
... these intraneuronal maps to plasticity in sensory maps. For instance, studies involving the effects of dark rearing on various visual maps could be metaphorically related to the studies involving activity blockade to a neuronal map. In both cases, the maps respond to changes in the environment by ch ...
... these intraneuronal maps to plasticity in sensory maps. For instance, studies involving the effects of dark rearing on various visual maps could be metaphorically related to the studies involving activity blockade to a neuronal map. In both cases, the maps respond to changes in the environment by ch ...
Glycine Immunoreactivity of Multipolar Neurons in the Ventral
... and Young, 1980; Young et al., 1988). These local circuits, however, do not account for all of the response properties of DCN neurons. For example, type II units of the DCN are relatively unresponsive to broadband stimuli even when the stimuli contain energy within the excitatory response area of th ...
... and Young, 1980; Young et al., 1988). These local circuits, however, do not account for all of the response properties of DCN neurons. For example, type II units of the DCN are relatively unresponsive to broadband stimuli even when the stimuli contain energy within the excitatory response area of th ...
Drosophila GABA, short neuropeptide F and their receptors
... Ca2+ channels particularly on the endoplasmatic reticulum, thus increasing the cytosolic levels of calcium. Calcium and DAG can activate protein kinase C that phosphorylates other molecules. Another function of the β/γ subunits is to act on G-protein coupled inward rectifying potassium channels (GIR ...
... Ca2+ channels particularly on the endoplasmatic reticulum, thus increasing the cytosolic levels of calcium. Calcium and DAG can activate protein kinase C that phosphorylates other molecules. Another function of the β/γ subunits is to act on G-protein coupled inward rectifying potassium channels (GIR ...