Leonardo da Vinci: Renaissance Man, pp. 74-75
... Painting: Mona Lisa and The Last Supper are da Vinci’s most famous works. Leonardo da Vinci was perhaps the greatest Renaissance painter, introducing new techniques. Many of his paintings, though, were left unfinished or have not survived. One project he did complete and that has survived is the Mon ...
... Painting: Mona Lisa and The Last Supper are da Vinci’s most famous works. Leonardo da Vinci was perhaps the greatest Renaissance painter, introducing new techniques. Many of his paintings, though, were left unfinished or have not survived. One project he did complete and that has survived is the Mon ...
Art of the Italian Renaissance A time of great change for art and
... York who created a PowerPoint of 89 slides on this subject and was good enough to share and post it on powerpointpalooza.com I have taken some of her slides and photographs and put them together into a shorter version that we can cover in one class. ...
... York who created a PowerPoint of 89 slides on this subject and was good enough to share and post it on powerpointpalooza.com I have taken some of her slides and photographs and put them together into a shorter version that we can cover in one class. ...
Content Outline HIS/113 Version 2 1 Week Two Content Outline
... discipline was architecture. Buildings were the most expensive investment patrons could make, and the technical knowledge necessary for their successful construction was immense. Not only did the architect design a building, he also served as its general contractor, its construction supervisor, and ...
... discipline was architecture. Buildings were the most expensive investment patrons could make, and the technical knowledge necessary for their successful construction was immense. Not only did the architect design a building, he also served as its general contractor, its construction supervisor, and ...
Important Renaissance People: Artists
... D.) a prince should be concerned only with power and be bound only by rules that would lead to success in political actions. “The End justifies the Means.” “Better to be feared than loved.” E.) believed that these rules could be discovered by deduction from the political practices of the time, as we ...
... D.) a prince should be concerned only with power and be bound only by rules that would lead to success in political actions. “The End justifies the Means.” “Better to be feared than loved.” E.) believed that these rules could be discovered by deduction from the political practices of the time, as we ...
The Renaissance - Christ the Redeemer Catholic Schools
... The Printing Press • No other invention has changed the world as much as the invention of the printing press • The rapid spread of Renaissance ideas was made possible by Johann Gutenberg ( 1399-1468) of Mainz, Germany, invented the mechanical printing press around the mid-1400’s • The Chinese had b ...
... The Printing Press • No other invention has changed the world as much as the invention of the printing press • The rapid spread of Renaissance ideas was made possible by Johann Gutenberg ( 1399-1468) of Mainz, Germany, invented the mechanical printing press around the mid-1400’s • The Chinese had b ...
The Renaissance:
... among, and competition between, European countries? How did increased trade lead to the emergence of powerful citystates, (i.e., Florence, Venice, Genoa)? In what ways did thinkers and philosophers influence society in the ...
... among, and competition between, European countries? How did increased trade lead to the emergence of powerful citystates, (i.e., Florence, Venice, Genoa)? In what ways did thinkers and philosophers influence society in the ...
Curriculum Vitae - Wake Forest University
... Chair of Committee on Academic Planning, Wake Forest, 2010-2012 Phi Beta Kappa, Wake Forest Chapter, Secretary-Treasurer, 2010-present; president, 19981999. Editorial Review Board, Sixteenth Century Journal, 2005-2008. Coordinator for Art History, Art Department, 2004-8 Director of the Teaching and ...
... Chair of Committee on Academic Planning, Wake Forest, 2010-2012 Phi Beta Kappa, Wake Forest Chapter, Secretary-Treasurer, 2010-present; president, 19981999. Editorial Review Board, Sixteenth Century Journal, 2005-2008. Coordinator for Art History, Art Department, 2004-8 Director of the Teaching and ...
Chapter 14 Section 1 notes
... • He was also a devout Catholic. • wrote literature of his own (Sonnets to Laura) • April 8, 1341: crowned poet laureate in Rome on Easter Sunday • The laurel wreath was identified by Petrarch as being the symbol of literary and poetic immortality. • July 13, 1374: died with “a pen in his hand and L ...
... • He was also a devout Catholic. • wrote literature of his own (Sonnets to Laura) • April 8, 1341: crowned poet laureate in Rome on Easter Sunday • The laurel wreath was identified by Petrarch as being the symbol of literary and poetic immortality. • July 13, 1374: died with “a pen in his hand and L ...
The Renaissance in the North
... An astounding invention aided the spread of the Renaissance. In about 1455, Johann Gutenberg (GOOT un burg) of Mainz, Germany, printed the first complete edition of the Bible using a printing press with movable type. A printing revolution had begun that would transform Europe. Before the printing pr ...
... An astounding invention aided the spread of the Renaissance. In about 1455, Johann Gutenberg (GOOT un burg) of Mainz, Germany, printed the first complete edition of the Bible using a printing press with movable type. A printing revolution had begun that would transform Europe. Before the printing pr ...
Renaissance Analysis and Discovery Assignments
... 4) What form of music did this composer prefer? 5) What was his most important composition? In addition, what was his important contribution to music? 6) Why or how is this individual still important and relevant today’s music? (Complete the following questions for the forms) 1) When and where did t ...
... 4) What form of music did this composer prefer? 5) What was his most important composition? In addition, what was his important contribution to music? 6) Why or how is this individual still important and relevant today’s music? (Complete the following questions for the forms) 1) When and where did t ...
How Did the City-State of Florence Reflect the Renaissance
... Florence, or Firenza in Italian, developed as a city-state in northcentral Italy. It was built on the Arno River, which had been a trade route for centuries. Merchants and traders had prospered in Florence since before the Roman Empire, but during the Renaissance, as trade increased, it became the c ...
... Florence, or Firenza in Italian, developed as a city-state in northcentral Italy. It was built on the Arno River, which had been a trade route for centuries. Merchants and traders had prospered in Florence since before the Roman Empire, but during the Renaissance, as trade increased, it became the c ...
AP Euro Unit 1 Renaissance and Exploration Outline
... Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! ...
... Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! Perspective! ...
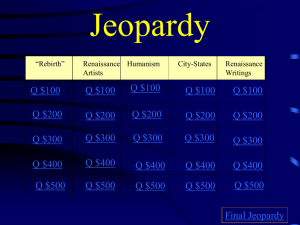
Hr 13 - Renaissance Jeopardy
... How did people’s way of thinking change between the Middle Ages & the Renaissance? ...
... How did people’s way of thinking change between the Middle Ages & the Renaissance? ...
architecture - cloudfront.net
... three stories, regularly spaced arched double windows, open courtyard & heavy overhanging roof / Brunelleschi (13771446) Sculptor-Architect / Alberti – wrote about the theories of art – & designed buildings Sculpture- increasing naturalism & Idealism based on Classical models / relief sculptors deve ...
... three stories, regularly spaced arched double windows, open courtyard & heavy overhanging roof / Brunelleschi (13771446) Sculptor-Architect / Alberti – wrote about the theories of art – & designed buildings Sculpture- increasing naturalism & Idealism based on Classical models / relief sculptors deve ...
Jeopardy - Menifee County Schools
... One of the biggest characteristics of the Italian Renaissance was the emergence of these states, of which Florence and Venice are examples. ...
... One of the biggest characteristics of the Italian Renaissance was the emergence of these states, of which Florence and Venice are examples. ...
The Renaissance (c1350–c1550) - andallthat.co.uk
... small minority achieved some fame. In the latter sixteenth century, at least 25 women published books in Italy. Laura Cereta (1469–1499) reflected the success and failure of humanist women. Educated in a convent, she learned languages, philosophy, theology, and mathematics. However, by 15, like othe ...
... small minority achieved some fame. In the latter sixteenth century, at least 25 women published books in Italy. Laura Cereta (1469–1499) reflected the success and failure of humanist women. Educated in a convent, she learned languages, philosophy, theology, and mathematics. However, by 15, like othe ...
Directions: Match the following vocabulary word with its definition by
... Extra detail - The powerful Medici Family became patrons of the arts in Florence and spent large amounts of money on art. Michelangelo even lived with this family for a while. 7-Secular- Non-religious ideas that became popular during the Renaissance. Extra detail – Authors like Dante Alighieri of Fl ...
... Extra detail - The powerful Medici Family became patrons of the arts in Florence and spent large amounts of money on art. Michelangelo even lived with this family for a while. 7-Secular- Non-religious ideas that became popular during the Renaissance. Extra detail – Authors like Dante Alighieri of Fl ...
i - CA.indd
... many masterpieces, including The Last Supper and the Mona Lisa. Michelangelo di Buonarroti Simoni was born in the Italian village of Caprese in 1475. He was trained mainly as a sculptor. Michelangelo completed many great works, including the sculpture Moses (1516) for the tomb of Pope Julius II. The ...
... many masterpieces, including The Last Supper and the Mona Lisa. Michelangelo di Buonarroti Simoni was born in the Italian village of Caprese in 1475. He was trained mainly as a sculptor. Michelangelo completed many great works, including the sculpture Moses (1516) for the tomb of Pope Julius II. The ...
10th Euro Studies 9.29.14
... Now one member from group write what they came up with on the white board. (3 minutes) • Let’s discuss…what do these positions have in common as far as leadership? • Keep in mind characteristics that you agree/disagree with… ...
... Now one member from group write what they came up with on the white board. (3 minutes) • Let’s discuss…what do these positions have in common as far as leadership? • Keep in mind characteristics that you agree/disagree with… ...
Historians of the Renaissance and their Perspectives
... Voltaire: (in 1756) the Renaissance as ‘beg[inning] to shake off that barbarous rust, with which Europe has been covered since the decline of the Roman Empire.’ Ferguson: Italians ‘turned for inspiration to the civilisation of Roman and Greek antiquity…[with] their reverence for classical culture’ g ...
... Voltaire: (in 1756) the Renaissance as ‘beg[inning] to shake off that barbarous rust, with which Europe has been covered since the decline of the Roman Empire.’ Ferguson: Italians ‘turned for inspiration to the civilisation of Roman and Greek antiquity…[with] their reverence for classical culture’ g ...
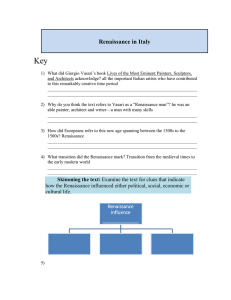
Renaissance in italy key
... often produced portraits of well-known figures of the day __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 64) How did classical Greek and Roman works influence Renaissance artists? They often revived many classical ...
... often produced portraits of well-known figures of the day __________________________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 64) How did classical Greek and Roman works influence Renaissance artists? They often revived many classical ...
Renaissance Example #5: Brief Biography of Leonardo da Vinci
... Latin in a “classical” style that was popular during the Renaissance. Alberti researched and wrote about many topics. Alberti wrote “On the Family,” a text written in Italian in which he communicated information he learned from Greek and Roman sources to other Italians about farming, the relationshi ...
... Latin in a “classical” style that was popular during the Renaissance. Alberti researched and wrote about many topics. Alberti wrote “On the Family,” a text written in Italian in which he communicated information he learned from Greek and Roman sources to other Italians about farming, the relationshi ...
Renaissance music

Renaissance music is music written in Europe during the Renaissance. Consensus among music historians – with notable dissent – has been to start the era around 1400, with the end of the medieval era, and to close it around 1600, with the beginning of the Baroque period, therefore commencing the musical Renaissance about a hundred years after the beginning of the Renaissance as understood in other disciplines. As in the other arts, the music of the period was significantly influenced by the developments which define the Early Modern period: the rise of humanistic thought; the recovery of the literary and artistic heritage of ancient Greece and Rome; increased innovation and discovery; the growth of commercial enterprise; the rise of a bourgeois class; and the Protestant Reformation. From this changing society emerged a common, unifying musical language, in particular the polyphonic style of the Franco-Flemish school.The invention of the Gutenberg press made distribution of music and musical theory possible on a wide scale. Demand for music as entertainment and as an activity for educated amateurs increased with the emergence of a bourgeois class. Dissemination of chansons, motets, and masses throughout Europe coincided with the unification of polyphonic practice into the fluid style which culminated in the second half of the sixteenth century in the work of composers such as Palestrina, Lassus, Victoria and William Byrd. Relative political stability and prosperity in the Low Countries, along with a flourishing system of music education in the area's many churches and cathedrals, allowed the training of hundreds of singers and composers. These musicians were highly sought throughout Europe, particularly in Italy, where churches and aristocratic courts hired them as composers and teachers. By the end of the 16th century, Italy had absorbed the northern influences, with Venice, Rome, and other cities being centers of musical activity, reversing the situation from a hundred years earlier. Opera arose at this time in Florence as a deliberate attempt to resurrect the music of ancient Greece (OED 2005).Music, increasingly freed from medieval constraints, in range, rhythm, harmony, form, and notation, became a vehicle for new personal expression. Composers found ways to make music expressive of the texts they were setting. Secular music absorbed techniques from sacred music, and vice versa. Popular secular forms such as the chanson and madrigal spread throughout Europe. Courts employed virtuoso performers, both singers and instrumentalists. Music also became more self-sufficient with its availability in printed form, existing for its own sake. Many familiar modern instruments (including the violin, guitar, lute and keyboard instruments), developed into new forms during the Renaissance responding to the evolution of musical ideas, presenting further possibilities for composers and musicians to explore. Modern woodwind and brass instruments like the bassoon and trombone also appeared; extending the range of sonic color and power. During the 15th century the sound of full triads became common, and towards the end of the 16th century the system of church modes began to break down entirely, giving way to the functional tonality which was to dominate western art music for the next three centuries.From the Renaissance era both secular and sacred music survives in quantity, and both vocal and instrumental. An enormous diversity of musical styles and genres flourished during the Renaissance, and can be heard on commercial recordings in the 21st century, including masses, motets, madrigals, chansons, accompanied songs, instrumental dances, and many others. Numerous early music ensembles specializing in music of the period give concert tours and make recordings, using a wide range of interpretive styles.