Ecology Extras - Solon City Schools
... 6. Thousands of acres of tropical rainforests are cut down each year, primarily for farming and wood products. Identify two negative environmental consequences of rainforest destruction. Explain the negative impact of each consequence. (4 points) Write the answer on separate paper. ...
... 6. Thousands of acres of tropical rainforests are cut down each year, primarily for farming and wood products. Identify two negative environmental consequences of rainforest destruction. Explain the negative impact of each consequence. (4 points) Write the answer on separate paper. ...
Chapter 5 Vocabulary Defined 1. Interspecific competition: attempts
... 10. Ecological succession: process in which communities of plant and animal species in a particular area are replaced over time by a series of different and often more complex communities ...
... 10. Ecological succession: process in which communities of plant and animal species in a particular area are replaced over time by a series of different and often more complex communities ...
Ecology - OCPS TeacherPress
... 4. All of the different populations living in an area (plants, rabbits, coyotes...) is called the _________________________ ...
... 4. All of the different populations living in an area (plants, rabbits, coyotes...) is called the _________________________ ...
Notes: Unit 1 Ecosystems and Biomes
... low reproductive rates (deer, cougar, eagle, oak tree etc). They are sometimes referred to as K-selective. 22. Adaptations in plants and animals occur as living conditions change over long periods of time. The process of developing adaptations is called Natural Selection. 23. Natural selection is dr ...
... low reproductive rates (deer, cougar, eagle, oak tree etc). They are sometimes referred to as K-selective. 22. Adaptations in plants and animals occur as living conditions change over long periods of time. The process of developing adaptations is called Natural Selection. 23. Natural selection is dr ...
glossary
... Extinction: When a species is no longer in existence, because it has died out. Background Extinction: The ongoing extinction of individual species due to environmental or ecological factors such as climate change, disease, loss of habitat, or competitive disadvantage in relation to other species. Ba ...
... Extinction: When a species is no longer in existence, because it has died out. Background Extinction: The ongoing extinction of individual species due to environmental or ecological factors such as climate change, disease, loss of habitat, or competitive disadvantage in relation to other species. Ba ...
Biology B CECA
... 17. What is the term for the fan-shaped array of bones in fish such as goldfish and tuna? (Ray-Fin) 18. Gills are large sheets of thin tissue that take in dissolved oxygen. 19. Insects, bats, and birds are the only living groups of animals that have evolved True Flight. 20. Which animals is a verteb ...
... 17. What is the term for the fan-shaped array of bones in fish such as goldfish and tuna? (Ray-Fin) 18. Gills are large sheets of thin tissue that take in dissolved oxygen. 19. Insects, bats, and birds are the only living groups of animals that have evolved True Flight. 20. Which animals is a verteb ...
GLOSSARY Alien species Species introduced deliberately or
... The use of components of biological diversity in a way and at a rate that does not lead to the long-term decline of biological diversity, thereby maintaining its potential to meet the needs and aspirations of present and future generations (Source: Convention on Biological Diversity). ...
... The use of components of biological diversity in a way and at a rate that does not lead to the long-term decline of biological diversity, thereby maintaining its potential to meet the needs and aspirations of present and future generations (Source: Convention on Biological Diversity). ...
Intro to the Biosphere
... of a given species in a specific area or region at a certain time. Its significance is more than that of a number of individuals because not all individuals are identical. Populations contain genetic variation within themselves and between other populations. Fundamental genetic differ slightly from ...
... of a given species in a specific area or region at a certain time. Its significance is more than that of a number of individuals because not all individuals are identical. Populations contain genetic variation within themselves and between other populations. Fundamental genetic differ slightly from ...
Ecological Principles
... • A relationship between organisms in which at least one of them benefits • Three types of symbiosis in ecosystems are mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. ...
... • A relationship between organisms in which at least one of them benefits • Three types of symbiosis in ecosystems are mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism. ...
Chapter 1 Lesson 3 Vocab Ecology
... A: Predator Apply: a decrease in prey will lead to decrease in predators ...
... A: Predator Apply: a decrease in prey will lead to decrease in predators ...
Natural Dist-Fire
... Breaking up of large continuous habitat into smaller and isolated parcels. Or transformation of original continuous forest landscape into smaller and isolated remnant patches of plantation or non-forest habitat. Or simply disruption of continuity. ...
... Breaking up of large continuous habitat into smaller and isolated parcels. Or transformation of original continuous forest landscape into smaller and isolated remnant patches of plantation or non-forest habitat. Or simply disruption of continuity. ...
BIO SOL Review 6
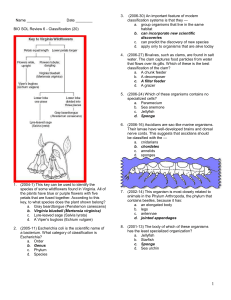
... 11. (2001-29) According to this chart, the insects that are most closely related are the — a. springtails and bristletails b. springtails and proturans c. bristletails and mayflies d. dragonflies and proturans 12. (2002-30) During a trip to a rain forest, a scientist discovered a new organism living ...
... 11. (2001-29) According to this chart, the insects that are most closely related are the — a. springtails and bristletails b. springtails and proturans c. bristletails and mayflies d. dragonflies and proturans 12. (2002-30) During a trip to a rain forest, a scientist discovered a new organism living ...
BIO SOL Review 6 - Classification
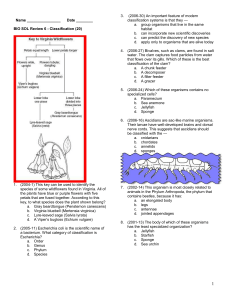
... 11. (2001-29) According to this chart, the insects that are most closely related are the — a. springtails and bristletails b. springtails and proturans c. bristletails and mayflies d. dragonflies and proturans 12. (2002-30) During a trip to a rain forest, a scientist discovered a new organism living ...
... 11. (2001-29) According to this chart, the insects that are most closely related are the — a. springtails and bristletails b. springtails and proturans c. bristletails and mayflies d. dragonflies and proturans 12. (2002-30) During a trip to a rain forest, a scientist discovered a new organism living ...
14.1 Habitat And Niche
... • A habitat is all aspects of the area in which an organism lives. – biotic factors – abiotic factors • An ecological niche includes all of the factors that a species needs to survive, stay healthy, and reproduce. – food – abiotic conditions – behavior ...
... • A habitat is all aspects of the area in which an organism lives. – biotic factors – abiotic factors • An ecological niche includes all of the factors that a species needs to survive, stay healthy, and reproduce. – food – abiotic conditions – behavior ...
Ecology - bulldog biology
... species in a community Species diversity – number of species in a community relative to the abundance of each species ...
... species in a community Species diversity – number of species in a community relative to the abundance of each species ...
Ecology - Elmwood Park Memorial High School
... • The occupation of an organism is called its niche. This includes how it gets food, reproduces, avoids predators, etc. • The niche of an organism determines its habitat. • The way an organism has evolved to survive determines where it can live. ...
... • The occupation of an organism is called its niche. This includes how it gets food, reproduces, avoids predators, etc. • The niche of an organism determines its habitat. • The way an organism has evolved to survive determines where it can live. ...
Notes: Unit 1 Ecosystems and Biomes
... eagle, oak tree etc) . They are sometimes referred to as K-selective. 23. Adaptations in plants and animals occur as living conditions change over long periods of time. The process of developing adaptations is called Natural Selection . 24. Natural selection is driven by selection pressures such as ...
... eagle, oak tree etc) . They are sometimes referred to as K-selective. 23. Adaptations in plants and animals occur as living conditions change over long periods of time. The process of developing adaptations is called Natural Selection . 24. Natural selection is driven by selection pressures such as ...
Ch 52 Ecology
... All the organisms in a community plus abiotic factors ecosystems are transformers of energy & processors of matter ...
... All the organisms in a community plus abiotic factors ecosystems are transformers of energy & processors of matter ...
Life Science Study Guide - Team 6
... 13. A ___decomposer_______________ breaks down dead plants and animals, and puts nutrients back into the soil. 14. What are 2 other names for a grassland? __Savanna_______________ and ____Prairie___________ 15. What biome is located near the poles? ___Tundra__________________________ 16. What biome ...
... 13. A ___decomposer_______________ breaks down dead plants and animals, and puts nutrients back into the soil. 14. What are 2 other names for a grassland? __Savanna_______________ and ____Prairie___________ 15. What biome is located near the poles? ___Tundra__________________________ 16. What biome ...
Unit 3 Sustainability and Interdependence Glossary
... ATP synthase membrane-bound enzyme that synthesises ATP back-cross cross between an F hybrid organism with a parental type to maintain characteristics of a new breed biodiversity variety and relative abundance of species biological control method of controlling pests using natural predators, parasit ...
... ATP synthase membrane-bound enzyme that synthesises ATP back-cross cross between an F hybrid organism with a parental type to maintain characteristics of a new breed biodiversity variety and relative abundance of species biological control method of controlling pests using natural predators, parasit ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.