* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Life Science Study Guide - Team 6
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Photosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Triclocarban wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Lake ecosystem wikipedia , lookup
Renewable resource wikipedia , lookup
Theoretical ecology wikipedia , lookup
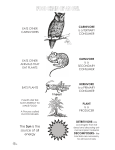
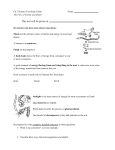
Name: ___ANSWER KEY_____________________________ Period: ___________ Life Science Study Guide Biomes/Ecosystems 1. A ___population______________ is all organisms OF ONE SPECIES living in a specific area at one time. 2. A ____community______________ is many DIFFERENT SPECIES living in a specific area at one time. 3. A(n) __ecosystem_______________________ contains the living AND non-living things in a specific area. 4. __Carrying_______ _____capacity_________ is the maximum number of organisms an ecosystem can support. 5. If the population of a species increases in an area, this means that the ____birth__ rate is HIGHER than the ___death______ rate. 6. ___Commensalism___________ is the relationship in which one species is HELPED but the other is NOT AFFECTED. 7. __Parasitism_____________ is the relationship in which one species is HELPED but the other species is HARMED. 8. __Mutualism_________ is the relationship in which both species benefit. 9. A ____predator___________ hunts another animal; ____prey_____ is the animal that is being hunted. 10. A(n) _____carnivore__________ eats only animals. A(n) _____herbivore_________ eats only plants. A(n) ____omnivore____________ eats both plants and animals. 11. A _____producer________________ makes its own food. An example is a(n) ___plant______. 12. A _____consumer____________ must eat food to get energy. An example is a(n) ____animal_____. 13. A ___decomposer_______________ breaks down dead plants and animals, and puts nutrients back into the soil. 14. What are 2 other names for a grassland? __Savanna_______________ and ____Prairie___________ 15. What biome is located near the poles? ___Tundra__________________________ 16. What biome contains the most diversity in terms of plants and animals? __Tropical Rainforest_____ 17. Which water biome contains a mix of salt water and fresh water? _Estuary_____________________ 18. Give an example of an animal adapting to its environment. ___________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ 19. ___Homeostasis__________ is a balance of items in an ecosystem, such as a rain forest supporting the basic needs of the plants and animals that live there with food, water, shelter, and air. 20. A(n) ____invasive_________ ______species______________ is a non-native organism that causes harm to the environment or disrupts an ecosystem. 21. Circle the correct answer in the parentheses. According to the graph on the right, the population (increases, decreases, stays the same) when the carrying capacity is reached. 22. What starts a food chain or food web? ___Sun___________________ 23. What ORGANISM starts a food chain or food web? __Producer/Plant___________ Use the food chain below to answer questions 24-30. Hawk Ladybug Finch Fungi Worm Bacteria 24. Name an herbivore. _Greenfly, Butterfly, Grasshopper, Mouse, Rabbit________ 25. Name a carnivore. __Ladybug, Dragonfly, Frog, Snake, Hawk, Fox_______________________ 26. Name an omnivore. ___Finch______________________ 27. Name a producer. __Berries/Plantain_______ 28. Name a decomposer. __Fungi/Worm/Bacteria_______ 29. Name a predator/prey relationship from the food web. __Hawk/Snake, Fox/Rabbit, etc.__________ 30. Create a food chain using 4 of the items listed above. EXAMPLE. There are other correct answers. ____Sun_______ ____Berries___________ ____Butterfly_________ ___Frog________ 31. If the frog population declined due to disease, what would happen to the other organisms in the food web? ___SAMPLE ANSWER: Snakes population would decline because it doesn’t have as much to eat. Dragonfly population would become larger because nothing is eating it, so the ladybugs may start to decline. ____________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________________________________ Plant Processes 32. All living things are made up of __cells___________, which are the basic unit of an organism. 33. Cells are mostly made up of ____water________. 34. __Photosynthesis_____________ is the process that plants use to make sugar. 35. Another name for the sugar that plants produce for food is ______glucose__________________. 36. Photosynthesis requires three reactants, which are _____water______________, ___sunlight_________________, and ______carbon dioxide______________. 37. The two things that are produced by photosynthesis are _______glucose/sugar________________ and ___oxygen________________________. 38. Photosynthesis occurs in the _____leaf_______________________ of a plant, specifically in the _____chloroplasts______________________ (cell organelle). 39. _____Chlorophyll_________________ is the green pigment that absorbs energy from the Sun. 40. During _____cellular_____________ _______respiration____________ energy is released from food in the form of ATP, or stored for later use. 41. Plants have ____cell________________ _________walls___________ that provide structure and support to the plant; animals cells do not have this.