What Shapes an Ecosystem? Section 4-2
... Notes will vary based upon individual class concept attainment. These notes will be modified with examples and more in depth information at the teacher’s discretion. Pioneer Species are the first to populate an area. Secondary Succession occurs when the community interaction restore an ecosystem to ...
... Notes will vary based upon individual class concept attainment. These notes will be modified with examples and more in depth information at the teacher’s discretion. Pioneer Species are the first to populate an area. Secondary Succession occurs when the community interaction restore an ecosystem to ...
Ecology 2.1
... volcanic islands, off the coast of South America, that are famous for their unusual plant and animal life. These islands are the habitat —the physical location—where these plants and animals live. Island habitats have certain physical characteristics that describe them, including the amount of preci ...
... volcanic islands, off the coast of South America, that are famous for their unusual plant and animal life. These islands are the habitat —the physical location—where these plants and animals live. Island habitats have certain physical characteristics that describe them, including the amount of preci ...
Notes Chapter 2
... Organization of the Environment • The biosphere is the part of the Earth that supports life. – Scattered throughout the biosphere is a wide range of habitats– dry deserts, lush rainforests, even dark caves. ...
... Organization of the Environment • The biosphere is the part of the Earth that supports life. – Scattered throughout the biosphere is a wide range of habitats– dry deserts, lush rainforests, even dark caves. ...
Interactions Among Living Things
... • Commensalism- the relation between two different kinds of organisms when one receives benefits from the other without affecting or damaging it. •Barnacles adhering to the skin of a whale or shell of a mollusk: barnacle is a mollusks that benefits by finding a habitat where nutrients are available ...
... • Commensalism- the relation between two different kinds of organisms when one receives benefits from the other without affecting or damaging it. •Barnacles adhering to the skin of a whale or shell of a mollusk: barnacle is a mollusks that benefits by finding a habitat where nutrients are available ...
Species Interaction
... Symbiosis and Adaptations (No picture necessary) Predation Parasitism Competition Mutualism Commensalism ...
... Symbiosis and Adaptations (No picture necessary) Predation Parasitism Competition Mutualism Commensalism ...
Ecosystems and Communities
... Habitat: the area where an organism lives, including the biotic and abiotic factors that affect it Niche: an organism’s habitat plus its role in an ecosystem ...
... Habitat: the area where an organism lives, including the biotic and abiotic factors that affect it Niche: an organism’s habitat plus its role in an ecosystem ...
Required information: 1. Common and Scientific Name of Species 2
... Ecology Project Rubric Assignment: Find all the information about the organism as shown below. ...
... Ecology Project Rubric Assignment: Find all the information about the organism as shown below. ...
jeopardy Unit 1
... Energy is lost as it moves up the food chain. Organism use it to function such as breathing, waste, etc ...
... Energy is lost as it moves up the food chain. Organism use it to function such as breathing, waste, etc ...
Chapter 6 6.3 Biodiversity
... – Many pollutants threaten biodiversity. – DDT, for example, prevents birds from laying healthy eggs. ...
... – Many pollutants threaten biodiversity. – DDT, for example, prevents birds from laying healthy eggs. ...
living
... fungus from the shark by feeding on it..... • That is Mutualism because both benefit • A tick sucks the blood from a deer... • That is Parasitism because the deer is harmed • A bird that lives in a hole in a tree is... • Commensalism (the tree is neither harmed nor helped, but the bird gets shelter) ...
... fungus from the shark by feeding on it..... • That is Mutualism because both benefit • A tick sucks the blood from a deer... • That is Parasitism because the deer is harmed • A bird that lives in a hole in a tree is... • Commensalism (the tree is neither harmed nor helped, but the bird gets shelter) ...
Guided Notes Ch 4, 5, 6
... Biodiversity • Biodiversity – _________________ of organisms living in an area at the same time includes # of different species & population size of each species. – _______________________ diversity – genes & pattern of variation – _______________________ diversity – variety & abundance of specie ...
... Biodiversity • Biodiversity – _________________ of organisms living in an area at the same time includes # of different species & population size of each species. – _______________________ diversity – genes & pattern of variation – _______________________ diversity – variety & abundance of specie ...
Soil types determine what plants and animals can live in an area
... Air gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide are needed by most species. ...
... Air gases such as oxygen, nitrogen, and carbon dioxide are needed by most species. ...
01 - Fort Bend ISD
... 6. Honeybees collect pollen from flowers. Butterflies collect nectar from flowers. This relationship is an example of _____________________. 7. The principle of ___________________________ states that when two species compete for the same resources, one species will be better adapted to the niche an ...
... 6. Honeybees collect pollen from flowers. Butterflies collect nectar from flowers. This relationship is an example of _____________________. 7. The principle of ___________________________ states that when two species compete for the same resources, one species will be better adapted to the niche an ...
What do Ecologists Study?
... – Biotic (living) vs. abiotic (non-living) factors (ex., floods, droughts) ...
... – Biotic (living) vs. abiotic (non-living) factors (ex., floods, droughts) ...
8C4Notes
... surface, and the atmosphere that surrounds Earth. 3. The biosphere is made up of different environment that are home to different kinds of organisms. 4. Ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in an area and the nonliving parts of their environment. example – In prairie ecosystem, bison, gras ...
... surface, and the atmosphere that surrounds Earth. 3. The biosphere is made up of different environment that are home to different kinds of organisms. 4. Ecosystem consists of all the organisms living in an area and the nonliving parts of their environment. example – In prairie ecosystem, bison, gras ...
Transect + species presentation
... Measuring the effect of abiotic factors on organisms within a habitat ...
... Measuring the effect of abiotic factors on organisms within a habitat ...
Notes Part 3 A habitat differs from a niche. A habitat is all aspects of
... Competitive exclusion keeps two species from occupying the ...
... Competitive exclusion keeps two species from occupying the ...
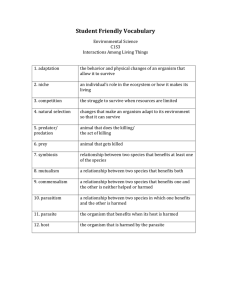
Student Friendly Vocabulary
... Student Friendly Vocabulary Environmental Science C1S3 Interactions Among Living Things 1. adaptation ...
... Student Friendly Vocabulary Environmental Science C1S3 Interactions Among Living Things 1. adaptation ...
Chapter 8 Study Guide (7th Grade Science) Lesson 8.1 *An
... Freshwater ecosystems include streams, rivers, ponds, and lakes. Marine ecosystems include ocean zones (intertidal, neritic, surface ocean, deep ocean). ...
... Freshwater ecosystems include streams, rivers, ponds, and lakes. Marine ecosystems include ocean zones (intertidal, neritic, surface ocean, deep ocean). ...
Extinction Processes
... • do not produce enough individuals to maintain themselves • rely on dispersers from other patches ...
... • do not produce enough individuals to maintain themselves • rely on dispersers from other patches ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.