Ecology - Humble ISD
... gas and this is returned to the atmosphere and increases the amount of CO2 gas in the air. ...
... gas and this is returned to the atmosphere and increases the amount of CO2 gas in the air. ...
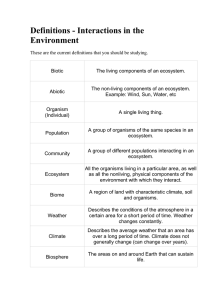
Definitions - Interactions in the Environment These are the current
... Describes the conditions of the atmosphere in a certain area for a short period of time. Weather changes constantly. ...
... Describes the conditions of the atmosphere in a certain area for a short period of time. Weather changes constantly. ...
“brains” of the cell, the nucleus directs cell activities and contains
... Organisms in the same genus with different species names or Organisms with the same species name but different genus ...
... Organisms in the same genus with different species names or Organisms with the same species name but different genus ...
Microorganisms and Climate Change
... rapid generation time. Many species require specific temperatures and atmospheric conditions for optimal growth. When present in communities, it is more difficult to determine specific changes in metabolism. Instead, the composition of species in the community is the best indicator of health and sta ...
... rapid generation time. Many species require specific temperatures and atmospheric conditions for optimal growth. When present in communities, it is more difficult to determine specific changes in metabolism. Instead, the composition of species in the community is the best indicator of health and sta ...
A. Ecology
... 5. Convergent Evolution – species from different evolutionary branches may come to resemble each other if they live in similar roles in the environment. ...
... 5. Convergent Evolution – species from different evolutionary branches may come to resemble each other if they live in similar roles in the environment. ...
Jungle Animals
... Amphibians are the earliest form of all land vertebrates. The word “amphibia” means both lives. These animals begin life in the water, spend their adult life on land, and return to the water to lay their eggs. They are born with gills to breathe under water. These are replaced by lungs at the end of ...
... Amphibians are the earliest form of all land vertebrates. The word “amphibia” means both lives. These animals begin life in the water, spend their adult life on land, and return to the water to lay their eggs. They are born with gills to breathe under water. These are replaced by lungs at the end of ...
Ecology Unit - Houston ISD
... - Carrying Capacity = the maximum number of individuals of a particular species that the environment can normally and consistently support - Population Crash = a dramatic decline in the size of a population - numerous reasons for this - Limiting Factor = the factor that has the greatest restraint on ...
... - Carrying Capacity = the maximum number of individuals of a particular species that the environment can normally and consistently support - Population Crash = a dramatic decline in the size of a population - numerous reasons for this - Limiting Factor = the factor that has the greatest restraint on ...
Ecosystems: Everything is Connected
... • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. ...
... • Every population is part of a community. • The most obvious difference between communities is the types of species they have. ...
GLOSSARY OF TERMS
... adaptation - Genetically determined characteristic (behavioral, morphological, physiological) that improves an organism’s ability to survive and successfully reproduce under prevailing environmental conditions. ancient forest - The late successional stages of forest development. Synonymous with oldg ...
... adaptation - Genetically determined characteristic (behavioral, morphological, physiological) that improves an organism’s ability to survive and successfully reproduce under prevailing environmental conditions. ancient forest - The late successional stages of forest development. Synonymous with oldg ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR ECOLOGY TEST
... 17. Two members of the same species compete over who gets a certain food. Members of different species try to take over a certain nesting area. These are both examples of___COMPETITION. 18. In which type of symbiosis do organisms help each other? ...
... 17. Two members of the same species compete over who gets a certain food. Members of different species try to take over a certain nesting area. These are both examples of___COMPETITION. 18. In which type of symbiosis do organisms help each other? ...
Questions: Ecological Succession is the natural, gradual changes in
... Starts with bare rock Pioneer Species – Lichen and Moss Secondary Succession begins in a place that already has soil and was once the home of living organisms. Examples: after forest fires, landslides, floods, or plowing Pioneer Species – Grasses and Weeds Climax Community is a stable group ...
... Starts with bare rock Pioneer Species – Lichen and Moss Secondary Succession begins in a place that already has soil and was once the home of living organisms. Examples: after forest fires, landslides, floods, or plowing Pioneer Species – Grasses and Weeds Climax Community is a stable group ...
Aquaculture is the farming of freshwater and saltwater organisms
... areas are revisited as development activities have changed. As part of this study we return to our historic study site and resample water quality parameter and ecosystem health to determine change over time. In addition, we are including modern technologies such as next-generation sequencing to eval ...
... areas are revisited as development activities have changed. As part of this study we return to our historic study site and resample water quality parameter and ecosystem health to determine change over time. In addition, we are including modern technologies such as next-generation sequencing to eval ...
Quick Reference: Climate Change Vulnerability
... beaches/dunes, estuaries, and rocky intertidal – exist at the land-sea interface. The 31 species assessed were scored as having highly variable adaptive capacity, from low to moderate-high, and highly variable exposure and sensitivity scores, from low-moderate to high. The majority of the ten specie ...
... beaches/dunes, estuaries, and rocky intertidal – exist at the land-sea interface. The 31 species assessed were scored as having highly variable adaptive capacity, from low to moderate-high, and highly variable exposure and sensitivity scores, from low-moderate to high. The majority of the ten specie ...
CLICK HERE! Ecology PowerPoint
... interacting organisms and their environment Biotic factors: The living or once-living parts of an ecosystem. Ex:animals, decayed remains, animal waste, plants, bacteria, fungi, etc. ...
... interacting organisms and their environment Biotic factors: The living or once-living parts of an ecosystem. Ex:animals, decayed remains, animal waste, plants, bacteria, fungi, etc. ...
Section 1 Environmental Problems Chapter 6 Habitat
... lumber, food, rubber, and paper. For some of these products, trees must be cut down. Deforestation is the clearing of forest lands. ...
... lumber, food, rubber, and paper. For some of these products, trees must be cut down. Deforestation is the clearing of forest lands. ...
Interactions in Ecosystems - Salisbury Composite High School
... early warning that an ecosystem is being affected by some factor. Usually, these species are very sensitive to changes in an ecosystem, or to specific changes of ecosystem conditions. ...
... early warning that an ecosystem is being affected by some factor. Usually, these species are very sensitive to changes in an ecosystem, or to specific changes of ecosystem conditions. ...
Ecosystems - Hardin County Schools
... interacting with each other and the nonliving parts of the environment ex. Rain forest, pond, lake, rivers, ocean, desert, grassland, tundra, caves… population– All of a certain species of living thing in a certain ecosystem. ex. school of fish, herd of deer, flock of birds, colony of ants biotic fa ...
... interacting with each other and the nonliving parts of the environment ex. Rain forest, pond, lake, rivers, ocean, desert, grassland, tundra, caves… population– All of a certain species of living thing in a certain ecosystem. ex. school of fish, herd of deer, flock of birds, colony of ants biotic fa ...
Ecology
... Secondary Succession Secondary succession takes place after a major disturbance to the biological community in a stable ecosystem. A community can be disturbed by a natural event, like fire or flood, or by human activity. Despite the disturbance, the soil remains there. The damage, is surface damag ...
... Secondary Succession Secondary succession takes place after a major disturbance to the biological community in a stable ecosystem. A community can be disturbed by a natural event, like fire or flood, or by human activity. Despite the disturbance, the soil remains there. The damage, is surface damag ...
Ecology
... Secondary Succession Secondary succession takes place after a major disturbance to the biological community in a stable ecosystem. A community can be disturbed by a natural event, like fire or flood, or by human activity. Despite the disturbance, the soil remains there. The damage, is surface damag ...
... Secondary Succession Secondary succession takes place after a major disturbance to the biological community in a stable ecosystem. A community can be disturbed by a natural event, like fire or flood, or by human activity. Despite the disturbance, the soil remains there. The damage, is surface damag ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.