File
... In a food chain, it is an animal that feeds on plants/producers. These animals are only herbivores. ...
... In a food chain, it is an animal that feeds on plants/producers. These animals are only herbivores. ...
Energy Classification
... Sea level= 1atm. Every 10 m(or 33ft) below sea level pressure increases by 1 atm. ...
... Sea level= 1atm. Every 10 m(or 33ft) below sea level pressure increases by 1 atm. ...
Name Class Date Species Interactions Vocabulary Define each
... how you will remember each. One term has been done for you. Term ...
... how you will remember each. One term has been done for you. Term ...
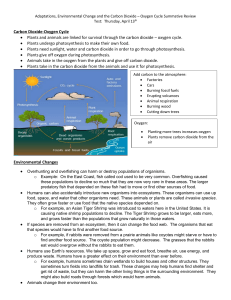
Carbon Dioxide-Oxygen Cycle • Plants and animals are linked for
... these populations to decline so much that they are now very rare in these areas. The larger predatory fish that depended on these fish had to move or find other sources of food. Humans can also accidentally introduce new organisms into ecosystems. These organisms can use up food, space, and water th ...
... these populations to decline so much that they are now very rare in these areas. The larger predatory fish that depended on these fish had to move or find other sources of food. Humans can also accidentally introduce new organisms into ecosystems. These organisms can use up food, space, and water th ...
Chapter 14 Interactions in Ecosystems Review
... 1. __Habitat_ is all aspects of the area in which an organism lives 2. ___Abiotic_or Density-Independent___ factors are non-living factors--temperature, rainfall, etc.. 3. __Biotic or Density-Dependent___ factors are living factors---plants and animals 4. __Ecological Niche___ includes all of the fa ...
... 1. __Habitat_ is all aspects of the area in which an organism lives 2. ___Abiotic_or Density-Independent___ factors are non-living factors--temperature, rainfall, etc.. 3. __Biotic or Density-Dependent___ factors are living factors---plants and animals 4. __Ecological Niche___ includes all of the fa ...
Life and the Environment
... Abiotic Factors • The non-living features or conditions of the environment. • Ex: soil, water, light, air and temperature. • Have effects on living things and often determine the organisms that are able to live in a certain environment. ...
... Abiotic Factors • The non-living features or conditions of the environment. • Ex: soil, water, light, air and temperature. • Have effects on living things and often determine the organisms that are able to live in a certain environment. ...
Slide 1
... beetle Fish share the pond while their leaves, on long flexible stems, float on the with turtles and other surface. animals. Many of them feed on insects at the water’s edge. Trout The bottom of the pond is inhabited by decomposers and Hydra other organisms that feed on particles drifting down from ...
... beetle Fish share the pond while their leaves, on long flexible stems, float on the with turtles and other surface. animals. Many of them feed on insects at the water’s edge. Trout The bottom of the pond is inhabited by decomposers and Hydra other organisms that feed on particles drifting down from ...
chsurveyppt
... Sec. 22.1 Terms Ecosystem—All the living and nonliving things that interact in a particular area Habitat—The place where an organism lives and that provides all the needs of that organism. Biotic Factors —The living parts of an ecosystem Abiotic Factors —the nonliving parts of an ecosystem ...
... Sec. 22.1 Terms Ecosystem—All the living and nonliving things that interact in a particular area Habitat—The place where an organism lives and that provides all the needs of that organism. Biotic Factors —The living parts of an ecosystem Abiotic Factors —the nonliving parts of an ecosystem ...
Teacher Support Pack Animal Adaptations 2016
... of different habitats. Students can describe the ecosystem in terms of its abiotic and biotic components, identify the challenges to survival and then investigate the different adaptations displayed. Below is an example of an ecosystem description: Challenge in the Savannah – Climatic changes and hu ...
... of different habitats. Students can describe the ecosystem in terms of its abiotic and biotic components, identify the challenges to survival and then investigate the different adaptations displayed. Below is an example of an ecosystem description: Challenge in the Savannah – Climatic changes and hu ...
Communities and Ecosystems
... End of an ice age, gradual warming, continental drift, silting in a body of water ...
... End of an ice age, gradual warming, continental drift, silting in a body of water ...
Earth*s Biomes - Bibb County Schools
... relate and interact with the environment in which they live. ...
... relate and interact with the environment in which they live. ...
What Shapes an Ecosystem?
... – all aspects of the area in which an organism lives (includes both biotic and abiotic). – Habitats may change or disappear due to natural causes or interference by man. ...
... – all aspects of the area in which an organism lives (includes both biotic and abiotic). – Habitats may change or disappear due to natural causes or interference by man. ...
ecology! - Midland ISD
... -Physical appearance, species diversity, species abundance, and niche structure. ...
... -Physical appearance, species diversity, species abundance, and niche structure. ...
Living Things - Madison County Schools
... things that interact in a particular area make-up an ecosystem. Organisms live in a particular place in an ecosystem. • An organism obtains food, water, shelter, and other things it needs to live, grow, and reproduce from its surroundings. • Remember: Some organisms can make their own food through p ...
... things that interact in a particular area make-up an ecosystem. Organisms live in a particular place in an ecosystem. • An organism obtains food, water, shelter, and other things it needs to live, grow, and reproduce from its surroundings. • Remember: Some organisms can make their own food through p ...
Wanted Poster - Spring Branch ISD
... it could have traveled from home area to new habitat. 5. Suspected Hideouts – 10 points Explain where new habitat is located. Is it different from its home area? 6. Crimes Committed – 20 points Explain what problems are caused by your organism MUST BE SPECIFIC TO YOUR ORGANISM, no general to a ...
... it could have traveled from home area to new habitat. 5. Suspected Hideouts – 10 points Explain where new habitat is located. Is it different from its home area? 6. Crimes Committed – 20 points Explain what problems are caused by your organism MUST BE SPECIFIC TO YOUR ORGANISM, no general to a ...
Community and Symbiosis
... affected. (from english “sharing of food” or from latin “sharing a table”) Originally, the term was used to describe the use of waste food by second animals (scavengers), like the carcass eaters that follow hunting animals, but wait until they have finished their meal. ...
... affected. (from english “sharing of food” or from latin “sharing a table”) Originally, the term was used to describe the use of waste food by second animals (scavengers), like the carcass eaters that follow hunting animals, but wait until they have finished their meal. ...
Fundamental niche - Gull Lake Community Schools
... higher biodiversity increased resiliency (“healthy” ecosystem). predation helps increase biodiversity …explain how this is possible. ...
... higher biodiversity increased resiliency (“healthy” ecosystem). predation helps increase biodiversity …explain how this is possible. ...
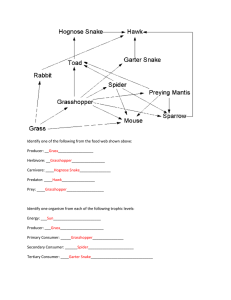
Identify one of the following from the food web shown above
... All of the following can overwhelm the stability of an ecosystem and result in long-term irreversible changes for organisms EXCEPT ___. A. loss of grasses and other vegetation due to sustained high temperatures accompanied with low precipitation B. loss of fish production in a stream, due to death o ...
... All of the following can overwhelm the stability of an ecosystem and result in long-term irreversible changes for organisms EXCEPT ___. A. loss of grasses and other vegetation due to sustained high temperatures accompanied with low precipitation B. loss of fish production in a stream, due to death o ...
Habitat
A habitat is an ecological or environmental area that is inhabited by human, a particular species of animal, plant, or other type of organism.A place where a living thing lives is its habitat. It is a place where it can find food, shelter, protection and mates for reproduction. It is the natural environment in which an organism lives, or the physical environment that surrounds a species population.A habitat is made up of physical factors such as soil, moisture, range of temperature, and availability of light as well as biotic factors such as the availability of food and the presence of predators. A habitat is not necessarily a geographic area—for a parasitic organism it is the body of its host, part of the host's body such as the digestive tract, or a cell within the host's body.