11/12/2014 Opioids
... via mu opioid receptors. GABA neurons inhibit dopamine releasing neurons. Opioids inhibit the inhibitors, increasing dopamine input in the nucleus accumbens and other areas of the brain’s reward pathway. ...
... via mu opioid receptors. GABA neurons inhibit dopamine releasing neurons. Opioids inhibit the inhibitors, increasing dopamine input in the nucleus accumbens and other areas of the brain’s reward pathway. ...
Loss of orexin/NARP neurons in human narcolepsy
... People with narcolepsy have a loss of orexin/hypocretin (ORX) immunoreactivity and mRNA, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of ORX are often reduced in patients with cataplexy. Mice and dogs lacking ORX or ORX receptors display narcolepsy-like symptoms similar to those observed in people. Further, mice ...
... People with narcolepsy have a loss of orexin/hypocretin (ORX) immunoreactivity and mRNA, and cerebrospinal fluid levels of ORX are often reduced in patients with cataplexy. Mice and dogs lacking ORX or ORX receptors display narcolepsy-like symptoms similar to those observed in people. Further, mice ...
Slide ()
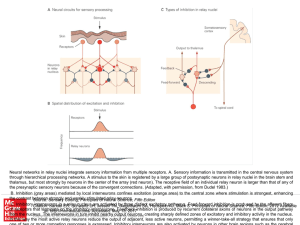
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
... Neural networks in relay nuclei integrate sensory information from multiple receptors. A. Sensory information is transmitted in the central nervous system through hierarchical processing networks. A stimulus to the skin is registered by a large group of postsynaptic neurons in relay nuclei in the br ...
2 - IS MU
... exist in two principal types that are named nicotinic and muscarinic after the two exogenous agonists. Nicotinic cholinergic receptors are acetylcholine-operated Na+/K+ channels (see picture 11); in the peripheral nervous system, they occur – in the dendrites of nearly all peripheral efferent neuron ...
... exist in two principal types that are named nicotinic and muscarinic after the two exogenous agonists. Nicotinic cholinergic receptors are acetylcholine-operated Na+/K+ channels (see picture 11); in the peripheral nervous system, they occur – in the dendrites of nearly all peripheral efferent neuron ...
ACh - Perkins Science
... between a neuron and the cell it is signaling a.In the CNS, this second cell will be another neuron. b.In the PNS, the second cell will be in a muscle or gland; often called myoneural or neuromuscular junctions ...
... between a neuron and the cell it is signaling a.In the CNS, this second cell will be another neuron. b.In the PNS, the second cell will be in a muscle or gland; often called myoneural or neuromuscular junctions ...
Bio70 Psychobiology Fall 2006 First Midterm October 12 Version A
... d. sympathetic nervous system. 50. Which of the following is NOT common in people with Parkinson's disease? a. difficulty initiating voluntary movements b. slowness of movements c. rigidity and tremors d. outbursts of emotions ...
... d. sympathetic nervous system. 50. Which of the following is NOT common in people with Parkinson's disease? a. difficulty initiating voluntary movements b. slowness of movements c. rigidity and tremors d. outbursts of emotions ...
Slide ()
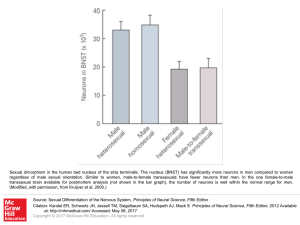
... Sexual dimorphism in the human bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. The nucleus (BNST) has significantly more neurons in men compared to women regardless of male sexual orientation. Similar to women, male-to-female transsexuals have fewer neurons than men. In the one female-to-male transsexual brain ...
... Sexual dimorphism in the human bed nucleus of the stria terminalis. The nucleus (BNST) has significantly more neurons in men compared to women regardless of male sexual orientation. Similar to women, male-to-female transsexuals have fewer neurons than men. In the one female-to-male transsexual brain ...
Modelling Argonaute protein interactions as predictors of local
... MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNAs encoded in the genome that mediate post-transcriptional silencing of messenger RNA (mRNA) targets by associating with Argonaute proteins in the RNAinduced silencing complex (RISC). Neuronal-specific miRNAs drive neuronal development and have important roles in vario ...
... MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small RNAs encoded in the genome that mediate post-transcriptional silencing of messenger RNA (mRNA) targets by associating with Argonaute proteins in the RNAinduced silencing complex (RISC). Neuronal-specific miRNAs drive neuronal development and have important roles in vario ...
Biology/ANNB 261 Exam 2
... c) Lesser; Na+ d) Lesser; K+ e) Greater; Cl17. In normal neurons, even though glutamate is called an excitatory neurotransmitter, when it binds to NMDA receptors, Vm of the postsynaptic membrane may change very little. This is likely due to the presence of a) Glutamic acid decarboxylase b) Glutamine ...
... c) Lesser; Na+ d) Lesser; K+ e) Greater; Cl17. In normal neurons, even though glutamate is called an excitatory neurotransmitter, when it binds to NMDA receptors, Vm of the postsynaptic membrane may change very little. This is likely due to the presence of a) Glutamic acid decarboxylase b) Glutamine ...
Physiology 2 - Sheet #6 - Dr.Loai Al-Zgoul - Done by: Yara
... Ischemia: is a restriction in blood supply to tissues, causing a shortage of oxygen and glucose supply to the cells which in turn stops the production of ATP. Glial cells have transporters which use ATP to reuptake the glutamate. When there is no ATP, glutamate molecules accumulate in the synaptic c ...
... Ischemia: is a restriction in blood supply to tissues, causing a shortage of oxygen and glucose supply to the cells which in turn stops the production of ATP. Glial cells have transporters which use ATP to reuptake the glutamate. When there is no ATP, glutamate molecules accumulate in the synaptic c ...
Cognitive Disorders
... – Protein filaments IN the neurons get twisted; interferes with neural communication and eventually kills the neurons ...
... – Protein filaments IN the neurons get twisted; interferes with neural communication and eventually kills the neurons ...
Crossing the Synaptic Gap
... 1. Review the steps in nervous system communication that students learned while playing “Locks & Keys” (see the activity, “Message in a Neuron”). Tell students that they will be simulating what happens when chemical messengers, or neurotransmitters, go from one neuron to the next. Point out that mos ...
... 1. Review the steps in nervous system communication that students learned while playing “Locks & Keys” (see the activity, “Message in a Neuron”). Tell students that they will be simulating what happens when chemical messengers, or neurotransmitters, go from one neuron to the next. Point out that mos ...
Psychology - Cobb Learning
... drug, prompting the is dependent on a user to increase the drug discontinues the dosage to achieve use of the drug effects previously obtained by lower – Withdrawal symptoms are usually doses of the drug the reverse of the drug’s effects. ...
... drug, prompting the is dependent on a user to increase the drug discontinues the dosage to achieve use of the drug effects previously obtained by lower – Withdrawal symptoms are usually doses of the drug the reverse of the drug’s effects. ...
Chemical Transmission BETWEEN Neurons
... (dendrites, cell body, axon, terminal buttons, synaptic vesicles, and receptor sites) ...
... (dendrites, cell body, axon, terminal buttons, synaptic vesicles, and receptor sites) ...
BIOPREPARATIONS OF FETAL ORIGIN
... efficiency as well as protein compounds intracellular synthesis ; nerve impulsing potentiation. Neuroprotection- neurons protection and their viability activation during acidosis, hypoxia, ischemia. Neurotoxins, free radicals and stimulating amino acids' damaging action reduction. Neurotrophic activ ...
... efficiency as well as protein compounds intracellular synthesis ; nerve impulsing potentiation. Neuroprotection- neurons protection and their viability activation during acidosis, hypoxia, ischemia. Neurotoxins, free radicals and stimulating amino acids' damaging action reduction. Neurotrophic activ ...
The Brain
... Cerebellum = deals with movement through regulation and coordination of bodily movements, posture and balance Pons = monitors the level of stimulation or consciousness and sleep (while asleep) Reticular Formation = monitors the state of the body and functions in such processes as arousal and s ...
... Cerebellum = deals with movement through regulation and coordination of bodily movements, posture and balance Pons = monitors the level of stimulation or consciousness and sleep (while asleep) Reticular Formation = monitors the state of the body and functions in such processes as arousal and s ...
2005-2007 - Parkinson Canada
... Dopamine neuron formation in the substantia nigra critically depends on two genes (called Ptx3 and Nurr1) activated in response to growth factors during brain development. It is not known however, whether a continual signal provided by these growth factors is required to stabilize the identity of do ...
... Dopamine neuron formation in the substantia nigra critically depends on two genes (called Ptx3 and Nurr1) activated in response to growth factors during brain development. It is not known however, whether a continual signal provided by these growth factors is required to stabilize the identity of do ...
Neuron Unit 3A
... • The best understood NT. Plays a role in learning and memory. ACh is the messenger at every junction of a motor neuron & skeletal muscle. If Ach transmission is blocked like anesthesia, muscles can’t contract ...
... • The best understood NT. Plays a role in learning and memory. ACh is the messenger at every junction of a motor neuron & skeletal muscle. If Ach transmission is blocked like anesthesia, muscles can’t contract ...
UNIVERSITY OF MALTA
... oscillations (Crunelli et al., 2005). In particular, the transient opening of T-type Ca2+ channels gives rise to low threshold Ca2+ potentials and associated high frequency bursts of action potentials that are present during sleep spindles and delta wave. In addition, the window component of the T-t ...
... oscillations (Crunelli et al., 2005). In particular, the transient opening of T-type Ca2+ channels gives rise to low threshold Ca2+ potentials and associated high frequency bursts of action potentials that are present during sleep spindles and delta wave. In addition, the window component of the T-t ...
Slide 1 - Elsevier Store
... release of glutamate into the synaptic cleft. (B) Excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) of hippocampal neurons comprise both AMPA- and NMDA-receptor components. EPSCs are upward-going at positive membrane potentials. Treatment with the NMDA receptor blocker D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (D- ...
... release of glutamate into the synaptic cleft. (B) Excitatory postsynaptic currents (EPSCs) of hippocampal neurons comprise both AMPA- and NMDA-receptor components. EPSCs are upward-going at positive membrane potentials. Treatment with the NMDA receptor blocker D-2-amino-5-phosphonopentanoic acid (D- ...
The Nervous System
... messages from one place to another. • Nerve cells (neurons) are the basic fundamental unit of the nervous system. ...
... messages from one place to another. • Nerve cells (neurons) are the basic fundamental unit of the nervous system. ...
Drugs and Teen Brain_12
... 3. When someone uses drugs repeatedly, their brain ________________ › A. becomes trained to crave the drug ...
... 3. When someone uses drugs repeatedly, their brain ________________ › A. becomes trained to crave the drug ...
Team 1
... patients. L-Dopa is used to help reduce brady-kinesia, rigidity and tremors. Other medications include Bromocriptine, Pramipexole, Ropinirole which all mimic dopamine in the brain. ...
... patients. L-Dopa is used to help reduce brady-kinesia, rigidity and tremors. Other medications include Bromocriptine, Pramipexole, Ropinirole which all mimic dopamine in the brain. ...
Nervous system 1 - INAYA Medical College
... Neurons What is neuron? Morphological classification of neurons Functional classification of neurons Parts of the brain & functions of each part Short notes on spinal cord, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) ...
... Neurons What is neuron? Morphological classification of neurons Functional classification of neurons Parts of the brain & functions of each part Short notes on spinal cord, meninges, cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.