Chapter 2
... Decrease = Alzheimer’s Disease Norephinephrine (or Noradrenaline) General arousal and mood Highly pleasurable reactions amphetamines Smoking Dopamine Influences learning and memory and emotional reactions Factor in schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome Blocking it used to treat psychosis ...
... Decrease = Alzheimer’s Disease Norephinephrine (or Noradrenaline) General arousal and mood Highly pleasurable reactions amphetamines Smoking Dopamine Influences learning and memory and emotional reactions Factor in schizophrenia and Tourette’s syndrome Blocking it used to treat psychosis ...
Abstract
... increasing neuronal excitability of these neurons by pharmacologically inhibiting their afterhyperpolarization decreased the rate of propulsive motility. Furthermore, by reducing neuronal excitability in inflamed preparations, I was able to restore colonic motor patterns. These findings indicate tha ...
... increasing neuronal excitability of these neurons by pharmacologically inhibiting their afterhyperpolarization decreased the rate of propulsive motility. Furthermore, by reducing neuronal excitability in inflamed preparations, I was able to restore colonic motor patterns. These findings indicate tha ...
LEC 4
... As activation of β1-adrenergic receptors in cardiac muscle results in activation of cAMP dependent protein kinase A, which phosphorylates and opens voltage operated calcium channels ,this increases calcium level in cell and results in increased rate and F.O.C. In contrast to activation of β2 adren ...
... As activation of β1-adrenergic receptors in cardiac muscle results in activation of cAMP dependent protein kinase A, which phosphorylates and opens voltage operated calcium channels ,this increases calcium level in cell and results in increased rate and F.O.C. In contrast to activation of β2 adren ...
Chapter 16A
... • Learning is the ability to acquire new knowledge or skills through instruction or experience • Memory is the process by which that knowledge is retained over time • For an experience to become part of memory, it must produce persistent structural and functional changes in the brain • The capab ...
... • Learning is the ability to acquire new knowledge or skills through instruction or experience • Memory is the process by which that knowledge is retained over time • For an experience to become part of memory, it must produce persistent structural and functional changes in the brain • The capab ...
studyingbrainpost
... Studying Cognitive Psychology: How the brain influences the mind and behavior ...
... Studying Cognitive Psychology: How the brain influences the mind and behavior ...
Nervous System
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite • The chemical signal gets transdu ...
... dendrites of many other nerve cells (synapses) • In a synapse, the axon and dendrite don’t touch, there is a gap • At each axon terminal, there are vesicles containing a neurotransmitter • Once the neurotransmitter is released, it binds to receptors on the dendrite • The chemical signal gets transdu ...
Psych B – Module 22
... drug, prompting the is dependent on a user to increase the drug discontinues the dosage to achieve use of the drug effects previously obtained by lower – Withdrawal symptoms are usually doses of the drug the reverse of the drug’s effects. ...
... drug, prompting the is dependent on a user to increase the drug discontinues the dosage to achieve use of the drug effects previously obtained by lower – Withdrawal symptoms are usually doses of the drug the reverse of the drug’s effects. ...
Motivation
... Both are active to some extent at the same time – not alternating. What happens during anger? ...
... Both are active to some extent at the same time – not alternating. What happens during anger? ...
electrochemical impulse - Glebe
... Parkinson’s disease Parkinson's disease belongs to a group of conditions called movement disorders. It is characterized by muscle rigidity, tremor, a slowing of physical movement (bradykinesia) and, in extreme cases, a loss of physical movement (akinesia). The primary symptoms are the results of dec ...
... Parkinson’s disease Parkinson's disease belongs to a group of conditions called movement disorders. It is characterized by muscle rigidity, tremor, a slowing of physical movement (bradykinesia) and, in extreme cases, a loss of physical movement (akinesia). The primary symptoms are the results of dec ...
Diapositive 1
... 1. They are not packaged in vesicles like most other neurotransmitters; instead, they are manufactured rapidly and on-demand. 2. 2. They are small and membrane pecrneable; once synthesized, they can diffuse rapidly across the membrane of their cell of origin to contact neighboring cells. 3. 3. They ...
... 1. They are not packaged in vesicles like most other neurotransmitters; instead, they are manufactured rapidly and on-demand. 2. 2. They are small and membrane pecrneable; once synthesized, they can diffuse rapidly across the membrane of their cell of origin to contact neighboring cells. 3. 3. They ...
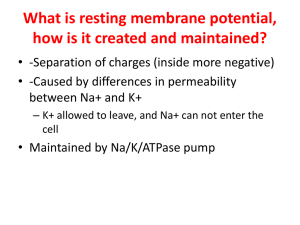
What is resting membrane potential, how is it created and maintained?
... action potential (nerve signal that travels to the brain) – Gustatory cortex where taste is interpreted ...
... action potential (nerve signal that travels to the brain) – Gustatory cortex where taste is interpreted ...
Demyelinating Diseases
... 1.Poverty of movement-hypertonia syndrome position: substantia nigra ;globus pallidus ex : Parkinson’ s disease 2.Increasing of movement-hypotonia syndrome position: caudate nucleus ;putamen nucleus ex : Chorea minor ...
... 1.Poverty of movement-hypertonia syndrome position: substantia nigra ;globus pallidus ex : Parkinson’ s disease 2.Increasing of movement-hypotonia syndrome position: caudate nucleus ;putamen nucleus ex : Chorea minor ...
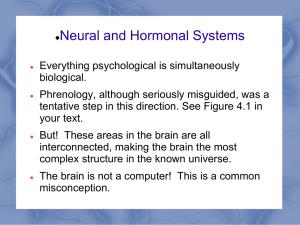
Module 4 Neural and Hormonal Systems
... recieving neuron and excite or inhibit a new action potential. The sender neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters. This is reuptake. ...
... recieving neuron and excite or inhibit a new action potential. The sender neuron reabsorbs excess neurotransmitters. This is reuptake. ...
Neurological Diseases ppt
... Seizure disorder of the brain, characterized by recurring and excessive discharge from neurons Seizures believed to be a result of spontaneous uncontrolled electrical activity of neurons Cause – Uncertain Diagnosed with EEG (electroencephalogram) ...
... Seizure disorder of the brain, characterized by recurring and excessive discharge from neurons Seizures believed to be a result of spontaneous uncontrolled electrical activity of neurons Cause – Uncertain Diagnosed with EEG (electroencephalogram) ...
Signal Transduction pt 1
... the kinase transfers a phosphate from ATP to tyrosine Phosphorylation of tyrosine triggers a cascade of reactions within the cell leading to a desired response One receptor can activate ten or more pathways / cellular response at once Important in regulating cell growth and reproduction ...
... the kinase transfers a phosphate from ATP to tyrosine Phosphorylation of tyrosine triggers a cascade of reactions within the cell leading to a desired response One receptor can activate ten or more pathways / cellular response at once Important in regulating cell growth and reproduction ...
The basics of brain communication
... and can occupy acetylcholine receptor sites, stimulating skeletal muscles and causing the heart to beat more rapidly. 2. Drugs can mimic or block the effects of a neurotransmitter by fitting into receptor sites and preventing the neurotransmitter from acting. • The drug curare produces almost instan ...
... and can occupy acetylcholine receptor sites, stimulating skeletal muscles and causing the heart to beat more rapidly. 2. Drugs can mimic or block the effects of a neurotransmitter by fitting into receptor sites and preventing the neurotransmitter from acting. • The drug curare produces almost instan ...
The Nervous System
... portion of the brain; controlling the senses, movement of muscles, thinking, and speech. CEREBELLUM – Section near the brain stem that controls balance, posture, and ...
... portion of the brain; controlling the senses, movement of muscles, thinking, and speech. CEREBELLUM – Section near the brain stem that controls balance, posture, and ...
Answers to Mastering Concepts Questions
... 1. The senses monitor internal and external stimuli, including blood pH, body temperature, levels of ions and water in interstitial fluids, and a host of other physical and chemical conditions. Information about these stimuli are transmitted to the central nervous system for processing and may trigg ...
... 1. The senses monitor internal and external stimuli, including blood pH, body temperature, levels of ions and water in interstitial fluids, and a host of other physical and chemical conditions. Information about these stimuli are transmitted to the central nervous system for processing and may trigg ...
A5: Neuropharamcology (student) - Ms De Souza`s Super Awesome
... of receptors on the post-synaptic membrane are reduced which leads to a decrease in the affect of the drugs. Increasing doses are needed to obtain the same ...
... of receptors on the post-synaptic membrane are reduced which leads to a decrease in the affect of the drugs. Increasing doses are needed to obtain the same ...
Biological Bases of Human Behavior
... Overall Learning Objectives: With the successful completion of this course, students will have a strong background in the science of the biological bases of human behavior. They will be able to account for human behavior on the basis of genetic and epi-genetic regulation of protein expression, the n ...
... Overall Learning Objectives: With the successful completion of this course, students will have a strong background in the science of the biological bases of human behavior. They will be able to account for human behavior on the basis of genetic and epi-genetic regulation of protein expression, the n ...
Chapter 9 Nervous
... Neuron immediately begins to repolarize. K ions diffuse rapidly out of the cell. Normal resting potential is reached. Impulses are transmitted to other neurons by a synapse. Neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine (ACH) help. ...
... Neuron immediately begins to repolarize. K ions diffuse rapidly out of the cell. Normal resting potential is reached. Impulses are transmitted to other neurons by a synapse. Neurotransmitters such as acetylcholine (ACH) help. ...
The Brain and the Neuron (1)
... Myelin Sheath • A layer of fatty tissue around the axon. This increases the speed of neural impulses and they pass from one node to the next. ...
... Myelin Sheath • A layer of fatty tissue around the axon. This increases the speed of neural impulses and they pass from one node to the next. ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.