Quiz: The Brain and Addiction
... 3. A: The “reward” system is part of the limbic system, which gets activated when you do something you like. Dopamine is a brain chemical that is released, producing feelings of pleasure and letting you know that something important is happening. 4. A: The brain is wired to remember feelings of plea ...
... 3. A: The “reward” system is part of the limbic system, which gets activated when you do something you like. Dopamine is a brain chemical that is released, producing feelings of pleasure and letting you know that something important is happening. 4. A: The brain is wired to remember feelings of plea ...
CH 8 Nervous part 1
... Ecstasy-related death is overheating (hyperthermia). MDMA interferes with the body's ability to regulate its own body temperature and to see other warning signs allowing the body to overheat without discomfort especially when dancing for hours in hot clubs. ...
... Ecstasy-related death is overheating (hyperthermia). MDMA interferes with the body's ability to regulate its own body temperature and to see other warning signs allowing the body to overheat without discomfort especially when dancing for hours in hot clubs. ...
Quiz: The Brain and Addiction
... the message to another neuron, the electrical impulse triggers the chemical signals called neurotransmitters, which flow into the synapse (the gap between the two neurons) and trigger an electrical impulse in the next neuron. Axons are the branches of a neuron that release the neurotransmitter. 8. B ...
... the message to another neuron, the electrical impulse triggers the chemical signals called neurotransmitters, which flow into the synapse (the gap between the two neurons) and trigger an electrical impulse in the next neuron. Axons are the branches of a neuron that release the neurotransmitter. 8. B ...
Psychopharmacology
... exposure was more disruptive – This exposure would affect the entire BFCS, rather than just one part (as in injection only in the nucleus basalis). ...
... exposure was more disruptive – This exposure would affect the entire BFCS, rather than just one part (as in injection only in the nucleus basalis). ...
No Slide Title
... Neurotransmitters effects on behavior depends on which receptor Acetylcholine (ACh) Motor control (paralysis) Attention and Memory (Alzheimer’s) ...
... Neurotransmitters effects on behavior depends on which receptor Acetylcholine (ACh) Motor control (paralysis) Attention and Memory (Alzheimer’s) ...
Study Guide
... elucidate its function, but is often difficult to do. When a protein’s 3D structure cannot be solved empirically, a “homology model” is often constructed, based on the solved structure of another similar protein. By aligning the amino acid sequences of the two proteins, the approximate shape of the ...
... elucidate its function, but is often difficult to do. When a protein’s 3D structure cannot be solved empirically, a “homology model” is often constructed, based on the solved structure of another similar protein. By aligning the amino acid sequences of the two proteins, the approximate shape of the ...
Nervous System Notes Outline
... 2. ________________ – large bridge of nerve fibers that connect right and left hemispheres of cerebral cortex 3. ________________ – monitors info from the autonomic N.S. and controls pituitary gland, regulates sleep and appetite 4. ________________ – transmits electrical signals from the eyes to the ...
... 2. ________________ – large bridge of nerve fibers that connect right and left hemispheres of cerebral cortex 3. ________________ – monitors info from the autonomic N.S. and controls pituitary gland, regulates sleep and appetite 4. ________________ – transmits electrical signals from the eyes to the ...
Chapter 11.1 Cell Communication
... movement of these receptors into the cell Ex: steroids – travel through the blood entering cells all over the body. - target cells only contain receptor molecule for that steroid in the cytoplasm, - binding occurs, then activation, in which receptor molecule enters nucleus to turn on specific genes ...
... movement of these receptors into the cell Ex: steroids – travel through the blood entering cells all over the body. - target cells only contain receptor molecule for that steroid in the cytoplasm, - binding occurs, then activation, in which receptor molecule enters nucleus to turn on specific genes ...
chapter 15 sensory, motor, and integrative systems
... c. They reach their effectors by way of the pyramidal pathways d. They are blocked by such drugs as Novocaine and morphine 8. Somatic pain that arises from stimulation of skin receptors is classified as _____ pain a. referred b. superficial somatic c. visceral d. deep somatic 9. Third-order neurons ...
... c. They reach their effectors by way of the pyramidal pathways d. They are blocked by such drugs as Novocaine and morphine 8. Somatic pain that arises from stimulation of skin receptors is classified as _____ pain a. referred b. superficial somatic c. visceral d. deep somatic 9. Third-order neurons ...
Chapter 2 PowerPoint
... • Deterioration of memory, reasoning, and language skills • Symptoms may be due to loss of ACh neurons ...
... • Deterioration of memory, reasoning, and language skills • Symptoms may be due to loss of ACh neurons ...
Neurons, neurotransmitters and other stuff we did last term…
... This is mostly review for those of you that took 2606 The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells ...
... This is mostly review for those of you that took 2606 The nervous system is made up, basically, of two types of cells ...
11/10/16 Memory Part 2 Reinforcement learning (12.2) • Involves a
... If two synapses, weak and strong, are stimulated at the same time (i.e. association), the weak synapse becomes stronger Associative LTP (12.9) o Many (almost simultaneous) inputs can be associated: “dendritic spike” o Memories are represented by patterns of synapses ...
... If two synapses, weak and strong, are stimulated at the same time (i.e. association), the weak synapse becomes stronger Associative LTP (12.9) o Many (almost simultaneous) inputs can be associated: “dendritic spike” o Memories are represented by patterns of synapses ...
Pharmacology II Tutoring: Drugs of abuse
... ABUSE THAT IS A DISSOCIATIVE ANESTHETIC AT HIGH DOSES? • A. Dimenhydrinate • B. Dextromethorphan ...
... ABUSE THAT IS A DISSOCIATIVE ANESTHETIC AT HIGH DOSES? • A. Dimenhydrinate • B. Dextromethorphan ...
Neuroscience in PT: Introduction and Review
... • Fast-acting MAJOR inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the entire CNS, e.g. inhibitory interneurons in spinal cord • Prevents excessive neural activity Barbiturates mimics the action of GABA and are used for sedation, as anticonvulsants. Baclofen, a muscle relaxant to control muscle spasticity, ...
... • Fast-acting MAJOR inhibitory neurotransmitter found in the entire CNS, e.g. inhibitory interneurons in spinal cord • Prevents excessive neural activity Barbiturates mimics the action of GABA and are used for sedation, as anticonvulsants. Baclofen, a muscle relaxant to control muscle spasticity, ...
MyersExpPsych7e_IM_Module 03 garber edited
... of the CNS when you sleep • Benzodiazepines (which include tranquilizers such as Valium) and alcohol work on GABA receptor complexes ...
... of the CNS when you sleep • Benzodiazepines (which include tranquilizers such as Valium) and alcohol work on GABA receptor complexes ...
What is the activation-synthesis hypothesis? What is an addiction
... suggests that dreams affect the motor commands of the brain but that the brain does not actually carried them out. ...
... suggests that dreams affect the motor commands of the brain but that the brain does not actually carried them out. ...
Gustation - West Virginia University
... cells are transformed epithelial cells that reside in taste buds in the papillae of the tongue, palate, pharynx, epiglottis, and esophagus Circumvallate Papillae Fungiform papillae Filliform papillae Saliva contacts the microvilli through the taste pore The solubility of a substance affects ...
... cells are transformed epithelial cells that reside in taste buds in the papillae of the tongue, palate, pharynx, epiglottis, and esophagus Circumvallate Papillae Fungiform papillae Filliform papillae Saliva contacts the microvilli through the taste pore The solubility of a substance affects ...
Name
... _____ 1. Sensory receptors found in the skin, which are specialized to detect temperature, pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes insid ...
... _____ 1. Sensory receptors found in the skin, which are specialized to detect temperature, pressure changes and pain. _____ 2. Specialized cells that myelinate the fibers of neurons found in the PNS _____ 3. Junction or point of close contact between neurons. _____ 4. Bundle of nerve processes insid ...
MAPPINGS BETWEEN BRAINS - Wichita State University
... • At what point do the neurons stop firing during ...
... • At what point do the neurons stop firing during ...
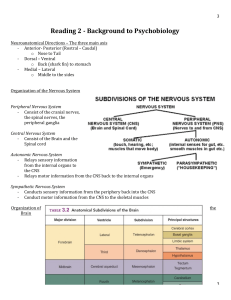
Reading 2 - Background to Psychobiology
... - Found in regions serving learning and memory - There are two kinds of ACh receptrors: 1. Nicotinic receptors – Ionotropic and found in muscle fibers as well as the CNS 2. Muscarinic receptors – Metabotropic and found in the CNS ...
... - Found in regions serving learning and memory - There are two kinds of ACh receptrors: 1. Nicotinic receptors – Ionotropic and found in muscle fibers as well as the CNS 2. Muscarinic receptors – Metabotropic and found in the CNS ...
How Opioid Drugs Bind to Receptors
... The four OR structures reveal opioid antagonist, have been solved . A side view of one of the The researchers speculate that this structures — that of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide (NOP) several evolutionarily conserved receptor — is depicted to show features shared by all four receptor pairing ...
... The four OR structures reveal opioid antagonist, have been solved . A side view of one of the The researchers speculate that this structures — that of the nociceptin/orphanin FQ peptide (NOP) several evolutionarily conserved receptor — is depicted to show features shared by all four receptor pairing ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.