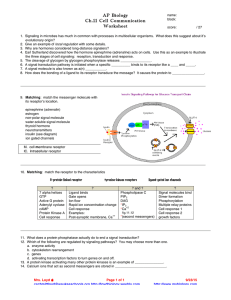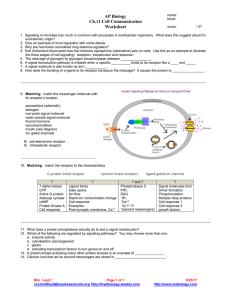
neuron
... Neuron Communication With Other Neurons • In order for one neuron to communicate with another it must pass a junction or gap called the synapse between the axon which is sending the signal and the dendrite which is receiving the signal. • At the ends of the axon, the terminal buttons release neur ...
... Neuron Communication With Other Neurons • In order for one neuron to communicate with another it must pass a junction or gap called the synapse between the axon which is sending the signal and the dendrite which is receiving the signal. • At the ends of the axon, the terminal buttons release neur ...
LECTURE23.EmotionDriveDrugs
... rates at different temperatures. Deviation from set point (37oC in humans) triggers other regions of hypothalamus initiate autonomic functions and behavioral drives Appetite: Hunger level is driven in part by hypothalamic control. Certain hypothalamic neurons have receptors for a hormone, leptin, wh ...
... rates at different temperatures. Deviation from set point (37oC in humans) triggers other regions of hypothalamus initiate autonomic functions and behavioral drives Appetite: Hunger level is driven in part by hypothalamic control. Certain hypothalamic neurons have receptors for a hormone, leptin, wh ...
How do neurotransmitters generate electrochemical signals in
... Transmission of Electrochemical Neural Signals and Neuropharmacology 1. How do neurotransmitters generate electrochemical signals in postsynaptic neurons? 2. What mechanisms terminate synaptic transmission? 3. What neurotransmitters have been identified? ...
... Transmission of Electrochemical Neural Signals and Neuropharmacology 1. How do neurotransmitters generate electrochemical signals in postsynaptic neurons? 2. What mechanisms terminate synaptic transmission? 3. What neurotransmitters have been identified? ...
Public Lecture - Indian Institute of Science Education and Research
... Abstract: The human brain is the interpreter of our senses, controller of movement and in fact responsible for all we embrace as civilisation. It consists of about 100 billion nerve cells which are interconnected through a million billion connections measuring up to 3.2 million kilometre of wiring. ...
... Abstract: The human brain is the interpreter of our senses, controller of movement and in fact responsible for all we embrace as civilisation. It consists of about 100 billion nerve cells which are interconnected through a million billion connections measuring up to 3.2 million kilometre of wiring. ...
KKDP4: The role of neurotransmitters in the transmission of neural
... KKDP4: The role of neurotransmitters in the transmission of neural information between neurons (lock-and-key process) to produce excitatory effects (as with glutamate) or inhibitory effects (as with gamma amino butyric acid [GABA]) ...
... KKDP4: The role of neurotransmitters in the transmission of neural information between neurons (lock-and-key process) to produce excitatory effects (as with glutamate) or inhibitory effects (as with gamma amino butyric acid [GABA]) ...
Answer Key
... Name: __________________________ Date: _____________ Units 3A & 3B Practice Questions 1. A person with schizophrenia may have an overactive dopamine system. Drugs used to treat this disorder prevent the action of dopamine by keeping it from binding to its receptors. These drugs are A) agonists. B) s ...
... Name: __________________________ Date: _____________ Units 3A & 3B Practice Questions 1. A person with schizophrenia may have an overactive dopamine system. Drugs used to treat this disorder prevent the action of dopamine by keeping it from binding to its receptors. These drugs are A) agonists. B) s ...
The Nervous System
... – Unfortunately, drugs used to increase acetylcholine to help restore normal levels appear to have small effects on improving memory ...
... – Unfortunately, drugs used to increase acetylcholine to help restore normal levels appear to have small effects on improving memory ...
Marina Florack
... o Gap is called the synaptic gap Neurtotransmitters: chemical messengers which cross synaptic gap b/t neurons o Receptor sites: “lock and key” o Acetylcholine: muscle action, learning and memory Alzheimer’s o Dopamine: perceptual awareness, muscle control Schizophrenia Parkinson’s disease o Se ...
... o Gap is called the synaptic gap Neurtotransmitters: chemical messengers which cross synaptic gap b/t neurons o Receptor sites: “lock and key” o Acetylcholine: muscle action, learning and memory Alzheimer’s o Dopamine: perceptual awareness, muscle control Schizophrenia Parkinson’s disease o Se ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Somatic Sensory System
... • More subjective that the other senses. The same stimulus can produce different responses in different individuals, or in the same individual in different circumstances. ...
... • More subjective that the other senses. The same stimulus can produce different responses in different individuals, or in the same individual in different circumstances. ...
Definitions
... • The ventral tegmentum or the ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum, Latin for covering) is part of the midbrain, lying close to the substantia nigra. • The ventral tegmentum is considered to be part of the pleasure system, or reward circuit, one of the major sources of incentive and behavioral m ...
... • The ventral tegmentum or the ventral tegmental area (VTA) (tegmentum, Latin for covering) is part of the midbrain, lying close to the substantia nigra. • The ventral tegmentum is considered to be part of the pleasure system, or reward circuit, one of the major sources of incentive and behavioral m ...
Psychoactive Drugs Power Point
... pain and anxiety and produce feelings of euphoria Mimic Endorphins to produce numbing of pain and good feeling • This causes brain to produce less in response so withdrawal is extremely difficult. Include: opium, morphine, heroin, methadone, Percodan, Demerol ...
... pain and anxiety and produce feelings of euphoria Mimic Endorphins to produce numbing of pain and good feeling • This causes brain to produce less in response so withdrawal is extremely difficult. Include: opium, morphine, heroin, methadone, Percodan, Demerol ...
How Does the Brain Work?
... The brain is a multilayered web of cells: nerve cells (neurons) and vastly more numerous glial cells that stabilize the chemical environment and regulate and protect neurons. The outermost layer, the cerebral cortex, is a fraction of an inch thick but contains 70 percent of all neurons. This most ev ...
... The brain is a multilayered web of cells: nerve cells (neurons) and vastly more numerous glial cells that stabilize the chemical environment and regulate and protect neurons. The outermost layer, the cerebral cortex, is a fraction of an inch thick but contains 70 percent of all neurons. This most ev ...
Claudia G. Almeida, Group leader CG Almeida graduated in
... CG Almeida graduated in Biochemistry by the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon in 1999. In 2002, she completed a Master degree in Neurosciences by the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Lisbon. During her master she found that the neuromodulator adenosine protects neurons from oxi ...
... CG Almeida graduated in Biochemistry by the Faculty of Sciences of the University of Lisbon in 1999. In 2002, she completed a Master degree in Neurosciences by the Faculty of Medicine of the University of Lisbon. During her master she found that the neuromodulator adenosine protects neurons from oxi ...
AChE inhibitor
... Loss of cholinergic neurons, in nucleus of Meynert, hippocampus & association cortices Loss of adrenergic neurons, in locus ceruleus Denudation of neurons, stripping of dendrites, damage to axons Increased microglia ...
... Loss of cholinergic neurons, in nucleus of Meynert, hippocampus & association cortices Loss of adrenergic neurons, in locus ceruleus Denudation of neurons, stripping of dendrites, damage to axons Increased microglia ...
Previously in Bio308
... Continuing from last time: Receptors 2 types of acetylcholine receptors: same ligand different response ...
... Continuing from last time: Receptors 2 types of acetylcholine receptors: same ligand different response ...
Targets for dopaminergic ligands
... between 0.2 and 0.6 were responders and all 7 outside this range were non-responders •This suggests that response could be improved by better regulation of the degree of transporter downregulation - See also( Meyer et al, Amer J Psych ...
... between 0.2 and 0.6 were responders and all 7 outside this range were non-responders •This suggests that response could be improved by better regulation of the degree of transporter downregulation - See also( Meyer et al, Amer J Psych ...
Neuroscience
... Neurons have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the cell body and axons take information away from the cell body. Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. Neurons contain some specialized structures (for example, synapses) ...
... Neurons have specialized extensions called dendrites and axons. Dendrites bring information to the cell body and axons take information away from the cell body. Neurons communicate with each other through an electrochemical process. Neurons contain some specialized structures (for example, synapses) ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.