Quiz Chapter 3 Brain Neural Communication Dr Myer How do
... What study methods will you use to remember this information? What functions is the Central Nervous System responsible for? What functions is the Peripheral Nervous System responsible for? What are two reasons that you need to know this information for a psychology class? What functions is t ...
... What study methods will you use to remember this information? What functions is the Central Nervous System responsible for? What functions is the Peripheral Nervous System responsible for? What are two reasons that you need to know this information for a psychology class? What functions is t ...
Basile, 1999
... The functional differences in dopamine affinity for each of these receptor alleles as expressed in CHO cell lines have been identified There is a higher dopamine affinity for the glycine homozygote cells, as compared to both heterozygote binding and serine/serine homozygotesin these cells. ...
... The functional differences in dopamine affinity for each of these receptor alleles as expressed in CHO cell lines have been identified There is a higher dopamine affinity for the glycine homozygote cells, as compared to both heterozygote binding and serine/serine homozygotesin these cells. ...
PPT File - Holden R
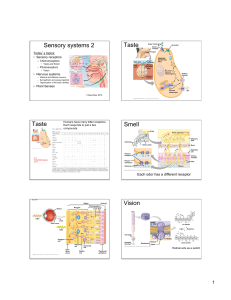
... information about environment and body – General: Distributed over large part of body • Somatic: Touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception, pain • Visceral: Internal organs and consist mostly of pain and ...
... information about environment and body – General: Distributed over large part of body • Somatic: Touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception, pain • Visceral: Internal organs and consist mostly of pain and ...
Chapter 14
... information about environment and body – General: Distributed over large part of body • Somatic: Touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception, pain • Visceral: Internal organs and consist mostly of pain and ...
... information about environment and body – General: Distributed over large part of body • Somatic: Touch, pressure, temperature, proprioception, pain • Visceral: Internal organs and consist mostly of pain and ...
Neuroscience - Instructional Resources
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
... size of the brain. They are not fully equipped, properly positioned, or completely functioning. 30,000 neurons would fit in the space the size of a pinhead. At birth, the brain’s cerebral cortex has 100 billion neurons; but few neurons are connected. ...
The Nervous System
... remembered they are stored in our long-term memory. Both memories store information in the cerebral cortex. ...
... remembered they are stored in our long-term memory. Both memories store information in the cerebral cortex. ...
Sensory Organs and Processes, Part II
... Activation by light closes sodium channels and hyperpolarizes the cell EXTRACELLULAR FLUID ...
... Activation by light closes sodium channels and hyperpolarizes the cell EXTRACELLULAR FLUID ...
The Nervous System - Needham.K12.ma.us
... Serotonin • An example of a neurotransmitter that affects mood, sleep, heart rate. • Can be a cause of depression and anxiety. – Depression—too little – Anxiety—too much What is depression? What is anxiety? Are these biological diseases? ...
... Serotonin • An example of a neurotransmitter that affects mood, sleep, heart rate. • Can be a cause of depression and anxiety. – Depression—too little – Anxiety—too much What is depression? What is anxiety? Are these biological diseases? ...
Learning Objectives
... Justify that acetylcholine has sympathetic & parasympathetic functions. Explain the mechanism of action of acetylcholine in modulating muscle contraction. Give the receptors through which these neurotransmitters carry out these functions. ...
... Justify that acetylcholine has sympathetic & parasympathetic functions. Explain the mechanism of action of acetylcholine in modulating muscle contraction. Give the receptors through which these neurotransmitters carry out these functions. ...
TEACHER`S GUIDE
... 5. Drugs interact with neurons at the synapse. Their targets can be receptors (e.g. for nicotine and marijuana) or uptake pumps (e.g. for cocaine). 6. By acting at the synapse, drugs change the way the brain functions and can affect behavior, thinking and learning, movement and sensations. Sometimes ...
... 5. Drugs interact with neurons at the synapse. Their targets can be receptors (e.g. for nicotine and marijuana) or uptake pumps (e.g. for cocaine). 6. By acting at the synapse, drugs change the way the brain functions and can affect behavior, thinking and learning, movement and sensations. Sometimes ...
PAPER #3: EMBARGOED PRESS RELEASE STRICTLY UNDER
... and the hyperactive release of dopamine. Over time, increasing activation of a key part of the extended amygdala-the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produces a long-lasting increase in signal transmission onto neurons that produce dopamine so that the rats became desensitized to the cocaine. Sin ...
... and the hyperactive release of dopamine. Over time, increasing activation of a key part of the extended amygdala-the bed nucleus of the stria terminalis produces a long-lasting increase in signal transmission onto neurons that produce dopamine so that the rats became desensitized to the cocaine. Sin ...
AP Psychology - Ms. Hofmann`s Website
... http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/morris2/chapter2/medialib/summary/1.html ...
... http://cwx.prenhall.com/bookbind/pubbooks/morris2/chapter2/medialib/summary/1.html ...
I Can Quit Anytime I Want by William D. Rogers Ball State University
... naltrexone that Sean had heard is sometimes used to help with drug dependence. “Why?” asked Sean as he sat in the examination room. He was trembling, sweating, and feeling like he was going to vomit. “I need to cure my addiction!” The doctor replied, “There is no cure for addiction. Naltrexone may h ...
... naltrexone that Sean had heard is sometimes used to help with drug dependence. “Why?” asked Sean as he sat in the examination room. He was trembling, sweating, and feeling like he was going to vomit. “I need to cure my addiction!” The doctor replied, “There is no cure for addiction. Naltrexone may h ...
Mod.73
... Patient is sedated & takes a muscle relaxer Causes a seizure which in some way shape of form changes the brain & can dramatically increase mood Current lasts 30 seconds to a minute, asleep for about an hour Three or more sessions between 2 to 4 week period—80% or more treated Can have some memory lo ...
... Patient is sedated & takes a muscle relaxer Causes a seizure which in some way shape of form changes the brain & can dramatically increase mood Current lasts 30 seconds to a minute, asleep for about an hour Three or more sessions between 2 to 4 week period—80% or more treated Can have some memory lo ...
handout
... and mediate fast transmission in the CNS via iR. In general, although not always (during development), GABA is inhibitory whereas glutamate is excitatory on post synaptic neurons. A) L-Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the mammalian CNS, acting through both ligand gated ion chann ...
... and mediate fast transmission in the CNS via iR. In general, although not always (during development), GABA is inhibitory whereas glutamate is excitatory on post synaptic neurons. A) L-Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the mammalian CNS, acting through both ligand gated ion chann ...
GABAB receptor binds a novel scaffolding protein that forms multiple
... suggested that Y2H assays can fail to detect certain protein:protein interactions. We have therefore undertaken a series of GST pull-down experiments to identify additional interactions between PICKl / GRIP and the glutamate receptor (GluR) subunits. GST-fusions were made for the cytoplasmic domain ...
... suggested that Y2H assays can fail to detect certain protein:protein interactions. We have therefore undertaken a series of GST pull-down experiments to identify additional interactions between PICKl / GRIP and the glutamate receptor (GluR) subunits. GST-fusions were made for the cytoplasmic domain ...
title of video - Discovery Education
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
... 2. Why are the basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem referred to as the "old brain"? The basal ganglia, limbic system and brain stem are called the "old brain" because they control the subconscious activities and are thought to have developed in humans before the more conscious brain structure ...
1 Introduction to Neurobiology Rudolf Cardinal NST 1B
... is required to bring the neuron to threshold and fire an AP. However, if enough EPSPs arrive at the neuron and are close enough to each other in space and time (and overcome any inhibition from IPSPs) they may sum and trigger an AP. In this way the postsynaptic neuron can integrate information from ...
... is required to bring the neuron to threshold and fire an AP. However, if enough EPSPs arrive at the neuron and are close enough to each other in space and time (and overcome any inhibition from IPSPs) they may sum and trigger an AP. In this way the postsynaptic neuron can integrate information from ...
Chapter 13 Review Question Answers
... combination prevents inactivation of levodopa to 3-O-methyldopa (3OMD). This metabolite may block uptake of levodopa into the brain. Ch. 13 Review Question Answers ...
... combination prevents inactivation of levodopa to 3-O-methyldopa (3OMD). This metabolite may block uptake of levodopa into the brain. Ch. 13 Review Question Answers ...
Chapter 5
... consists of the brain and spinal cord. The key structures and areas of the CNS include the reticular activating system (RAS), hypothalmus, cerebral cortex, limbic system, medial forebrain bundle, basal ganglia, and the brain stem. ...
... consists of the brain and spinal cord. The key structures and areas of the CNS include the reticular activating system (RAS), hypothalmus, cerebral cortex, limbic system, medial forebrain bundle, basal ganglia, and the brain stem. ...
File
... Cells have proteins called receptors that bind to signaling molecules and initiate a physiological response. Different receptors are specific for different molecules. Dopamine receptors bind dopamine, insulin receptors bind insulin, nerve growth factor receptors bind nerve growth factor, and so on. ...
... Cells have proteins called receptors that bind to signaling molecules and initiate a physiological response. Different receptors are specific for different molecules. Dopamine receptors bind dopamine, insulin receptors bind insulin, nerve growth factor receptors bind nerve growth factor, and so on. ...
Neuronal signaling and synapses
... -substantia nigra – midbrain; projects to the striatum (caudate & putamen) facilitating voluntary movement degeneration of dopaminergic cells in the substantia nigra produces Parkinson’s disease -ventral tegmental area – midbrain; projects to part of the forebrain (prefrontal cortex) and parts of ...
... -substantia nigra – midbrain; projects to the striatum (caudate & putamen) facilitating voluntary movement degeneration of dopaminergic cells in the substantia nigra produces Parkinson’s disease -ventral tegmental area – midbrain; projects to part of the forebrain (prefrontal cortex) and parts of ...
Molecular prosthetics for vision restoration based on freely
... Molecular prosthetics for vision restoration based on freely-diffusible and covalently bound photoswitches Light-regulated drugs allow remotely photoswitching biological activity and enable plausible therapies based on small molecules. We develop efficient compounds to manipulate neuronal activity f ...
... Molecular prosthetics for vision restoration based on freely-diffusible and covalently bound photoswitches Light-regulated drugs allow remotely photoswitching biological activity and enable plausible therapies based on small molecules. We develop efficient compounds to manipulate neuronal activity f ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.