Neurophysiology of the Regulation of Food Intake
... Drug and Food Reinforcement leads to an increase in the release of dopamine from the presynaptic neuron Dopamine reuptake is blocked at the synapse leading to an accumulation in the synaptic cleft Coupled, these lead to an increased stimulation of dopamine receptors ...
... Drug and Food Reinforcement leads to an increase in the release of dopamine from the presynaptic neuron Dopamine reuptake is blocked at the synapse leading to an accumulation in the synaptic cleft Coupled, these lead to an increased stimulation of dopamine receptors ...
CNS - Misericordia University
... • Slow wave sleep is thought to be restorative to brain function (Children have more total sleep time and are in stage 4 more than adults); Elderly have about the same total sleep time as adults but broken into smaller episodes, also spend less time in REM. Time spent in Stage 4 declines with age. • ...
... • Slow wave sleep is thought to be restorative to brain function (Children have more total sleep time and are in stage 4 more than adults); Elderly have about the same total sleep time as adults but broken into smaller episodes, also spend less time in REM. Time spent in Stage 4 declines with age. • ...
Module 3 - DHS Home
... • One reason the nucleus accumbens acts up more in adolescence is due to the different ways the younger brains deal with the neurotransmitter dopamine. • Dopamine, the brain chemical involved in motivation and in reinforcing behavior, is particularly abundant and active in the teen years (Wallis, 20 ...
... • One reason the nucleus accumbens acts up more in adolescence is due to the different ways the younger brains deal with the neurotransmitter dopamine. • Dopamine, the brain chemical involved in motivation and in reinforcing behavior, is particularly abundant and active in the teen years (Wallis, 20 ...
Media:oreilly_genpsych_ch2_neuron
... Neurons integrate electrical signals (depolarization) received via synapses on their dendrites, from axons of other neurons When membrane potential exceeds threshold, action potential (spike) is sent down axon, triggering release of neurotransmitter in synapse, which opens ion channels on receiving ...
... Neurons integrate electrical signals (depolarization) received via synapses on their dendrites, from axons of other neurons When membrane potential exceeds threshold, action potential (spike) is sent down axon, triggering release of neurotransmitter in synapse, which opens ion channels on receiving ...
2002-2003 - Parkinson Canada
... Lay Summary: The cause of Parkinson's disease remains unknown. For several decades, environmental factors were thought to be primarily responsible for causing the death of the cells that produce dopamine. However, recently investigators from around the world have identified specific changes in certa ...
... Lay Summary: The cause of Parkinson's disease remains unknown. For several decades, environmental factors were thought to be primarily responsible for causing the death of the cells that produce dopamine. However, recently investigators from around the world have identified specific changes in certa ...
Parkinson`s Disease Glossary A guide to the scientific language of
... cause a form of early onset Parkinson’s. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Part of the peripheral nervous system, consisting of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves that control involuntary actions, in particular the heart, smooth muscle (such as bladder and blood vessels) and glands. Autophagy: the ...
... cause a form of early onset Parkinson’s. Autonomic Nervous System (ANS): Part of the peripheral nervous system, consisting of sympathetic and parasympathetic nerves that control involuntary actions, in particular the heart, smooth muscle (such as bladder and blood vessels) and glands. Autophagy: the ...
Brain Structure and Function
... - emotional responses such as euphoria or pleasure. Newer antipsychotic medication focus on particular dopaminergic pathways in the brain. Lessening EPSE’s. ...
... - emotional responses such as euphoria or pleasure. Newer antipsychotic medication focus on particular dopaminergic pathways in the brain. Lessening EPSE’s. ...
The nervous system
... Dopamine: It is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which means that when it comes to its receptor sites, it blocks the tendency of that neuron to fire. Dopamine is associated with reward mechanisms in the brain. Severe deficiency and overabundance of this neurotransmitter can cause drastic results. It ...
... Dopamine: It is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, which means that when it comes to its receptor sites, it blocks the tendency of that neuron to fire. Dopamine is associated with reward mechanisms in the brain. Severe deficiency and overabundance of this neurotransmitter can cause drastic results. It ...
Neurons - WordPress.com
... Kinds of Neurotransmitters • Dopamine • Discovered in 1950’s • Arvid Carlsson • It is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning that when it finds its way to its receptor sites, it blocks the tendency of that neuron to fire. • If it feels good, dopamine neurons are probably involved • Drugs like coca ...
... Kinds of Neurotransmitters • Dopamine • Discovered in 1950’s • Arvid Carlsson • It is an inhibitory neurotransmitter, meaning that when it finds its way to its receptor sites, it blocks the tendency of that neuron to fire. • If it feels good, dopamine neurons are probably involved • Drugs like coca ...
C! **D!**E!**F! - Amherst College
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
... • Before it was understood that nerves signal using electricity, what mode of signalling was attributed to nerves? • What is the earliest experiment (as distinct from observation) cited in Chapter 1? • What are the arguments that experiments on animals such as rats can be relevant to understanding h ...
Can Parkinsons disease be cured by an injection of fetal
... Fox has managed the symptoms of his disease with the drug combining carbidopa and levodopa, but the deterioration is progressive. Parkinson’s is marked by degeneration of motor function, such as trembling, unsteady walking gait and muscle rigidity or other loss of function. It was first documented i ...
... Fox has managed the symptoms of his disease with the drug combining carbidopa and levodopa, but the deterioration is progressive. Parkinson’s is marked by degeneration of motor function, such as trembling, unsteady walking gait and muscle rigidity or other loss of function. It was first documented i ...
neurons
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
... Cell Body: Life support center of the neuron. Dendrites: Branching extensions at the cell body. Receive messages from other neurons. Axon: Long single extension of a neuron, covered with myelin [MY-uh-lin] sheath to insulate and speed up messages through neurons. Terminal Branches of axon: Branched ...
Excitatory Amino Acids Brochure
... Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and dysfunction of glutamate transmission is the likely cause of a variety of diseases including neurodegeneration following cerebral ischemia, Huntington's chorea, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, epilepsy, spasticity, emesis, chronic pa ...
... Glutamate is the major excitatory neurotransmitter in the brain and dysfunction of glutamate transmission is the likely cause of a variety of diseases including neurodegeneration following cerebral ischemia, Huntington's chorea, amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, epilepsy, spasticity, emesis, chronic pa ...
Ch 13 - lanoue
... thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates their reaction time. Repeat twice. Record the results. Challenge: Try the experiment again while the catcher recites addition or multiplication facts. Compare the results. What happened to ...
... thumb and index finger. The distance the ruler falls before he/she stops it with his thumb and finger indicates their reaction time. Repeat twice. Record the results. Challenge: Try the experiment again while the catcher recites addition or multiplication facts. Compare the results. What happened to ...
Chapter 15: Neurological Disorders
... Flajolet, M., Greengard, P. (2010). Lowering beta-amyloid levels rescues learning and memory in a Down syndrome mouse model. PLoS One. 5(6):e10943. ...
... Flajolet, M., Greengard, P. (2010). Lowering beta-amyloid levels rescues learning and memory in a Down syndrome mouse model. PLoS One. 5(6):e10943. ...
Lecture 8 Basics: Organelles Overview: Types of signaling Types of
... Binding of a ligand to a ligand gated ion channel: A. Causes a conformational change in the protein B. Allows ions to flow across the membrane against their concentration gradients C. Causes the movement of a G-protein D. Results in the hydrolysis of ATP E. Both A and B ...
... Binding of a ligand to a ligand gated ion channel: A. Causes a conformational change in the protein B. Allows ions to flow across the membrane against their concentration gradients C. Causes the movement of a G-protein D. Results in the hydrolysis of ATP E. Both A and B ...
Document
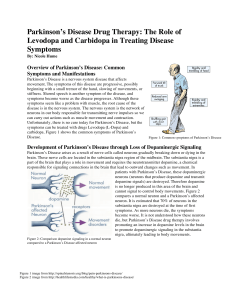
... responsible for signaling connections in the brain that lead to outward changes such as movement. In patients with Parkinson’s Disease, these dopaminergic neurons (neurons that produce dopamine and transmit dopamine signals) are destroyed. Therefore dopamine is no longer produced in this area of the ...
... responsible for signaling connections in the brain that lead to outward changes such as movement. In patients with Parkinson’s Disease, these dopaminergic neurons (neurons that produce dopamine and transmit dopamine signals) are destroyed. Therefore dopamine is no longer produced in this area of the ...
Autonomic Nervous System
... •The concentration of neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft and the number of receptors on target cells determine the magnitude of the synaptic response. ...
... •The concentration of neurotransmitter in the synaptic cleft and the number of receptors on target cells determine the magnitude of the synaptic response. ...
Structure of the Brain PowerPoint Notes
... – relatively short neuron whose primary task is making connections between other neurons • _________________neuron – carry information awayfrom the spinal cord to produce responses in various muscles and organs throughout the body ...
... – relatively short neuron whose primary task is making connections between other neurons • _________________neuron – carry information awayfrom the spinal cord to produce responses in various muscles and organs throughout the body ...
Lecture 9: Cell signaling
... ERK translocates to the nucleus and phosphorylates the transcription factor Elk-1. Elk-1 binds to the serum response element (SRE) in a complex with serum response factor (SRF). ...
... ERK translocates to the nucleus and phosphorylates the transcription factor Elk-1. Elk-1 binds to the serum response element (SRE) in a complex with serum response factor (SRF). ...
The Nervous System
... 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
... 1. Control center for all body activities 2. Responds and adapts to changes that occur both inside and outside the body (Ex: pain, temperature, pregnancy) ...
NATURAL PRODUCT EXTRACTS TO PROTECT
... several plant-‐derived natural extracts (“Aldonts”) that potently neutralize the toxic damage to human neurons inflicted by several insults that include ferrous ion (relevant to multiple sclerosis, stroke and trau ...
... several plant-‐derived natural extracts (“Aldonts”) that potently neutralize the toxic damage to human neurons inflicted by several insults that include ferrous ion (relevant to multiple sclerosis, stroke and trau ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.