1 Pathophysiology of Alzheimer`s Disease Alzheimer`s disease (AD
... later onset (>60) and 5-15% are familial in origin (late onset FAD) with ½ of these occurring before age 60(familial early onset FAD). (Beers et al, 2006) These early onset familial cases involve 3 known gene defects which include: amyloid precursor protein gene on chromosome 21; presenilin 1 on chr ...
... later onset (>60) and 5-15% are familial in origin (late onset FAD) with ½ of these occurring before age 60(familial early onset FAD). (Beers et al, 2006) These early onset familial cases involve 3 known gene defects which include: amyloid precursor protein gene on chromosome 21; presenilin 1 on chr ...
Chapter 2: Neuroscience and Behavior
... Dopamine imbalance also involved in schizophrenia See Video—Living with Schizophrenia ...
... Dopamine imbalance also involved in schizophrenia See Video—Living with Schizophrenia ...
Ions in Your Life
... from being used. Excitation and extra excitation occurs and neurotransmitter stops being produced by the body itself. Neurotransmitters are blocked from going through reuptake transporters by original neuron. Extra excitation occurs and body stops producing neurotransmitter. ...
... from being used. Excitation and extra excitation occurs and neurotransmitter stops being produced by the body itself. Neurotransmitters are blocked from going through reuptake transporters by original neuron. Extra excitation occurs and body stops producing neurotransmitter. ...
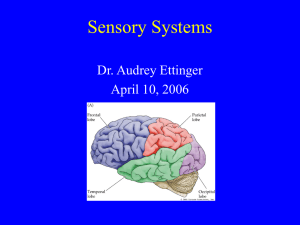
The Senses
... • Produces a receptor potential, a graded change in response to opening or closing ion channels • Neurotransmitter release is increased to signal the CNS ▫ The rate change in action potentials signals the brain ...
... • Produces a receptor potential, a graded change in response to opening or closing ion channels • Neurotransmitter release is increased to signal the CNS ▫ The rate change in action potentials signals the brain ...
lec#10 done by Dima Kilani
... major NT of the sympathetic system. It's released in the synapse between the postganglionic neuron and the effectors and interact with different adrenergic receptors on them (α1, α2, β1 , β2) the sympathetic effect on sweat glands follows the same mechanism except that Ach is the major (final) sympa ...
... major NT of the sympathetic system. It's released in the synapse between the postganglionic neuron and the effectors and interact with different adrenergic receptors on them (α1, α2, β1 , β2) the sympathetic effect on sweat glands follows the same mechanism except that Ach is the major (final) sympa ...
BC368 Metabolic Disorders Poster Session Spring 2015 Glycogen
... Porphyrias result in enzymatic deficiencies of the heme biosynthesis pathway, which predominates in the liver and in erythrocytes. Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP) results from a deficiency in porphobinlinogen (PBG) deaminase, an enzyme in the heme biosynthesis pathway, causing the buildup of PBG ...
... Porphyrias result in enzymatic deficiencies of the heme biosynthesis pathway, which predominates in the liver and in erythrocytes. Acute Intermittent Porphyria (AIP) results from a deficiency in porphobinlinogen (PBG) deaminase, an enzyme in the heme biosynthesis pathway, causing the buildup of PBG ...
Gill_poster_SL - University of Kentucky
... • These preliminary data suggest that chronic exposure of CP 55,940 during adolescence may alter glutamate transmission in the forebrain motive circuit via changes in GLT1 expression. However, such changes seem reversible if there is no additional treatment. • Along with changes in glutamate transmi ...
... • These preliminary data suggest that chronic exposure of CP 55,940 during adolescence may alter glutamate transmission in the forebrain motive circuit via changes in GLT1 expression. However, such changes seem reversible if there is no additional treatment. • Along with changes in glutamate transmi ...
Chapter 34-4B: Second Messengers
... Some of membrane proteins are receptors of signal transduction. Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters bind the signal transduction receptors located on the surface of target cell membranes. Signals are transferred to the inside of target cell through the transmembrane receptor protein. Sign ...
... Some of membrane proteins are receptors of signal transduction. Hormones, growth factors and neurotransmitters bind the signal transduction receptors located on the surface of target cell membranes. Signals are transferred to the inside of target cell through the transmembrane receptor protein. Sign ...
Chapter 48 p. 1040-1053
... memorization requires rapid changes in strength of nerve connections long-term depression (LTD): postsynaptic cell’s decreased responsiveness to action potential long-term potentiation(LTP): enhanced responsiveness to action potentials; associated with release of neurotransmitter glutamate (bi ...
... memorization requires rapid changes in strength of nerve connections long-term depression (LTD): postsynaptic cell’s decreased responsiveness to action potential long-term potentiation(LTP): enhanced responsiveness to action potentials; associated with release of neurotransmitter glutamate (bi ...
Metabolism of Amino Acids with Branched Radicals
... Block 1. Phenylketonuria (PKU) – hereditary disease (phenyl-pyruvic oligofhrenia), caused by the lack of phenylalanine 4-monooxigenase synthesis in the liver. The disease is connected with phenylalanine and phenyl pyruvate accumulation. If untreated it can cause problems with brain development, lead ...
... Block 1. Phenylketonuria (PKU) – hereditary disease (phenyl-pyruvic oligofhrenia), caused by the lack of phenylalanine 4-monooxigenase synthesis in the liver. The disease is connected with phenylalanine and phenyl pyruvate accumulation. If untreated it can cause problems with brain development, lead ...
W10 Brain Development
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
... ▫ Undergoes significant changes during adolescence Not fully developed until mid-20’s. ...
Unit 3- Biological Psychology Study Guide
... Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolutionary perspective and its relationship to biological psychology. Understand and identify the intricate weaving between t ...
... Discuss chromosomal abnormalities (common), molecular genetics, and the gene-environment interaction in terms of their relations to biological psychology. Also, discuss the evolutionary perspective and its relationship to biological psychology. Understand and identify the intricate weaving between t ...
Application Six - Sheila Tooker Impey
... The patient is an adult. Adult mammals no longer produce the chemical and molecular conditions that stimulate and guide neural growth (Garrett, 2011). Although axons do not regenerate and neuron replacement is limited at best, it is possible for some function recovery through compensation (Garrett, ...
... The patient is an adult. Adult mammals no longer produce the chemical and molecular conditions that stimulate and guide neural growth (Garrett, 2011). Although axons do not regenerate and neuron replacement is limited at best, it is possible for some function recovery through compensation (Garrett, ...
Molecular Identification and the Immunolocalization of Purinergic Signaling Receptors in... Mammalian Vomeronasal Organ
... Information about the external world is conveyed through the nervous system via specialized sensory organs such as the vomeronasal organ (VNO). The VNO is crucial for pheromone detection and the regulation of social behavior in many mammals. Recent research has shown that purinergic signaling pathwa ...
... Information about the external world is conveyed through the nervous system via specialized sensory organs such as the vomeronasal organ (VNO). The VNO is crucial for pheromone detection and the regulation of social behavior in many mammals. Recent research has shown that purinergic signaling pathwa ...
Instructor`s Answer Key
... to molecules that are dissolved in fluid, and are thus classified as chemoreceptors. These chemoreceptors are further classified as exteroceptors, which respond to chemical changes in the external environment. Taste receptors are specialized epithelial cells with microvilli. These receptors are not ...
... to molecules that are dissolved in fluid, and are thus classified as chemoreceptors. These chemoreceptors are further classified as exteroceptors, which respond to chemical changes in the external environment. Taste receptors are specialized epithelial cells with microvilli. These receptors are not ...
Brain Parts Matching Review - District 196 e
... _______ 5. a structure in the limbic system linked to memory. _______ 6. the master endocrine gland. _______ 7. includes the visual areas, which receive visual information from the opposite visual field. _______ 8. a nerve network in the brain stem that plays an important role in controlling arousal ...
... _______ 5. a structure in the limbic system linked to memory. _______ 6. the master endocrine gland. _______ 7. includes the visual areas, which receive visual information from the opposite visual field. _______ 8. a nerve network in the brain stem that plays an important role in controlling arousal ...
Week 14 The Memory Function of Sleep
... What happens to coherence in CA1 and CA3, and what might that mean? What IS coherence? • Coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of single or multiple waves. There is both spatial and temporal coherence. • During REM sleep, there is reduced coherence betwee ...
... What happens to coherence in CA1 and CA3, and what might that mean? What IS coherence? • Coherence describes all properties of the correlation between physical quantities of single or multiple waves. There is both spatial and temporal coherence. • During REM sleep, there is reduced coherence betwee ...
BL 616 Test 1 study guide. The test will probably have 20 multiple
... Ch 6-7 amino acids, protein structure Be able to draw generic amino acid, peptide bond between two amino acids You will be provided with a diagram of the amino acid side chains if that is needed Describe the different levels of protein structure – what is quaternary What is difference between a poly ...
... Ch 6-7 amino acids, protein structure Be able to draw generic amino acid, peptide bond between two amino acids You will be provided with a diagram of the amino acid side chains if that is needed Describe the different levels of protein structure – what is quaternary What is difference between a poly ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. The self-examination of
... b) is based on naturalistic observation. c) leads us to underestimate the causal relationships between events. d) may be unrepresentative of what is generally true. 11. An axon is: a) the extension of a neuron that carries messages away from the cell body. b) a cell that serves as the basic building ...
... b) is based on naturalistic observation. c) leads us to underestimate the causal relationships between events. d) may be unrepresentative of what is generally true. 11. An axon is: a) the extension of a neuron that carries messages away from the cell body. b) a cell that serves as the basic building ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.