II. ORGANIZATION OF THE HUMAN NERVOUS
... Pituitary Gland - _”Master Gland”_____. Releases _hormones___ that regulate other endocrine glands. Pineal Gland – Light-sensitive gland that secretes hormone called _melatonin___; regulates _”internal clock”________. V. DISEASES & CONDITIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (pp. 798-799) A. Meningitis – I ...
... Pituitary Gland - _”Master Gland”_____. Releases _hormones___ that regulate other endocrine glands. Pineal Gland – Light-sensitive gland that secretes hormone called _melatonin___; regulates _”internal clock”________. V. DISEASES & CONDITIONS OF THE NERVOUS SYSTEM (pp. 798-799) A. Meningitis – I ...
MRI Center for Biomedical Imaging
... Cognition after menopause and COMT genotype Cannabis, schizophrenia and reward: Self medication and agonist treatment? ...
... Cognition after menopause and COMT genotype Cannabis, schizophrenia and reward: Self medication and agonist treatment? ...
Review of Neurobiology
... Bind to receptors on dendrite of another cell Postsynaptic cell Receptors are specific Dopamine receptors will only bind dopamine ...
... Bind to receptors on dendrite of another cell Postsynaptic cell Receptors are specific Dopamine receptors will only bind dopamine ...
PPTX - Bonham Chemistry
... gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse) or over a long distance (from the secretory organ, th ...
... gland into the bloodstream and transported therein to reach its target cell. The distinction between a neurotransmitter and a hormone is physiological, not chemical. It depends on whether the molecule acts over a short distance (across a synapse) or over a long distance (from the secretory organ, th ...
A Data Mining Survey of the Allen Brain Atlas
... anatomical database called the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas has been conducted to reveal a detailed analysis of these neuromodulatory systems. The Allen Mouse Brain Atlas is an interactive, genome-wide image database of gene expression. A combination of RNA in situ hybridization data, detailed Reference ...
... anatomical database called the Allen Mouse Brain Atlas has been conducted to reveal a detailed analysis of these neuromodulatory systems. The Allen Mouse Brain Atlas is an interactive, genome-wide image database of gene expression. A combination of RNA in situ hybridization data, detailed Reference ...
2015-2016_1Semester_Exam1_050116
... photoreceptor cells. In the dark, rods and cones are depolarized. In the presence of light, the photobleaching of rhodopsin takes place that triggers downstream actions resulting in hyperpolarization of the receptors. The projecting neurons of the retina are called optic nerves . The image of an obj ...
... photoreceptor cells. In the dark, rods and cones are depolarized. In the presence of light, the photobleaching of rhodopsin takes place that triggers downstream actions resulting in hyperpolarization of the receptors. The projecting neurons of the retina are called optic nerves . The image of an obj ...
The Biological Bases of Behavior
... motor neurons and voluntary muscles contributes to attention, arousal and memory ...
... motor neurons and voluntary muscles contributes to attention, arousal and memory ...
Lecture 6C
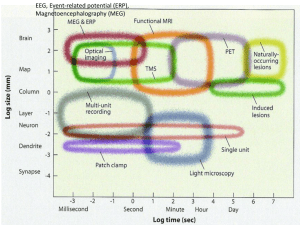
... experiment, the animals were sacrificed and the cortical radioactivity pattern was analyzed. This method provides high resolution radioactive labeling of active neurons. The physical pattern of active neurons (right panel, darker pixels correspond to greater neuronal activity) is clearly a geometric ...
... experiment, the animals were sacrificed and the cortical radioactivity pattern was analyzed. This method provides high resolution radioactive labeling of active neurons. The physical pattern of active neurons (right panel, darker pixels correspond to greater neuronal activity) is clearly a geometric ...
Nervous-System
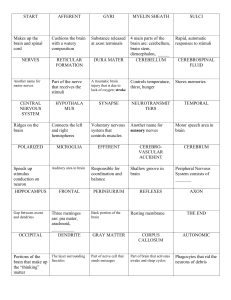
... cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord causes bleeding in the brain Cerebral Palsy – Neuromuscular disability in which voluntary muscles are poorly controlled and become spastic – Most likely due to lack of oxygen during delivery Cerebrovascular Accident (A.K.A Stroke) – Blood ...
... cerebrospinal fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord causes bleeding in the brain Cerebral Palsy – Neuromuscular disability in which voluntary muscles are poorly controlled and become spastic – Most likely due to lack of oxygen during delivery Cerebrovascular Accident (A.K.A Stroke) – Blood ...
I. The Nervous System
... • It is not true that you use only 10% of your brain • 100 billion neurons ...
... • It is not true that you use only 10% of your brain • 100 billion neurons ...
Fill in the blanks on LB page 67-68.
... 1. As the body develops tolerance to a drug, larger and more frequent doses are needed to produce the same effect; this reflects physical drug dependence. 2. Psychological drug dependence, or habituation, develops when a user begins to crave the feelings associated with using a particular drug and c ...
... 1. As the body develops tolerance to a drug, larger and more frequent doses are needed to produce the same effect; this reflects physical drug dependence. 2. Psychological drug dependence, or habituation, develops when a user begins to crave the feelings associated with using a particular drug and c ...
The retinal toxicity of an antiepileptic drug blocking the GABA
... By contrast to brain structures, GABA, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter, remains excitatory in the adult retinal network. Furthermore, it can activate GABAc receptors, which do not desensitize and thus generate large sustained responses. These specificities could explain the retinal toxicity of ...
... By contrast to brain structures, GABA, the main inhibitory neurotransmitter, remains excitatory in the adult retinal network. Furthermore, it can activate GABAc receptors, which do not desensitize and thus generate large sustained responses. These specificities could explain the retinal toxicity of ...
210_Lecture6_motor
... weakness, fatigue, droopy eyelids, slurred speech, difficulty swallowing and breathing Treatments include medications that suppress the immune system or inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
... weakness, fatigue, droopy eyelids, slurred speech, difficulty swallowing and breathing Treatments include medications that suppress the immune system or inhibit acetylcholinesterase (AChE) ...
Biopsychology - WordPress.com
... Neuroplasticity and learning Emotions, stress, illness (schizophrenia, anxiety, etc) Language and cognition Lateralization of function ...
... Neuroplasticity and learning Emotions, stress, illness (schizophrenia, anxiety, etc) Language and cognition Lateralization of function ...
48.5, .6, .7
... • Mature neurons are unable to undergo cell division • Progenitor- fact that stem cells are committed to becoming either neurons or glia ...
... • Mature neurons are unable to undergo cell division • Progenitor- fact that stem cells are committed to becoming either neurons or glia ...
Mod 07-Lecture - Phoenix Military Academy
... NTs will only fit into particular receptor sites, like keys that only fit certain locks. NTs have either an excitatory effect, making it more likely the receiving neuron will fire; or an inhibitory effect, making it less likely. Particular NTs seem to effect particular behavior and emotions. Dopamin ...
... NTs will only fit into particular receptor sites, like keys that only fit certain locks. NTs have either an excitatory effect, making it more likely the receiving neuron will fire; or an inhibitory effect, making it less likely. Particular NTs seem to effect particular behavior and emotions. Dopamin ...
Eagleman Ch 16. Neurological and Psychiatric Disorders
... Environmental factors during fetal development or early life seem important in the incidence of schizophrenia. ...
... Environmental factors during fetal development or early life seem important in the incidence of schizophrenia. ...
The First Year - Archbishop Hoban High School
... skills. How the brain takes shape in a baby’s first year of life has profound effects on the baby’s life. Newborns learn about the world primarily through their senses----sight, hearing, smell, taste, and touch. ...
... skills. How the brain takes shape in a baby’s first year of life has profound effects on the baby’s life. Newborns learn about the world primarily through their senses----sight, hearing, smell, taste, and touch. ...
Slide
... • Concurrent stimulation of weak and strong synapses to a given neuron strengthens the weak ones. ...
... • Concurrent stimulation of weak and strong synapses to a given neuron strengthens the weak ones. ...
Nervous System Outline
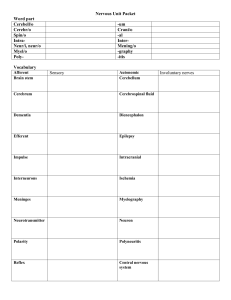
... - Basic element of nervous system - Separated by synapses o - Neurotransmitters o ...
... - Basic element of nervous system - Separated by synapses o - Neurotransmitters o ...
Snow Shaun Snow Professor: William Green Biology 1090, 8am
... the requirement of assistance in simple tasks. Stage 6 is when most care takers will also require professional help. This stage consists of constant fluctuations in personalities, worsening of memory, and unpredictable sleep patterns and actions. Once stage 7 is reached the command in the brain for ...
... the requirement of assistance in simple tasks. Stage 6 is when most care takers will also require professional help. This stage consists of constant fluctuations in personalities, worsening of memory, and unpredictable sleep patterns and actions. Once stage 7 is reached the command in the brain for ...
Examples of the value of animal use in neuroscience from the FENS
... advances in fundamental knowledge about the function of the brain and nervous system. Such knowledge is essential for understanding and treating neurological and mental illnesses. Neurological and mental illnesses affect people throughout the life span from childhood to ...
... advances in fundamental knowledge about the function of the brain and nervous system. Such knowledge is essential for understanding and treating neurological and mental illnesses. Neurological and mental illnesses affect people throughout the life span from childhood to ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.