Reward” and “Punishment” Function of the Limbic System
... Schizophrenia. is a group of psychotic disorders characterized by a loss of the normal perceptions of reality evidenced by delusions, hallucinations, and disordered speech and behavior. Dopamine antagonists are effective when used as antipsychotic (neuroleptic) drugs due to the inhibition of dopamin ...
... Schizophrenia. is a group of psychotic disorders characterized by a loss of the normal perceptions of reality evidenced by delusions, hallucinations, and disordered speech and behavior. Dopamine antagonists are effective when used as antipsychotic (neuroleptic) drugs due to the inhibition of dopamin ...
Final Review
... • Schaffer collaterals (pyramidal cells in the CA3 -> pyramidal cells in the CA1) ...
... • Schaffer collaterals (pyramidal cells in the CA3 -> pyramidal cells in the CA1) ...
brain
... • Olfactory receptors in upper nasal passages detect molecules in the air • Odor molecules come in many shapes and sizes, so we have many different receptors to detect them ...
... • Olfactory receptors in upper nasal passages detect molecules in the air • Odor molecules come in many shapes and sizes, so we have many different receptors to detect them ...
PHARMACOKINETICS: What the body does to a drug
... fraction eliminated per unit of time. Note problems arising from zero order kinetics e.g. alcohol Plasma half-life-time taken to decline to half of a drug’s previous level. Only useful when first order kinetics apply Steady state-usually reached in dosing after 5 half-lives of the drug have elapsed ...
... fraction eliminated per unit of time. Note problems arising from zero order kinetics e.g. alcohol Plasma half-life-time taken to decline to half of a drug’s previous level. Only useful when first order kinetics apply Steady state-usually reached in dosing after 5 half-lives of the drug have elapsed ...
Nervous System Function
... Nerve – collection of axons in PNS Ganglia – collection of cell bodies & dendrites Tract – collection of axons in CNS (White Matter) Nuclei – collection of cell bodies (Grey Matter) ...
... Nerve – collection of axons in PNS Ganglia – collection of cell bodies & dendrites Tract – collection of axons in CNS (White Matter) Nuclei – collection of cell bodies (Grey Matter) ...
Autonomic Nervous System Period 5 Jacquelene Hanein, Karina
... autonomic functions like breathing, digestion, circulatory system function, swallowing, sneezing ...
... autonomic functions like breathing, digestion, circulatory system function, swallowing, sneezing ...
Neurons
... the end of the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit the neural impulse over synapse PSP – postsynaptic potential – change in membrane potential: ...
... the end of the axon of one neuron and the dendrites of another Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit the neural impulse over synapse PSP – postsynaptic potential – change in membrane potential: ...
Document
... receive input from other neurons are called: A. dendrites B. axons C. vesicles D. myelins ...
... receive input from other neurons are called: A. dendrites B. axons C. vesicles D. myelins ...
Purinergic signalling in neuroregeneration
... neuroprotection and neuroregeneration (Burnstock, 2015). Trauma, ischaemia and stroke result in release of ATP/adenosine from cells in the central nervous system (CNS), which can either enhance neuronal and glial cell damage or serve as neuroprotectors. Injury produces upregulation of both P2X and P ...
... neuroprotection and neuroregeneration (Burnstock, 2015). Trauma, ischaemia and stroke result in release of ATP/adenosine from cells in the central nervous system (CNS), which can either enhance neuronal and glial cell damage or serve as neuroprotectors. Injury produces upregulation of both P2X and P ...
Computer Research II Drugs and Mind
... 3a. How many nerve cells are there in the brain? ____________________________________ 4a. What is a special cell in the brain and what does it do? _____________________________ Click BACK and go to The Neuron and choose Millions and Billions of Cells http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/cells.html ...
... 3a. How many nerve cells are there in the brain? ____________________________________ 4a. What is a special cell in the brain and what does it do? _____________________________ Click BACK and go to The Neuron and choose Millions and Billions of Cells http://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/cells.html ...
The Psychopathology of Pain
... • NMDA normally quiet BUT – In tissue injury, increased neurotransmitter release results in depolarization that activates NMDA receptors Ca++ influx strengthened connection btwn nociceptor and pain-transmitting DH neuron heightened response to noxious stimuli = ...
... • NMDA normally quiet BUT – In tissue injury, increased neurotransmitter release results in depolarization that activates NMDA receptors Ca++ influx strengthened connection btwn nociceptor and pain-transmitting DH neuron heightened response to noxious stimuli = ...
Nervous System Outline 1
... A. Starts with the evolution of an organism wide Nerve Net in Cnidarians (Jellyfish) to help “control” movement. B. Evolution of a brain (a mass of neurons) leads to greater control of the system. It utilizes a nerve cord to span the body. C. The evolution of other sensory organs in the head region, ...
... A. Starts with the evolution of an organism wide Nerve Net in Cnidarians (Jellyfish) to help “control” movement. B. Evolution of a brain (a mass of neurons) leads to greater control of the system. It utilizes a nerve cord to span the body. C. The evolution of other sensory organs in the head region, ...
pain - MEFST
... breathing) – “second” “slower” pain, conducted via C-fibers Deep burning dull difuze pain from internal organs, muscles and joints – often called “referred pain” ...
... breathing) – “second” “slower” pain, conducted via C-fibers Deep burning dull difuze pain from internal organs, muscles and joints – often called “referred pain” ...
Novel cognitive enhancers (CE): influence on working memory and
... reasoning, and judgment. Cognitive functions mainly categorized into memory, attention, creativity and intelligence. Studies of cognition have shown that certain pharmacological compounds can exert ‘procognitive’ and/or nootropic effects, improving cognition and memory in otherwise normal laboratory ...
... reasoning, and judgment. Cognitive functions mainly categorized into memory, attention, creativity and intelligence. Studies of cognition have shown that certain pharmacological compounds can exert ‘procognitive’ and/or nootropic effects, improving cognition and memory in otherwise normal laboratory ...
Organization of the nervous system
... determines whether it will fire •Axon:Extending fiber that conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other cells. ...
... determines whether it will fire •Axon:Extending fiber that conducts impulses away from the cell body and transmits to other cells. ...
somatosensation
... • The transduction by mechanoreceptors (sense of touch) involves “stretch-sensitive” ion (sodium) channels on the membrane of the touch receptors • A mechanical deformation of the skin opens the channels and sodium enters into the « nerve » terminal, inducing a depolarization, corresponding to a rec ...
... • The transduction by mechanoreceptors (sense of touch) involves “stretch-sensitive” ion (sodium) channels on the membrane of the touch receptors • A mechanical deformation of the skin opens the channels and sodium enters into the « nerve » terminal, inducing a depolarization, corresponding to a rec ...
FINAL241NSCC
... B. What protective fluid layer occurs within these? ____________________________________________ C. Name the cells that produce and secrete this fluid. __________________________________________ D. Name one protective cell in epithelia of the digestive tract and trachea. _________________________ E. ...
... B. What protective fluid layer occurs within these? ____________________________________________ C. Name the cells that produce and secrete this fluid. __________________________________________ D. Name one protective cell in epithelia of the digestive tract and trachea. _________________________ E. ...
neurotransmitter testing in dried urine
... prescription drugs in the U.S. in 2014 included antipsychotics, antidepressants, and attention-deficit disorder drugs2. The current treatment paradigm in addressing poor brain health relies on diagnostic tools that encompass the evaluation of clinical signs and symptoms. Despite the lack of testable ...
... prescription drugs in the U.S. in 2014 included antipsychotics, antidepressants, and attention-deficit disorder drugs2. The current treatment paradigm in addressing poor brain health relies on diagnostic tools that encompass the evaluation of clinical signs and symptoms. Despite the lack of testable ...
Synapses and neurotransmitters
... • Basically, five conditions must be met before we call something a neurotransmitter – Present in terminal – Released on firing – Placing substance on organ or another neuron emulates firing – Uptake for inactivation – Inactivation blocks stimulation ...
... • Basically, five conditions must be met before we call something a neurotransmitter – Present in terminal – Released on firing – Placing substance on organ or another neuron emulates firing – Uptake for inactivation – Inactivation blocks stimulation ...
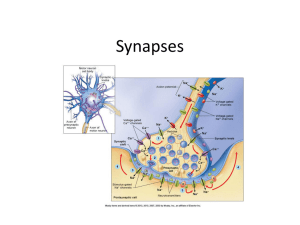
4. Nervous System: Synapses
... several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
... several working together or “rapid fire” of repeated stimulation= summation • Does all sensory information received by sensory neurons get transmitted to conscious part of brain? ...
APP Ch_3 Outline
... Monoamines – 3 Neurotransmitters: Dopamine, Norepinephrine, and Serotonin. Dopamine – Used by Neurons that Control Voluntary Movement. 1. Degeneration of Dopamine leads to Parkinson’s disease. Serotonin – Plays a prominent role in sleep, wakefulness, and eating Behavior. Abnormal levels of M ...
... Monoamines – 3 Neurotransmitters: Dopamine, Norepinephrine, and Serotonin. Dopamine – Used by Neurons that Control Voluntary Movement. 1. Degeneration of Dopamine leads to Parkinson’s disease. Serotonin – Plays a prominent role in sleep, wakefulness, and eating Behavior. Abnormal levels of M ...
Study Questions - Nervous System
... 22. Explain how a neurotransmitter can be excitatory (meaning what?) or inhibitory. ...
... 22. Explain how a neurotransmitter can be excitatory (meaning what?) or inhibitory. ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.