Carriers of Disease
... • Flagella – most common form of movement, extension of plasma membrane • Spirochetes – spiral shaped that may have slimy chemicals excreted and a flagella • Taxis – have an attraction to chemical that may be beneficial or harmful ...
... • Flagella – most common form of movement, extension of plasma membrane • Spirochetes – spiral shaped that may have slimy chemicals excreted and a flagella • Taxis – have an attraction to chemical that may be beneficial or harmful ...
Cell Signalling
... Responses induced by the activation of a nuclear hormone receptor. (A) Early primary response and (B) delayed secondary response. The figure shows the responses to a steroid hormone, but the same principles apply for all ligands that activate this family of receptor proteins. Some of the primary-re ...
... Responses induced by the activation of a nuclear hormone receptor. (A) Early primary response and (B) delayed secondary response. The figure shows the responses to a steroid hormone, but the same principles apply for all ligands that activate this family of receptor proteins. Some of the primary-re ...
Nervous Tissue
... What is the main function of this tissue? Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors that control their activity ...
... What is the main function of this tissue? Transmit electrical signals from sensory receptors and to effectors that control their activity ...
Sleep and Dreams - VCC Library
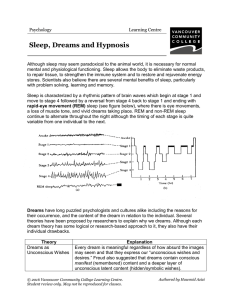
... (relationships, work, health etc.) and provide an opportunity to resolve current concerns and problems. In this theory, symbols of a dream convey its true meaning. Dream as a modified version of the cognitive activity that goes on when we are awake; brain is doing the same work as if it was awake, w ...
... (relationships, work, health etc.) and provide an opportunity to resolve current concerns and problems. In this theory, symbols of a dream convey its true meaning. Dream as a modified version of the cognitive activity that goes on when we are awake; brain is doing the same work as if it was awake, w ...
Sleep and Dreams - VCC Library
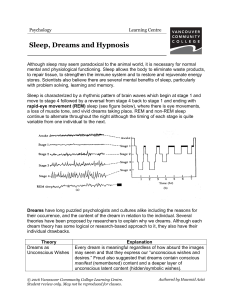
... (relationships, work, health etc.) and provide an opportunity to resolve current concerns and problems. In this theory, symbols of a dream convey its true meaning. Dream as a modified version of the cognitive activity that goes on when we are awake; brain is doing the same work as if it was awake, w ...
... (relationships, work, health etc.) and provide an opportunity to resolve current concerns and problems. In this theory, symbols of a dream convey its true meaning. Dream as a modified version of the cognitive activity that goes on when we are awake; brain is doing the same work as if it was awake, w ...
The Other Senses
... • Endogenous opioids (enkephalins, endorphins and dynorphins) – neuromodulators: inhibit Ca+ influx into pre-synaptic neuron or open K+ channels in post-synaptic neuron ...
... • Endogenous opioids (enkephalins, endorphins and dynorphins) – neuromodulators: inhibit Ca+ influx into pre-synaptic neuron or open K+ channels in post-synaptic neuron ...
vocabulary worksheet
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
... 27. The _______________ is the outermost covering of the brain consisting of densely packed neurons, responsible for higher thought processes and interpretation of sensory input. 28. The thick band of neurons that connects the right and left cerebral hemispheres is called the _________________ _____ ...
sensory receptors, neuronal circuits for processing information
... mechanoreceptors because even weak mechanical stimulation of the skin induces them to produce action potentials. All low-threshold mechanoreceptors are innervated by relatively large myelinated axons ensuring the rapid central transmission of tactile information. ...
... mechanoreceptors because even weak mechanical stimulation of the skin induces them to produce action potentials. All low-threshold mechanoreceptors are innervated by relatively large myelinated axons ensuring the rapid central transmission of tactile information. ...
Biology 232
... sensation – conscious or subconscious awareness of internal or external stimuli perception – conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations (occurs in thalamus and cerebral cortex) Basic Sensory Pathway 1) sensory receptor – specialized cell or dendrites that detect stimuli stimulus – change i ...
... sensation – conscious or subconscious awareness of internal or external stimuli perception – conscious awareness and interpretation of sensations (occurs in thalamus and cerebral cortex) Basic Sensory Pathway 1) sensory receptor – specialized cell or dendrites that detect stimuli stimulus – change i ...
pharm chapter 8 [3-16
... Divided into catecholamines (dopamine, norepi, epi; derivatives of tyrosine), indoleamine (serotonin; synthesized from tryptophan), histamine (formed from histidine) o Catecholamines formed tyrosine L-DOPA dopamine norepi epi Levodopa is L-DOPA; used to compensate for loss of dopaminergic ...
... Divided into catecholamines (dopamine, norepi, epi; derivatives of tyrosine), indoleamine (serotonin; synthesized from tryptophan), histamine (formed from histidine) o Catecholamines formed tyrosine L-DOPA dopamine norepi epi Levodopa is L-DOPA; used to compensate for loss of dopaminergic ...
xpx tampa bay
... XPX TAMPA BAY The Self Aware Advisor: The Key to Seeing and influencing Others September 11, 2013 ...
... XPX TAMPA BAY The Self Aware Advisor: The Key to Seeing and influencing Others September 11, 2013 ...
Chapter 14 - The Nervous System: Organization
... called meninges. Meningitis is an infection of these coverings. • The brain contains fluid-filled ventricles that are continuous with the central canal of the cord. ...
... called meninges. Meningitis is an infection of these coverings. • The brain contains fluid-filled ventricles that are continuous with the central canal of the cord. ...
Function
... Its substantia nigra is closely associated with motor system pathways of the basal ganglia. ...
... Its substantia nigra is closely associated with motor system pathways of the basal ganglia. ...
Module 04
... (for example, the bricks) that make up a structure (for example, a house). The structure of our nervous system, or neural information system, is made up of neurons (they are its building blocks). To fathom our thoughts and actions, memories and moods, we must first understand how neurons work and co ...
... (for example, the bricks) that make up a structure (for example, a house). The structure of our nervous system, or neural information system, is made up of neurons (they are its building blocks). To fathom our thoughts and actions, memories and moods, we must first understand how neurons work and co ...
PAIN - ISpatula
... – stimulation produce potent antinociception • LOCUS COERULEUS (LC) – noradrenergic containing neurones – diffusely innnervates CNS at all levels – descending fibres inhibit dorsal horn nociceptive activity and spinal nociceptive reflexes ...
... – stimulation produce potent antinociception • LOCUS COERULEUS (LC) – noradrenergic containing neurones – diffusely innnervates CNS at all levels – descending fibres inhibit dorsal horn nociceptive activity and spinal nociceptive reflexes ...
Slide 1
... FIGURE 15-5: The biosynthesis and catabolism of serotonin. Not only does 5-HT have important physiological effects of its own, but also it is the precursor of the hormone melatonin. Note that in the pineal gland, which lies “outside” the blood–brain barrier, serotonin is converted enzymatically to ...
... FIGURE 15-5: The biosynthesis and catabolism of serotonin. Not only does 5-HT have important physiological effects of its own, but also it is the precursor of the hormone melatonin. Note that in the pineal gland, which lies “outside” the blood–brain barrier, serotonin is converted enzymatically to ...
100 - Bloomfield Central School
... If an axon were able to produce larger or smaller action potentials at different times, what would this violate? ...
... If an axon were able to produce larger or smaller action potentials at different times, what would this violate? ...
Exam 3 Review KEY
... 6) The smaller / bigger the size of the nerve fiber, the slower / faster the speed of nerve impulse. And the less / more myelin, which means larger diameter of the nerve fiber, the greater the speed. 7) Bundles of afferent and efferent neurons outside the CNS but inside the PNS are referred to as ne ...
... 6) The smaller / bigger the size of the nerve fiber, the slower / faster the speed of nerve impulse. And the less / more myelin, which means larger diameter of the nerve fiber, the greater the speed. 7) Bundles of afferent and efferent neurons outside the CNS but inside the PNS are referred to as ne ...
Powerpoint slides are here
... symptoms: hard to initiate and maintain movements (bradykinesia) death of dopaminergic substantia nigra neurons dying cells have Lewy bodies, ...
... symptoms: hard to initiate and maintain movements (bradykinesia) death of dopaminergic substantia nigra neurons dying cells have Lewy bodies, ...
What is the Nervous System?
... Neurons – individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. Parts of the Neuron: ...
... Neurons – individual cells in the nervous system that receive, integrate, and transmit information. Parts of the Neuron: ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.