AUTONOMIC NERVOUS SYSTEM REVIEW QUESTIONS:
... 7. How can emotional states effect such things as digestive and cardiac function? Control of the ANS is overseen by higher centres – for example the thalamus and the hypothalamus. Therefore, emotional states can affect visceral organ activity. Emotional states may influence increased heart rate, or ...
... 7. How can emotional states effect such things as digestive and cardiac function? Control of the ANS is overseen by higher centres – for example the thalamus and the hypothalamus. Therefore, emotional states can affect visceral organ activity. Emotional states may influence increased heart rate, or ...
3 - CSU, Chico
... it early, for a young brain is more likely to recover normal function than an older brain. However, when the damage is to an area of the brain that is involved with more general cognitive functioning rather than with a specific cognitive ability such as language, the reverse is often true. ...
... it early, for a young brain is more likely to recover normal function than an older brain. However, when the damage is to an area of the brain that is involved with more general cognitive functioning rather than with a specific cognitive ability such as language, the reverse is often true. ...
Brain Matters - FirstClass Login
... The human brain only weighs 3lbs. It consumes up to 20% of your body energy The brain makes up less than 2.5% of your total body weight ...
... The human brain only weighs 3lbs. It consumes up to 20% of your body energy The brain makes up less than 2.5% of your total body weight ...
Real Neurons for Engineers
... • Potassium channels return the cell to a resting state. They often control the overall time constant. • Chloride channels may be inhibitory, shunting (desensitizing) and even facilitatory. They tend to have longer time constants. • Sodium channels are typically depolarizing. Short time constants. • ...
... • Potassium channels return the cell to a resting state. They often control the overall time constant. • Chloride channels may be inhibitory, shunting (desensitizing) and even facilitatory. They tend to have longer time constants. • Sodium channels are typically depolarizing. Short time constants. • ...
Nervous System - Gordon State College
... Acetylcholine (ACh): involved in muscle contraction, cognition, and memory formation Dopamine (DA): controls large muscle movements; influences pleasure and motivation ...
... Acetylcholine (ACh): involved in muscle contraction, cognition, and memory formation Dopamine (DA): controls large muscle movements; influences pleasure and motivation ...
Slide ()
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
... A. The morphology of peripheral somatic sensory receptors on hairy skin (left) and hairless, or glabrous, skin (right). B. The muscle spindle organ (top inset) is a stretch receptor located within the muscle. It receives an efferent innervation from the spinal cord that maintains receptor sensitivit ...
NEUROTRANSMITTERS AND RECEPTORS
... • There is a link between acetylcholine and Alzheimer's disease: There is something on the order of a 90% loss of acetylcholine in the brains of people suffering from Alzheimer's, which is a major cause of senility. ...
... • There is a link between acetylcholine and Alzheimer's disease: There is something on the order of a 90% loss of acetylcholine in the brains of people suffering from Alzheimer's, which is a major cause of senility. ...
Illegal Drugs
... possess • Synthetic Drugs: Chemical drugs artificially made in a laboratory • Illicit Drug Use: use or sale of any illegal substance or drug ...
... possess • Synthetic Drugs: Chemical drugs artificially made in a laboratory • Illicit Drug Use: use or sale of any illegal substance or drug ...
Chapter 12
... Sensory adaptation: the ability to ignore unimportant stimuli (Olfactory and taste receptors adapt quickly; pain receptors do not.) 3. Touch and Pressure Senses 3 kinds of touch and pressure receptors areas follows: Lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscles; in subcutaneous tissue, ligaments and tendons; det ...
... Sensory adaptation: the ability to ignore unimportant stimuli (Olfactory and taste receptors adapt quickly; pain receptors do not.) 3. Touch and Pressure Senses 3 kinds of touch and pressure receptors areas follows: Lamellated (Pacinian) corpuscles; in subcutaneous tissue, ligaments and tendons; det ...
psy221 tutorial kit - Covenant University
... chemical messengers called____ neurotransmitters. 7. The sympathetic nervous system arouses us for action and the parasympathetic nervous system calms us down. Together, the two systems make up the______ peripheral nervous system. 8. What part of the nervous system would neurons of the spinal cord b ...
... chemical messengers called____ neurotransmitters. 7. The sympathetic nervous system arouses us for action and the parasympathetic nervous system calms us down. Together, the two systems make up the______ peripheral nervous system. 8. What part of the nervous system would neurons of the spinal cord b ...
Physical Development Use pp. 411-417, 445-448, and 455
... _______________ pitches cannot be distinguished as clearly. The retina receives about _______________ as much light as it used to because the _______________ is now less transparent. In the elderly, the immune system _______________ against “big” illnesses, such as _______________ and ______________ ...
... _______________ pitches cannot be distinguished as clearly. The retina receives about _______________ as much light as it used to because the _______________ is now less transparent. In the elderly, the immune system _______________ against “big” illnesses, such as _______________ and ______________ ...
Auditory: Stimulus Auditory
... cochlea by the tectorial membrane • Afferent Signals: unevenly distributed to allow most signals for range of human speech • Pathway: contralateral to primary auditory cortex • CNS Areas: Primary in superior temporal lobe; Wernicke’s, Broca’s, and right hemisphere specializations • Perception: C ...
... cochlea by the tectorial membrane • Afferent Signals: unevenly distributed to allow most signals for range of human speech • Pathway: contralateral to primary auditory cortex • CNS Areas: Primary in superior temporal lobe; Wernicke’s, Broca’s, and right hemisphere specializations • Perception: C ...
Overview of the Nervous System
... Alzheimer Disease (AD) • Neurofibrillary tangles • Senile plaques • Clinical manifestations – Forgetfulness, emotional upset, disorientation, confusion, lack of concentration, decline in abstraction, problem solving, and judgment ...
... Alzheimer Disease (AD) • Neurofibrillary tangles • Senile plaques • Clinical manifestations – Forgetfulness, emotional upset, disorientation, confusion, lack of concentration, decline in abstraction, problem solving, and judgment ...
FYI information about sensory perception
... the optic nerve. These events cannot be repeated in a given receptor until the rhodopsin is regenerated, and this requires a series of chemical reactions. In other words, after the visual pigment has been "bleached" by the image of an object (i.e., after the rhodopsin has dissociated under the influ ...
... the optic nerve. These events cannot be repeated in a given receptor until the rhodopsin is regenerated, and this requires a series of chemical reactions. In other words, after the visual pigment has been "bleached" by the image of an object (i.e., after the rhodopsin has dissociated under the influ ...
Biological and Psychology Why are psychologists concerned about
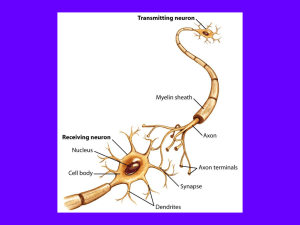
... Synapse - a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal but ...
... Synapse - a junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or cell body of the receiving neuron. This tiny gap is called the synaptic gap or cleft. Neurotransmitters – chemicals that transmit information from one neuron to another. Stored in small sacs within the terminal but ...
My-B-Tabs™ Myoden Spray - wm
... Adenosine Monophosphate is purine nucleotide that is an intermediate in cellular metabolism and nucleic acid metabolism. AMP is directly involved in many normal biochemical processes including protein synthesis (intermediate to Krebs cycle) and is precursor to the energy carrier molecule Adenosine T ...
... Adenosine Monophosphate is purine nucleotide that is an intermediate in cellular metabolism and nucleic acid metabolism. AMP is directly involved in many normal biochemical processes including protein synthesis (intermediate to Krebs cycle) and is precursor to the energy carrier molecule Adenosine T ...
E.4.4 List three examples of excitatory and three examples of
... • inhibiting the release of neurotransmitters from the pre-synaptic neurons such as GABA • the reduction in GABA frees dopaminergic synapses from inhibition • leading to increase in dopamine release in the pleasure pathway ...
... • inhibiting the release of neurotransmitters from the pre-synaptic neurons such as GABA • the reduction in GABA frees dopaminergic synapses from inhibition • leading to increase in dopamine release in the pleasure pathway ...
States of Consciuosnes
... It works on a biological clock schedule to ensure that we have the opportunity to sleep NREM (typically dreamless) = bodily restoration and REM (dream) = mind restoration ...
... It works on a biological clock schedule to ensure that we have the opportunity to sleep NREM (typically dreamless) = bodily restoration and REM (dream) = mind restoration ...
Neural Oscillators on the Edge: Harnessing Noise to Promote Stability
... Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, Harvard University ...
... Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering, Harvard University ...
UNIT 2: Internal geological agents
... It consists of neurons which transmit It consists og endocrine glands which release information through electrical and chemical hormons signals. A -Nervous system: It follows the following pathway: Stimulus→Repectors→Effectors→Answer There are two types of stimuli: External stimuli: Chemical sustunc ...
... It consists of neurons which transmit It consists og endocrine glands which release information through electrical and chemical hormons signals. A -Nervous system: It follows the following pathway: Stimulus→Repectors→Effectors→Answer There are two types of stimuli: External stimuli: Chemical sustunc ...
RAPID REVIEW The nervous system is made up of a complex
... into the receptor sites of target cells when they get into our nervous system. Agonists lead to a similar response in the target cell as the neurotransmitter itself, while antagonists block or reduce the action of the neurotransmitter on the target cell. There are at least 50-100 different types of ...
... into the receptor sites of target cells when they get into our nervous system. Agonists lead to a similar response in the target cell as the neurotransmitter itself, while antagonists block or reduce the action of the neurotransmitter on the target cell. There are at least 50-100 different types of ...
Neurobiology of Addiction - The University of Sydney
... including biological (neurobiology), social (family, friends, work) and personal (psychological processes relating to addiction). ...
... including biological (neurobiology), social (family, friends, work) and personal (psychological processes relating to addiction). ...
The Impact of Ecstasy on the Brain
... • Numerous short-term and long-term side effects occur when taking Ecstasy. • Lacing or substitution in pills make it difficult to predict which effects may occur. • Further studies must be conducted to understand the lasting effects the drugs has on the mind and body. ...
... • Numerous short-term and long-term side effects occur when taking Ecstasy. • Lacing or substitution in pills make it difficult to predict which effects may occur. • Further studies must be conducted to understand the lasting effects the drugs has on the mind and body. ...
Brain Organization or, why everyone should have some
... say the CNS and the PNS is really about anatomy Nothing wrong with this, but the distinction is not as much about physiology Physiologically we can talk about the cranial nervous system and the spinal nervous system ...
... say the CNS and the PNS is really about anatomy Nothing wrong with this, but the distinction is not as much about physiology Physiologically we can talk about the cranial nervous system and the spinal nervous system ...
Clinical neurochemistry

Clinical neurochemistry is the field of neurological biochemistry which relates biochemical phenomena to clinical symptomatic manifestations in humans. While neurochemistry is mostly associated with the effects of neurotransmitters and similarly-functioning chemicals on neurons themselves, clinical neurochemistry relates these phenomena to system-wide symptoms. Clinical neurochemistry is related to neurogenesis, neuromodulation, neuroplasticity, neuroendocrinology, and neuroimmunology in the context of associating neurological findings at both lower and higher level organismal functions.